Selecting Candidate Manufacturing Process Procedure and Calculator

The selection of a suitable manufacturing process is crucial for producing high-quality products while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. With numerous manufacturing processes available, choosing the right one can be a daunting task. A well-defined procedure and calculator can help streamline this process, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions and optimize their production workflows. This article provides an overview of the key considerations and tools involved in selecting a candidate manufacturing process, including process evaluation, cost estimation, and production planning. By following a structured approach, manufacturers can ensure the best possible outcome for their products.
- Selecting Candidate Manufacturing Process Procedure and Calculator
- How to select a manufacturing process?
- What are the four types of manufacturing processes?
- How to establish a manufacturing process?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the importance of selecting the right candidate manufacturing process?
- How do I determine the most suitable manufacturing process for my product?
- What are the key considerations when selecting a candidate manufacturing process procedure?
- How can a calculator be used to support the selection of a candidate manufacturing process?
Selecting Candidate Manufacturing Process Procedure and Calculator
The selection of a suitable manufacturing process is a critical step in the production of any product. It involves evaluating various factors such as production volume, product complexity, material requirements, and cost constraints to determine the most appropriate process for producing a high-quality product at a competitive cost. In this response, we will discuss the key considerations involved in selecting a candidate manufacturing process and the use of calculators to support this decision-making process.
Introduction to Manufacturing Process Selection
Manufacturing process selection is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. It involves evaluating the production requirements, material properties, and equipment capabilities to determine the most suitable process for producing a product. The selection process typically starts with an analysis of the product design and the identification of the key manufacturing processes that can be used to produce the product. The use of calculators and simulation tools can help to evaluate the feasibility of different processes and identify the most promising candidates.
Factors to Consider in Manufacturing Process Selection
Several factors must be considered when selecting a manufacturing process. These include:
Production volume: The number of units to be produced can influence the choice of process, with high-volume production often requiring more automated and efficient processes.
Product complexity: The complexity of the product design can affect the choice of process, with more complex products often requiring more specialized and precise processes.
Material requirements: The type and properties of the materials used in the product can influence the choice of process, with different processes being more suitable for different materials.
Cost constraints: The production cost is a critical factor in the selection of a manufacturing process, with the chosen process needing to be cost-effective and competitive.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Production Volume | The number of units to be produced |
| Product Complexity | The complexity of the product design |
| Material Requirements | The type and properties of the materials used |
| Cost Constraints | The production cost and competitiveness |
Manufacturing Process Options
Several manufacturing process options are available, including:
Casting: A process in which molten material is poured into a mold to produce a product.
Machining: A process in which material is removed from a workpiece using cutting tools.
Forming: A process in which material is shaped using various techniques such as rolling, forging, or extrusion.
Joining: A process in which two or more parts are joined together using techniques such as welding, brazing, or adhesive bonding.
Calculator Tools for Manufacturing Process Selection
Various calculator tools are available to support the selection of a manufacturing process. These tools can help to evaluate the feasibility of different processes and identify the most promising candidates. Some common calculator tools include:
Cost estimators: Tools that estimate the production cost of a product based on various factors such as material costs, labor costs, and equipment costs.
Process simulators: Tools that simulate the manufacturing process to evaluate its feasibility and identify potential issues.
Material selectors: Tools that help to select the most suitable materials for a product based on various factors such as strength, durability, and cost.
Benefits of Using Calculators in Manufacturing Process Selection
The use of calculators in manufacturing process selection can provide several benefits, including:
Improved accuracy: Calculators can help to evaluate the feasibility of different processes and identify the most promising candidates.
Increased efficiency: Calculators can help to streamline the selection process and reduce the time and effort required to evaluate different options.
Cost savings: Calculators can help to identify the most cost-effective process and reduce production costs.
Enhanced productivity: Calculators can help to optimize the manufacturing process and improve product quality.
How to select a manufacturing process?
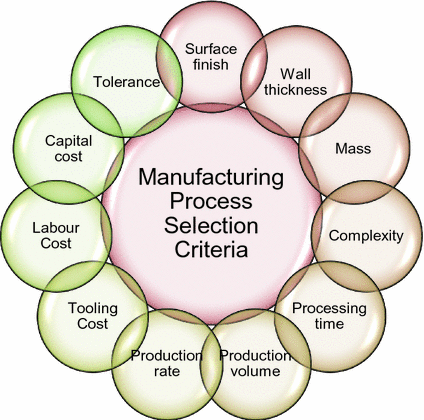
To select a manufacturing process, it's essential to consider several factors that impact the production of a product. The process involves evaluating various techniques, technologies, and resources to determine the most suitable method for producing a product. The goal is to choose a process that ensures efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness while meeting the required production volume and customer demand.
Understanding Production Requirements
Understanding the production requirements is crucial in selecting a manufacturing process. This involves analyzing the product's design, material specifications, and production volume. The process requires identifying the machinery and equipment needed to produce the product, as well as the labor skills and training required to operate the equipment.
- Define the product's specifications and requirements
- Determine the production volume and schedule
- Identify the necessary machinery and equipment
Evaluating Manufacturing Technologies
Evaluating manufacturing technologies is a critical step in selecting a manufacturing process. This involves assessing various technologies, such as automation, robotics, and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), to determine their suitability for the production process. The goal is to choose a technology that enhances productivity, quality, and efficiency while reducing labor costs and material waste.
- Assess the benefits and limitations of each technology
- Evaluate the cost of implementation and maintenance
- Consider the potential impact on product quality and customer satisfaction
Assessing Production Costs and Budget
Assessing production costs and budget is essential in selecting a manufacturing process. This involves evaluating the cost of materials, labor, equipment, and overhead to determine the total production cost. The goal is to choose a process that minimizes costs while ensuring quality and efficiency.
- Calculate the total production cost
- Evaluate the cost-benefit analysis of each process
- Consider the potential impact on profit margins and competitiveness
Considering Quality and Regulatory Requirements
Considering quality and regulatory requirements is crucial in selecting a manufacturing process. This involves evaluating the process's ability to meet quality standards, regulations, and industry certifications. The goal is to choose a process that ensures compliance and quality while minimizing the risk of defects and rework.
- Identify the relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards
- Evaluate the process's ability to meet quality standards
- Consider the potential impact on customer satisfaction and brand reputation
Implementing and Monitoring the Manufacturing Process
Implementing and monitoring the manufacturing process is essential to ensure its efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. This involves training personnel, testing equipment, and evaluating the process's performance. The goal is to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed to optimize the process.
- Develop a training program for personnel
- Implement a quality control system
- Monitor and evaluate the process's performance regularly
What are the four types of manufacturing processes?
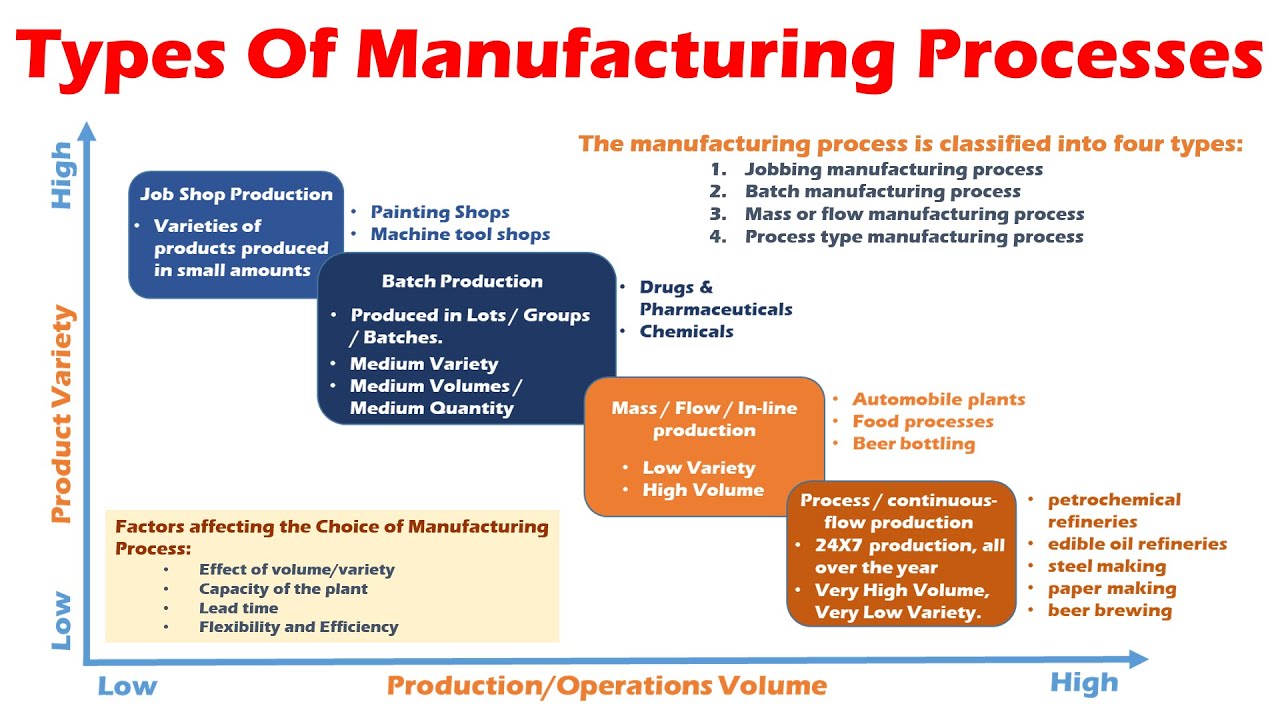
The four types of manufacturing processes are process manufacturing, discrete manufacturing, repetitive manufacturing, and job shop manufacturing. These categories are based on the type of product being manufactured and the production process used. Process manufacturing involves the production of goods in a continuous process, such as chemicals or food products. Discrete manufacturing involves the production of distinct items, such as cars or electronics. Repetitive manufacturing involves the production of the same product over and over, such as a production line. Job shop manufacturing involves the production of custom or unique items, such as a bespoke piece of furniture.
Types of Manufacturing Processes
The different types of manufacturing processes have distinct characteristics and requirements. Some of the key factors that distinguish these processes include the type of product being manufactured, the production volume, and the level of customization required. In process manufacturing, the production process is continuous, and the product is produced in a specific sequence. This type of manufacturing is often used for products such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food products. Some examples of products manufactured using this process include:
- Chemicals
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food products
Discrete Manufacturing Process
Discrete manufacturing involves the production of distinct items, such as cars, electronics, or appliances. This type of manufacturing is often used for products that require a high degree of precision and customization. The production process typically involves a series of distinct steps, and the product is assembled from a variety of components. Some of the key advantages of discrete manufacturing include:
- High degree of precision and accuracy
- Ability to produce complex products
- Flexibility in production scheduling
Repetitive Manufacturing Process
Repetitive manufacturing involves the production of the same product over and over, such as a production line. This type of manufacturing is often used for high-volume products, such as cars or consumer electronics. The production process is typically highly automated, and the product is produced in a continuous sequence. Some of the key benefits of repetitive manufacturing include:
- High production volumes
- Low production costs
- Consistent product quality
Job Shop Manufacturing Process
Job shop manufacturing involves the production of custom or unique items, such as a bespoke piece of furniture or a one-off prototype. This type of manufacturing is often used for products that require a high degree of customization or specialization. The production process typically involves a range of skills and techniques, and the product is produced in a specific sequence. Some of the key characteristics of job shop manufacturing include:
- High degree of customization
- Low production volumes
- High level of skill and expertise required
Comparison of Manufacturing Processes
The different types of manufacturing processes have distinct advantages and disadvantages. Process manufacturing is often used for high-volume products, while discrete manufacturing is used for products that require a high degree of precision and customization. Repetitive manufacturing is used for high-volume products, while job shop manufacturing is used for custom or unique items. Some of the key factors to consider when choosing a manufacturing process include:
- Production volume
- Product complexity
- Level of customization required
How to establish a manufacturing process?
To establish a manufacturing process, it is essential to follow a series of steps that ensure the efficient and effective production of goods. The process begins with planning and design, where the product and production line are conceptualized and laid out. This involves defining the product specifications, identifying the necessary materials and equipment, and determining the labour requirements. The next step is implementation, where the production line is set up, and the necessary training is provided to the operators. The process also involves quality control measures to ensure that the products meet the required standards.
Defining Product Requirements
Defining product requirements is a critical step in establishing a manufacturing process. This involves specifying the product's dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics. The product requirements should be clear, concise, and unambiguous to ensure that the production team understands what is expected of them. The following are some key considerations when defining product requirements:
- The product's functional and aesthetic requirements should be clearly specified.
- The materials and components used in the product should be identified and specified.
- The product's safety and regulatory requirements should be addressed.
Designing the Production Line
Designing the production line involves laying out the equipment and workstations in a way that maximizes efficiency and productivity. This requires a thorough understanding of the production process and the equipment used. The following are some key considerations when designing the production line:
- The equipment and machinery used in the production process should be selected based on their capability and reliability.
- The workstations should be designed to minimize waste and maximize productivity.
- The production line should be flexible enough to accommodate changes in production volumes and product mix.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Implementing quality control measures is essential to ensure that the products meet the required standards. This involves establishing quality control procedures and protocols that are followed throughout the production process. The following are some key considerations when implementing quality control measures:
- The quality control procedures should be clearly documented and communicated to the production team.
- The quality control measures should be implemented at every stage of the production process.
- The quality control results should be monitored and analyzed to identify areas for improvement.
Training and development of operators is crucial to ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their tasks efficiently and effectively. This involves providing training and development opportunities that are relevant to the production process. The following are some key considerations when training and developing operators:
- The training programmes should be designed to meet the specific needs of the production process.
- The operators should be encouraged to participate in continuous learning and development activities.
- The training results should be monitored and evaluated to identify areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Continuous improvement and monitoring is essential to ensure that the manufacturing process remains competitive and efficient. This involves monitoring key performance indicators and identifying areas for improvement. The following are some key considerations when implementing continuous improvement and monitoring:
- The key performance indicators should be clearly defined and monitored.
- The production process should be continuously evaluated and improved.
- The results of the continuous improvement efforts should be monitored and analyzed to identify areas for further improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the importance of selecting the right candidate manufacturing process?
The selection of the right candidate manufacturing process is crucial for the success of a product. It involves evaluating different production methods and choosing the one that best meets the product's design requirements, quality standards, and cost constraints. A well-chosen manufacturing process can help reduce production costs, improve product quality, and increase efficiency. On the other hand, a poorly chosen process can lead to delays, defects, and cost overruns. Therefore, it is essential to carefully evaluate different manufacturing options and select the one that best aligns with the product's specifications and objectives. This requires a thorough understanding of manufacturing technologies, process capabilities, and industry trends.
How do I determine the most suitable manufacturing process for my product?
Determining the most suitable manufacturing process for a product involves a thorough analysis of the product's design, materials, and production requirements. It is essential to consider factors such as production volume, part complexity, tolerances, and surface finish. Additionally, cost, lead time, and quality must be carefully evaluated. A process selection matrix can be a useful tool in evaluating different manufacturing processes and identifying the most suitable option. This matrix typically includes factors such as process capabilities, equipment requirements, and operator skills. By carefully evaluating these factors and using tools such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, manufacturers can select the most suitable manufacturing process for their product and ensure efficient and cost-effective production.
What are the key considerations when selecting a candidate manufacturing process procedure?
When selecting a candidate manufacturing process procedure, there are several key considerations that must be taken into account. First, the process must be capable of producing parts that meet the design specifications and quality standards. This requires a thorough understanding of the process capabilities and limitations. Additionally, the process must be efficient and cost-effective, with minimal waste and energy consumption. Safety and ergonomics are also essential considerations, as the process must be safe for operators and ergonomically designed to minimize fatigue and injury. Furthermore, the process must be flexible and adaptable, with the ability to accommodate changes in production volume and product design. By carefully evaluating these factors, manufacturers can select a candidate manufacturing process procedure that meets their needs and ensures successful and efficient production.
How can a calculator be used to support the selection of a candidate manufacturing process?
A calculator can be a valuable tool in supporting the selection of a candidate manufacturing process. By inputting key variables such as production volume, part complexity, and material costs, manufacturers can quickly and easily evaluate different manufacturing processes and identify the most cost-effective and efficient option. A calculator can also help to identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement, allowing manufacturers to optimize their production process and minimize waste. Additionally, a calculator can be used to compare different manufacturing processes and evaluate the impact of process changes on production costs and product quality. By using a calculator to support the selection of a candidate manufacturing process, manufacturers can make informed decisions and ensure that their production process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with their business objectives. Spreadsheets and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software can also be used to support the selection of a candidate manufacturing process, providing a range of tools and features to support process evaluation and optimization.
Deja una respuesta


Entradas Relacionadas