Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator

The shear sheetmetal force equation is a fundamental concept in engineering, particularly in the field of mechanical engineering. It is used to calculate the force required to shear a sheet of metal, taking into account the material's thickness, shear strength, and the length of the cut. This equation is crucial in designing and optimizing metal cutting processes, ensuring safety and efficiency. The calculator accompanying this equation simplifies the calculation process, allowing engineers to quickly determine the required force and make informed decisions about their manufacturing operations. Understanding this equation is essential for metal fabrication and processing.
- Understanding Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator
- How do you calculate the shearing force of sheet metal?
- How do you calculate shear force?
- How do you calculate the force required to shear?
- What is the formula for shear calculator?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and how is it used in calculations?
- How does the Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator work and what are its benefits?
- What are the key factors that affect the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and how do they impact the calculation?
- How can the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator be applied in real-world scenarios and what are the potential applications?
Understanding Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation is a fundamental concept in engineering and manufacturing, particularly in the field of sheet metal fabrication. It is used to calculate the force required to shear a sheet metal, which is essential in designing and optimizing manufacturing processes. The equation takes into account various parameters such as the thickness of the sheet metal, the shear strength of the material, and the area of the sheet being sheared.
Introduction to Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation is based on the principle that the force required to shear a sheet metal is equal to the shear strength of the material multiplied by the area of the sheet being sheared. The equation is typically expressed as: F = τ A, where F is the force required, τ is the shear strength, and A is the area of the sheet. This equation is widely used in the industry to calculate the force required for various sheet metal operations such as cutting, punching, and shearing.
Key Parameters in Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation involves several key parameters that affect the calculation of the force required. These parameters include the thickness of the sheet metal, the shear strength of the material, and the area of the sheet being sheared. The thickness of the sheet metal is a critical parameter, as it directly affects the force required. The shear strength of the material is also an important parameter, as it determines the maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing. The area of the sheet being sheared is another critical parameter, as it determines the amount of material being sheared.
Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator
A Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator is a tool used to calculate the force required to shear a sheet metal. The calculator typically takes into account the thickness of the sheet metal, the shear strength of the material, and the area of the sheet being sheared. The calculator can be used to optimize manufacturing processes by determining the minimum force required to shear a sheet metal. This can help reduce energy consumption, improve productivity, and minimize waste.
Applications of Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation has numerous applications in the industry, particularly in the field of sheet metal fabrication. It is used to calculate the force required for various sheet metal operations such as cutting, punching, and shearing. The equation is also used to design and optimize manufacturing processes, such as die design and tooling. Additionally, the equation is used to select the appropriate machinery and equipment for sheet metal fabrication.
Limitations and Assumptions of Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation has several limitations and assumptions that must be considered when using it. One of the limitations is that the equation assumes a uniform distribution of stress across the sheet metal, which may not always be the case. Another limitation is that the equation does not take into account the friction and wear that occurs during the shearing process. The equation also assumes that the shear strength of the material is constant, which may not always be the case.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Thickness | The thickness of the sheet metal |
| Shear Strength | The maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing |
| Area | The area of the sheet being sheared |
| Force | The force required to shear the sheet metal |
| Energy | The energy consumed during the shearing process |
How do you calculate the shearing force of sheet metal?

To calculate the shearing force of sheet metal, you need to consider the material properties, thickness, and shearing process. The shearing force can be calculated using the formula: F = (τ A) / (σ t), where F is the shearing force, τ is the shear strength, A is the cross-sectional area, σ is the yield strength, and t is the thickness of the sheet metal.
Understanding Material Properties
When calculating the shearing force of sheet metal, it's essential to understand the material properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and shear strength. These properties can be found in the material's datasheet or by conducting tensile tests. The shear strength is a critical factor in determining the shearing force, as it represents the maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing.
- Tensile strength: the maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing
- Yield strength: the stress at which the material begins to deform plastically
- Shear strength: the maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing in shear
Calculating Cross-Sectional Area
The cross-sectional area of the sheet metal is another crucial factor in calculating the shearing force. The cross-sectional area can be calculated by multiplying the width and thickness of the sheet metal. It's essential to ensure that the cross-sectional area is calculated accurately, as it directly affects the shearing force.
- Width: the width of the sheet metal
- Thickness: the thickness of the sheet metal
- Cross-sectional area: the area of the sheet metal perpendicular to the shearing direction
Determining Shear Strength
The shear strength of the sheet metal is a critical factor in calculating the shearing force. The shear strength can be determined by conducting shear tests or by using the material's datasheet. The shear strength is typically expressed in units of pounds per square inch (psi) or pascals (Pa).
- Shear test: a test used to determine the shear strength of a material
- Material's datasheet: a document that provides information about the material's properties
- Shear strength: the maximum stress that the material can withstand without failing in shear
Considering Shearing Process
The shearing process also affects the shearing force of the sheet metal. The shearing process can be either mechanical or thermal, and each process has its own set of parameters that need to be considered. For example, mechanical shearing involves using a shearing machine to cut the sheet metal, while thermal shearing involves using heat to cut the sheet metal.
- Mechanical shearing: a process that uses a shearing machine to cut the sheet metal
- Thermal shearing: a process that uses heat to cut the sheet metal
- Shearing parameters: the parameters that affect the shearing process, such as speed, pressure, and temperature
Applying Safety Factors
Finally, when calculating the shearing force of sheet metal, it's essential to apply safety factors to ensure that the design is safe and reliable. The safety factors can be applied by increasing the shearing force by a certain percentage or by using a factor of safety. The factor of safety is a dimensionless value that represents the margin of safety between the design and the failure.
- Safety factor: a factor that is applied to the design to ensure that it is safe and reliable
- Factor of safety: a dimensionless value that represents the margin of safety between the design and the failure
- Margin of safety: the difference between the design and the failure
How do you calculate shear force?

To calculate shear force, you need to understand the concept of stress and strain on an object. Shear force is a type of force that causes an object to deform by sliding along a plane parallel to the direction of the force. The calculation of shear force involves determining the load or force applied to the object, as well as the area over which it is applied.
Understanding Shear Force Formula
The shear force formula is given by F = (τ A), where F is the shear force, τ is the shear stress, and A is the cross-sectional area of the object. To calculate shear force, you need to know the shear stress and the area over which it is applied. The following steps can be taken to calculate shear force:
- Determine the load or force applied to the object
- Calculate the shear stress using the formula τ = F / A
- Use the shear stress and area to calculate the shear force using the formula F = (τ A)
Factors Affecting Shear Force
Several factors can affect the shear force on an object, including the material properties, size and shape of the object, and the type of load applied. The shear force can be affected by the yield strength and ultimate strength of the material, as well as the strain rate and temperature. The following factors can influence the shear force:
- Material properties, such as yield strength and ultimate strength
- Size and shape of the object, including the cross-sectional area
- Type of load, including tensile, compressive, and torsional loads
Calculating Shear Force in Beams
When calculating shear force in beams, you need to consider the load applied to the beam, as well as the length and cross-sectional area of the beam. The shear force can be calculated using the formula V = (M c) / I, where V is the shear force, M is the bending moment, c is the distance from the neutral axis, and I is the moment of inertia. The following steps can be taken to calculate shear force in beams:
- Determine the load applied to the beam
- Calculate the bending moment using the formula M = (F L) / 2
- Use the bending moment and moment of inertia to calculate the shear force
Shear Force in Structural Members
In structural members, such as columns and beams, the shear force can be critical in determining the stability and strength of the member. The shear force can cause failure of the member, especially if it is not properly designed and constructed. The following types of structural members are prone to shear force:
- Columns, which are subject to axial loads and bending moments
- Beams, which are subject to bending moments and shear forces
- Connections, which can be subject to shear forces and moments
Importance of Shear Force in Engineering Design
The shear force is an important consideration in engineering design, as it can affect the stability and strength of a structure or component. The shear force can cause failure of a structure or component, especially if it is not properly designed and constructed. The following reasons highlight the importance of shear force in engineering design:
- Structural integrity, which requires consideration of shear force and other loads
- Material selection, which depends on the shear strength and other properties of the material
- Safety factors, which must be considered to ensure that the structure or component can withstand shear forces and other loads
How do you calculate the force required to shear?
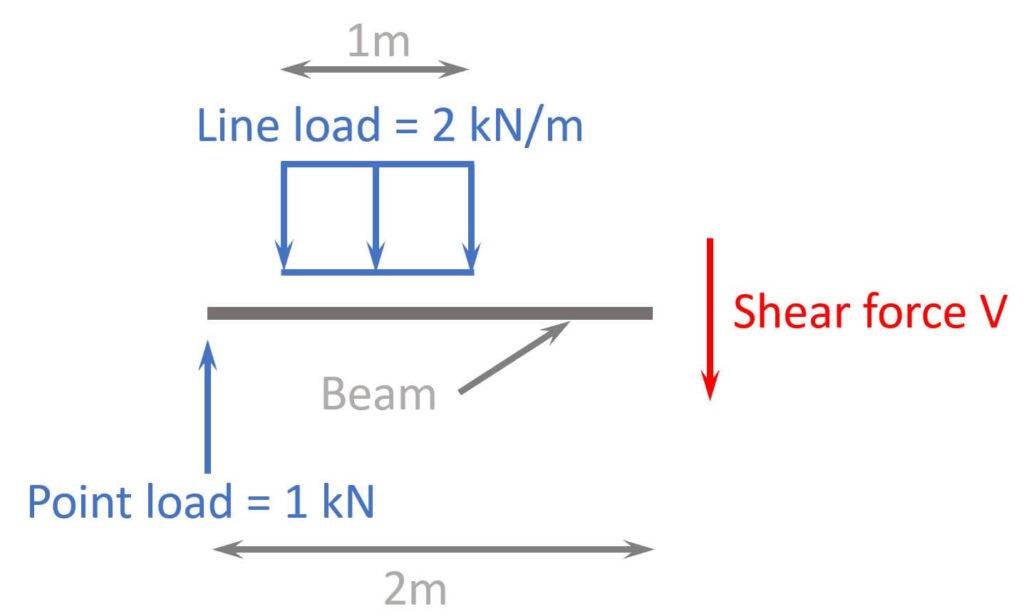
To calculate the force required to shear, you need to understand the mechanics of the shearing process and the properties of the material being sheared. The force required to shear a material depends on its shear strength, which is a measure of the material's ability to resist deformation and failure. The shear strength of a material can be determined through laboratory tests, such as the shear test, which involves applying a force to a sample of the material until it fails.
Understanding Shear Strength
The shear strength of a material is an important factor in determining the force required to shear. Shear strength is typically measured in units of pressure, such as pounds per square inch (psi) or pascals (Pa). To calculate the force required to shear, you need to know the shear strength of the material, as well as the area of the material that will be sheared. The following are some key factors to consider:
- The type of material being sheared, as different materials have different shear strengths.
- The thickness of the material, as thicker materials require more force to shear.
- The angle of the shear, as the force required to shear can vary depending on the angle of the shear.
Calculating Shear Force
To calculate the force required to shear, you can use the following formula: F = τ A, where F is the force required to shear, τ is the shear strength of the material, and A is the area of the material that will be sheared. The shear strength of a material can be determined through laboratory tests, such as the shear test. The following are some key factors to consider:
- The units of measurement, as the force required to shear is typically measured in units of force, such as newtons (N) or pounds (lb).
- The material properties, as different materials have different shear strengths and properties.
- The shear angle, as the force required to shear can vary depending on the angle of the shear.
Factors Affecting Shear Force
There are several factors that can affect the force required to shear a material, including the type of material, the thickness of the material, and the angle of the shear. The following are some key factors to consider:
- The temperature of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by temperature.
- The moisture content of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by moisture.
- The surface roughness of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by surface roughness.
Shear Force in Different Materials
The force required to shear a material can vary greatly depending on the type of material. For example, metals typically require more force to shear than plastics, while woods require more force to shear than fabrics. The following are some key factors to consider:
- The density of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by density.
- The elasticity of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by elasticity.
- The viscosity of the material, as the shear strength of a material can be affected by viscosity.
Applications of Shear Force Calculation
The calculation of shear force is important in a variety of applications, including engineering, manufacturing, and construction. The following are some key factors to consider:
- The design of machines and structures, as the shear force calculation can help determine the strength and stability of a machine or structure.
- The selection of materials, as the shear force calculation can help determine the suitability of a material for a particular application.
- The testing of materials, as the shear force calculation can help determine the shear strength of a material.
What is the formula for shear calculator?

The formula for a shear calculator is used to calculate the shear stress and shear strain of a material. The formula for shear stress is: τ = F / A, where τ is the shear stress, F is the force applied, and A is the area of the material. The formula for shear strain is: γ = Δx / L, where γ is the shear strain, Δx is the deformation of the material, and L is the length of the material.
Understanding Shear Stress
Shear stress is a critical factor in determining the strength and durability of a material. It is calculated using the formula τ = F / A, where τ is the shear stress, F is the force applied, and A is the area of the material. The units of shear stress are typically measured in pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi). To calculate shear stress, you need to know the force applied and the area of the material. Here are the steps to calculate shear stress:
- Identify the force applied to the material
- Measure the area of the material
- Use the formula τ = F / A to calculate the shear stress
Calculating Shear Strain
Shear strain is a measure of the deformation of a material under a shear force. It is calculated using the formula γ = Δx / L, where γ is the shear strain, Δx is the deformation of the material, and L is the length of the material. The units of shear strain are typically measured in radians (rad) or degrees (°). To calculate shear strain, you need to know the deformation of the material and the length of the material. Here are the steps to calculate shear strain:
- Measure the deformation of the material
- Measure the length of the material
- Use the formula γ = Δx / L to calculate the shear strain
Shear Calculator Applications
A shear calculator has various applications in engineering and physics. It is used to calculate the shear stress and shear strain of a material, which is essential in designing and analyzing structural elements such as beams, columns, and shafts. The shear calculator is also used in materials science to determine the mechanical properties of a material. Here are some of the applications of a shear calculator:
- Designing structural elements
- Analyzing materials
- Determining mechanical properties
Shear Calculator Limitations
A shear calculator has some limitations. It assumes that the material is homogeneous and isotropic, which means that the material has the same properties in all directions. It also assumes that the force applied is uniform and constant, which may not be the case in reality. Additionally, the shear calculator does not take into account the non-linear behavior of materials, which can occur at high stresses and strains. Here are some of the limitations of a shear calculator:
- Assumes homogeneous and isotropic material
- Assumes uniform and constant force
- Does not account for non-linear behavior
Advantages of Using a Shear Calculator
Using a shear calculator has several advantages. It allows for quick and accurate calculation of shear stress and shear strain, which is essential in designing and analyzing structural elements. It also helps to reduce errors and improve efficiency in the design process. Additionally, a shear calculator can be used to compare the properties of different materials and to optimize the design of structural elements. Here are some of the advantages of using a shear calculator:
- Quick and accurate calculation
- Reduces errors and improves efficiency
- Allows for comparison and optimization of materials
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and how is it used in calculations?
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation is a mathematical formula used to calculate the force required to shear a sheet of metal. This equation is essential in the field of engineering and manufacturing, where sheet metal is commonly used in the production of various products, such as automobiles, aircraft, and machinery. The equation takes into account the thickness of the metal sheet, the shear strength of the material, and the length of the cut. By using this equation, engineers and manufacturers can determine the necessary force to shear the metal sheet, which helps in selecting the appropriate machinery and tools for the job. The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation is a valuable tool in ensuring the efficiency and accuracy of the shearing process.
How does the Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator work and what are its benefits?
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator is a tool designed to simplify the calculation of the force required to shear a sheet of metal. This calculator uses the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation to determine the necessary force, taking into account the input values such as the thickness of the metal sheet, the shear strength of the material, and the length of the cut. The calculator provides a quick and accurate way to calculate the force required, which helps in saving time and reducing errors. The benefits of using the Shear Sheetmetal Force Calculator include increased productivity, improved accuracy, and reduced costs. By using this calculator, engineers and manufacturers can optimize their shearing process, ensuring that the necessary force is applied to achieve the desired results.
What are the key factors that affect the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and how do they impact the calculation?
The key factors that affect the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation include the thickness of the metal sheet, the shear strength of the material, and the length of the cut. These factors have a significant impact on the calculation, as they determine the necessary force required to shear the metal sheet. The thickness of the metal sheet is a critical factor, as it directly affects the strength and resistance of the material. The shear strength of the material is also an important factor, as it determines the maximum stress that the material can withstand before failing. The length of the cut is also a key factor, as it affects the amount of force required to shear the metal sheet. By understanding these key factors, engineers and manufacturers can optimize their shearing process, ensuring that the necessary force is applied to achieve the desired results.
How can the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator be applied in real-world scenarios and what are the potential applications?
The Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator can be applied in various real-world scenarios, including manufacturing, engineering, and construction. In manufacturing, the equation and calculator can be used to optimize the shearing process, ensuring that the necessary force is applied to achieve the desired results. In engineering, the equation and calculator can be used to design and develop new products, such as automobiles and aircraft. In construction, the equation and calculator can be used to calculate the force required to cut and shape metal sheets for use in buildings and bridges. The potential applications of the Shear Sheetmetal Force Equation and Calculator are numerous, and include improving efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing productivity. By using this equation and calculator, engineers and manufacturers can achieve these goals, and produce high-quality products that meet the required standards.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas