Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator

The pipe diameter required for a specific application can be determined using a factor calculator. This calculator takes into account various factors such as flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties to provide an accurate calculation. By inputting the necessary values, users can determine the minimum pipe diameter required to ensure efficient and safe operation. The calculator is a valuable tool for engineers, contractors, and facility managers responsible for designing and maintaining piping systems. It helps to optimize pipe size, reducing costs and ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. Accurate calculations are crucial for system performance.
- Calculating Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator
- How to calculate required pipe diameter?
- How to select pipe size based on flow rate?
-
How do I calculate what size pipe I need?
- Understanding Pipe Sizing Formulas
- The pipe material is a critical factor in determining the required pipe size. Different materials have different friction factors, which affect the pressure drop along the pipe. For example, copper pipes have a lower friction factor than steel pipes, which means they can carry the same flow rate with a smaller diameter. Copper pipes are often used for hot water systems and gas lines Steel pipes are commonly used for high-pressure applications, such as oil and gas pipelines PVC pipes are often used for wastewater and stormwater systems Calculating Pipe Size Using Nomograms
- Accounting for Pipe Fittings and Valves
- Using Pipe Sizing Software
- What is the rule of thumb for pipe sizes?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the purpose of the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
- How does the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator work?
- What are the benefits of using the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
- What are the limitations of the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
Calculating Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator
The calculation of pipe diameter is a critical aspect of engineering, particularly in the fields of fluid mechanics and pipe flow. To determine the required pipe diameter, a factor calculator is often employed, taking into account various factors such as flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties. By using a factor calculator, engineers can ensure that the pipe diameter is sufficient to handle the required flow rate while minimizing energy loss and cost.
Understanding the Basics of Pipe Flow
Pipe flow is a fundamental concept in fluid mechanics, involving the movement of fluids through a pipeline. The flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties are all critical factors that influence the pipe diameter required. The Reynolds number is also an essential parameter, as it determines the nature of the flow, whether laminar or turbulent.
Factors Influencing Pipe Diameter Calculation
Several factors influence the calculation of pipe diameter, including:
- Flow rate: The volume of fluid that flows through the pipe per unit time.
- Pressure drop: The decrease in pressure along the length of the pipe.
- Fluid properties: Such as viscosity, density, and velocity.
- Pipe material: The type of material used for the pipe, which affects its roughness and hydraulic gradient.
Using a Factor Calculator for Pipe Diameter
A factor calculator is a useful tool for determining the required pipe diameter based on various factors. The calculator typically takes into account the flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties to calculate the required pipe diameter. The calculator may also consider other factors such as pipe length, fittings, and valves.
Importance of Accurate Pipe Diameter Calculation
Accurate calculation of pipe diameter is crucial to ensure efficient and cost-effective pipeline operation. A pipe diameter that is too small can result in excessive pressure drop, while a diameter that is too large can lead to wasted energy and increased costs. Therefore, it is essential to use a reliable factor calculator to determine the required pipe diameter.
Advantages of Using a Pipe Diameter Calculator
Using a pipe diameter calculator offers several advantages, including:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Accurate calculations | Ensures precise calculation of pipe diameter based on various factors. |
| Time-saving | Reduces the time and effort required to calculate pipe diameter manually. |
| Cost-effective | Helps minimize costs by optimizing pipe diameter and reducing energy loss. |
| Improved efficiency | Enables efficient pipeline operation by ensuring the correct pipe diameter. |
| Reduced errors | Minimizes the risk of errors in pipe diameter calculation, which can lead to serious consequences. |
By using a pipe diameter calculator, engineers can ensure accurate calculations, time-saving, cost-effective solutions, improved efficiency, and reduced errors in pipeline design and operation. The calculator is an essential tool for determining the required pipe diameter based on various factors, including flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties.
How to calculate required pipe diameter?

To calculate the required pipe diameter, several factors need to be considered, including the flow rate, fluid properties, pressure drop, and pipe material. The calculation typically involves using the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation, which take into account the friction factor, velocity, and head loss. These equations help to determine the minimum pipe diameter required to convey a certain flow rate while maintaining a specified pressure drop.
Understanding Fluid Properties
When calculating the required pipe diameter, it's essential to understand the fluid properties, such as density, viscosity, and velocity. These properties affect the flow rate and pressure drop, which in turn impact the required pipe diameter. To calculate the required pipe diameter, the following steps can be taken:
- Determine the fluid properties, such as density and viscosity.
- Calculate the Reynolds number to determine the flow regime.
- Use the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation to calculate the required pipe diameter.
Using the Darcy-Weisbach Equation
The Darcy-Weisbach equation is a widely used equation for calculating the head loss in a pipe. The equation takes into account the friction factor, velocity, and pipe length. To use the Darcy-Weisbach equation, the following steps can be taken:
- Determine the friction factor using the Colebrook-White equation or the Moody diagram.
- Calculate the velocity using the flow rate and pipe cross-sectional area.
- Use the Darcy-Weisbach equation to calculate the required pipe diameter.
Considering Pipe Material and Roughness
The pipe material and roughness can significantly impact the required pipe diameter. Different pipe materials, such as steel, copper, or PVC, have varying roughness values, which affect the friction factor. To consider the pipe material and roughness, the following steps can be taken:
- Determine the pipe material and roughness value.
- Use the Colebrook-White equation or the Moody diagram to determine the friction factor.
- Calculate the required pipe diameter using the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation.
Accounting for Pressure Drop and Head Loss
The pressure drop and head loss are critical factors in calculating the required pipe diameter. A higher pressure drop or head loss requires a larger pipe diameter to maintain a specified flow rate. To account for pressure drop and head loss, the following steps can be taken:
- Determine the pressure drop or head loss requirements.
- Use the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation to calculate the required pipe diameter.
- Consider the pipe material and roughness to ensure accurate calculations.
Verifying Calculations with Example Problems
To verify the calculations, example problems can be used to demonstrate the application of the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation. These examples can help to ensure that the calculations are accurate and reliable. To verify the calculations, the following steps can be taken:
- Select an example problem with known fluid properties and pipe characteristics.
- Calculate the required pipe diameter using the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation.
- Compare the calculated pipe diameter with the known value to verify the accuracy of the calculation.
How to select pipe size based on flow rate?
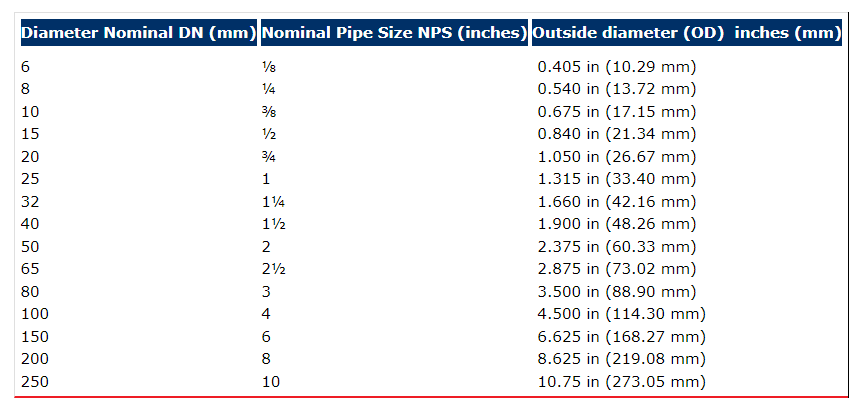
To select pipe size based on flow rate, it is essential to consider several factors, including the type of fluid being transported, the desired pressure drop, and the velocity of the fluid. The flow rate is typically measured in units of volume per unit time, such as gallons per minute (gpm) or cubic meters per second (m³/s). The pipe size is usually specified in terms of its nominal diameter, which is the diameter of the pipe in inches or millimeters.
Understanding Flow Rate and Pipe Size
The flow rate and pipe size are closely related, as a larger pipe size can accommodate a higher flow rate. However, a larger pipe size also increases the cost of the piping system and may not be necessary for lower flow rates. To select the correct pipe size, it is necessary to calculate the required flow rate and then use a pipe sizing chart or equation to determine the minimum pipe size required. Some key factors to consider when selecting a pipe size based on flow rate include:
- The type of fluid being transported, as different fluids have different viscosities and densities that affect the flow rate.
- The desired pressure drop, as a higher pressure drop requires a smaller pipe size to maintain the desired flow rate.
- The velocity of the fluid, as a higher velocity requires a larger pipe size to prevent turbulence and erosion.
Using Pipe Sizing Charts
Pipe sizing charts are a useful tool for selecting the correct pipe size based on flow rate. These charts typically plot the flow rate against the pipe size and pressure drop, allowing the user to quickly determine the minimum pipe size required for a given flow rate and pressure drop. To use a pipe sizing chart, simply locate the flow rate and pressure drop on the chart and read off the corresponding pipe size. Some key considerations when using pipe sizing charts include:
- The chart should be based on the type of fluid being transported, as different fluids have different viscosities and densities.
- The chart should account for the desired pressure drop, as a higher pressure drop requires a smaller pipe size.
- The chart should provide the minimum pipe size required, as well as any maximum pipe size limitations.
Calculating Pipe Size Based on Flow Rate
In addition to using pipe sizing charts, it is also possible to calculate the pipe size based on flow rate using a pipe sizing equation. One common equation is the Hazen-Williams equation, which relates the flow rate to the pipe size and pressure drop. To use this equation, simply plug in the flow rate, pressure drop, and pipe length, and solve for the pipe size. Some key considerations when calculating pipe size include:
- The equation should be based on the type of fluid being transported, as different fluids have different viscosities and densities.
- The equation should account for the desired pressure drop, as a higher pressure drop requires a smaller pipe size.
- The equation should provide the minimum pipe size required, as well as any maximum pipe size limitations.
Considering Velocity and Pressure Drop
When selecting a pipe size based on flow rate, it is essential to consider the velocity and pressure drop of the fluid. A higher velocity requires a larger pipe size to prevent turbulence and erosion, while a higher pressure drop requires a smaller pipe size to maintain the desired flow rate. To balance these competing factors, it is necessary to use a pipe sizing chart or equation that accounts for both velocity and pressure drop. Some key considerations when considering velocity and pressure drop include:
- The maximum velocity should not exceed the critical velocity to prevent turbulence and erosion.
- The minimum pressure drop should be sufficient to maintain the desired flow rate.
- The pipe size should be selected to balance velocity and pressure drop while minimizing cost and installation complexity.
Verifying Pipe Size Selection
After selecting a pipe size based on flow rate, it is essential to verify the selection to ensure that it meets the required flow rate and pressure drop. This can be done by using a pipe sizing chart or equation and checking the calculated pipe size against the selected pipe size. Additionally, it is necessary to consider any system constraints, such as pump capacity and valve sizing, to ensure that the selected pipe size is compatible with the overall system design. Some key considerations when verifying pipe size selection include:
- The selected pipe size should meet the required flow rate and pressure drop.
- The selected pipe size should be compatible with the system constraints, such as pump capacity and valve sizing.
- The selected pipe size should be verified using a pipe sizing chart or equation to ensure accuracy and reliability.
How do I calculate what size pipe I need?

To calculate the size of the pipe you need, you must consider several factors, including the flow rate of the fluid, the pressure drop along the pipe, and the material of the pipe. The flow rate is the volume of fluid that flows through the pipe per unit time, typically measured in cubic feet per second or gallons per minute. The pressure drop is the decrease in pressure along the length of the pipe, which is affected by the friction between the fluid and the pipe walls. The material of the pipe, such as copper, steel, or PVC, also affects the calculation, as different materials have different friction factors.
Understanding Pipe Sizing Formulas
To calculate the size of the pipe, you can use various formulas, such as the Hazen-Williams equation or the Darcy-Weisbach equation. These formulas take into account the flow rate, pressure drop, and friction factor to determine the required pipe size. For example, the Hazen-Williams equation is:
- Q = (C A (2 g h)^0.54) / (d^0.04 L^0.54)
- Where Q is the flow rate, C is the Hazen-Williams coefficient, A is the cross-sectional area of the pipe, g is the acceleration due to gravity, h is the head loss, d is the diameter of the pipe, and L is the length of the pipe
- The Hazen-Williams coefficient (C) is a dimensionless value that depends on the pipe material and roughness
The pipe material is a critical factor in determining the required pipe size. Different materials have different friction factors, which affect the pressure drop along the pipe. For example, copper pipes have a lower friction factor than steel pipes, which means they can carry the same flow rate with a smaller diameter.
- Copper pipes are often used for hot water systems and gas lines
- Steel pipes are commonly used for high-pressure applications, such as oil and gas pipelines
- PVC pipes are often used for wastewater and stormwater systems
Calculating Pipe Size Using Nomograms
Nomograms are graphical representations of the relationships between flow rate, pressure drop, and pipe size. They can be used to quickly estimate the required pipe size for a given application.
- A nomogram typically consists of a series of curves that represent different pipe sizes and flow rates
- The user can enter the flow rate and pressure drop values and read off the corresponding pipe size from the nomogram
- Nomograms are often used for preliminary design calculations, and the results should be verified using more detailed calculations
Accounting for Pipe Fittings and Valves
Pipe fittings and valves can significantly affect the pressure drop along the pipe, and must be accounted for in the calculation.
- Elbows, tees, and reductions can all contribute to pressure drop
- Valves, such as gate valves and ball valves, can also cause significant pressure drop
- The equivalent length of the pipe fittings and valves must be added to the total pipe length to account for the extra pressure drop
Using Pipe Sizing Software
There are many software programs available that can help with pipe sizing calculations, such as pipe flow calculators and hydraulic simulation software.
- These programs can quickly and accurately calculate the required pipe size based on input values such as flow rate, pressure drop, and pipe material
- They can also take into account pipe fittings and valves, as well as other factors that affect pressure drop
- Pipe sizing software can save time and reduce errors in the design process
What is the rule of thumb for pipe sizes?
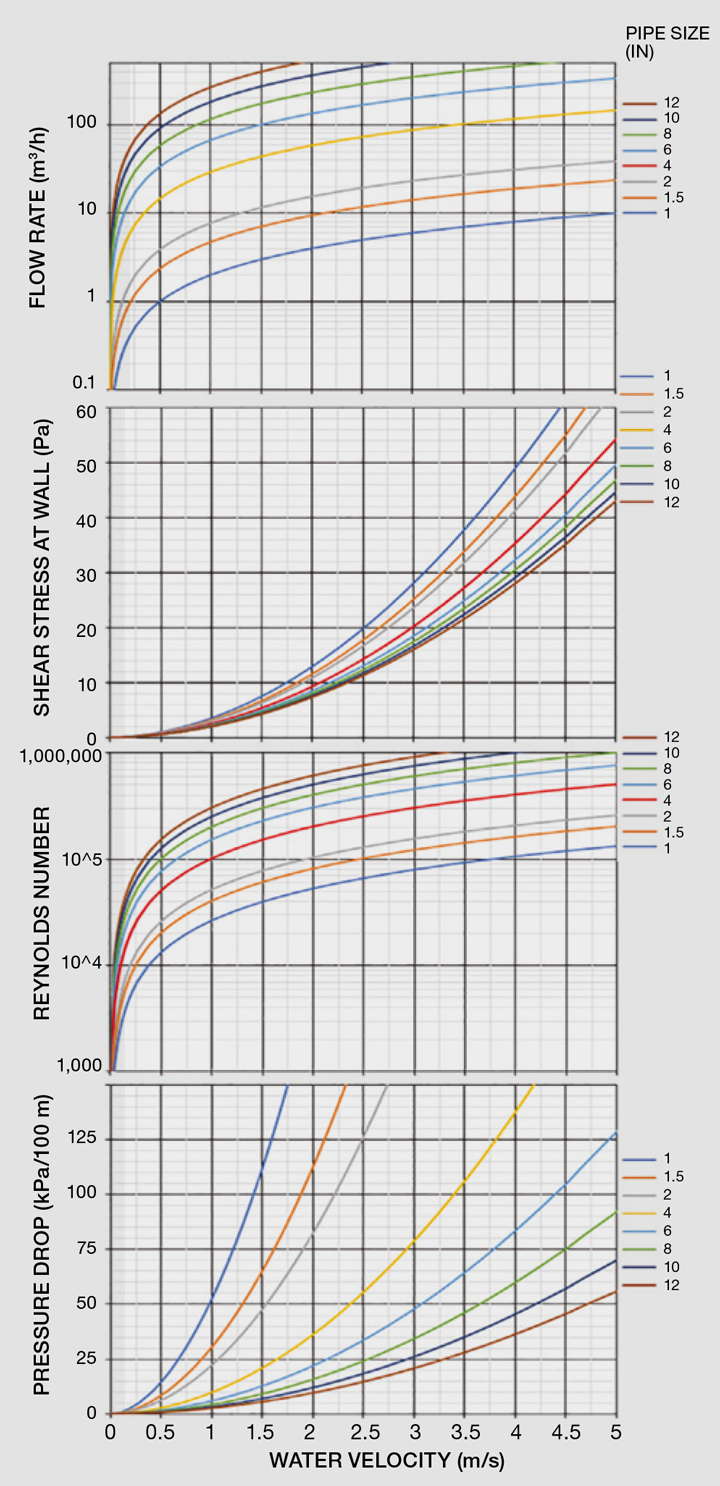
The rule of thumb for pipe sizes is to ensure that the pipe diameter is sufficient to handle the required flow rate and pressure drop. This is typically determined by using pipe sizing charts or calculations that take into account the fluid properties, flow rate, and pressure drop. The goal is to select a pipe size that minimizes pressure drop while also considering cost, space, and installation constraints.
Understanding Pipe Sizing Fundamentals
Understanding the fundamentals of pipe sizing is crucial in determining the correct pipe size. This involves considering factors such as fluid density, viscosity, and flow rate, as well as the pipe material and roughness. The following are key points to consider:
- Fluid properties: The density and viscosity of the fluid being transported affect the pipe size required.
- Flow rate: The flow rate of the fluid determines the minimum pipe size required to handle the flow.
- Pressure drop: The pressure drop across the pipe affects the pipe size required, with larger pipes resulting in lower pressure drops.
Pipe Sizing Methods
There are several pipe sizing methods available, including the use of pipe sizing charts, calculations, and computer simulations. The most common method involves using pipe sizing charts, which provide a quick and easy way to determine the required pipe size based on the flow rate and pressure drop. The following are key points to consider:
- Pipe sizing charts: These charts provide a graphical representation of the relationship between flow rate, pressure drop, and pipe size.
- Calculations: These involve using equations to determine the required pipe size based on the fluid properties and flow rate.
- Computer simulations: These involve using software to model the pipe system and determine the required pipe size.
Pipe Material Selection
The pipe material selected can affect the pipe size required. Different materials have different roughness values, which can affect the pressure drop across the pipe. The following are key points to consider:
- Material selection: The selection of the pipe material affects the pipe size required, with different materials having different roughness values.
- Roughness values: The roughness value of the pipe material affects the pressure drop across the pipe.
- Cost and availability: The cost and availability of the pipe material can also affect the pipe size required.
Pressure Drop Considerations
Pressure drop is a critical consideration in pipe sizing, as it can affect the pipe size required and the energy required to transport the fluid. The following are key points to consider:
- Pressure drop calculations: These involve using equations to determine the pressure drop across the pipe based on the fluid properties and flow rate.
- Pressure drop limitations: The pressure drop across the pipe should be limited to ensure that the pipe system operates within safe and efficient limits.
- Energy consumption: The energy required to transport the fluid is affected by the pressure drop across the pipe.
pipe System Design Considerations
The pipe system design should take into account various factors, including pipe size, material, and layout, to ensure that the system operates efficiently and safely. The following are key points to consider:
- Pipe layout: The pipe layout should be designed to minimize pressure drop and energy consumption.
- Valve and fitting selection: The selection of valves and fittings can affect the pipe size required and the pressure drop across the pipe.
- System operation: The pipe system should be designed to operate within safe and efficient limits, with consideration given to startup and shutdown procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
The Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator is a tool designed to help engineers and plumbing professionals determine the required diameter of a pipe based on various factors such as flow rate, pressure drop, and fluid properties. This calculator is essential in ensuring that the pipe diameter is sufficient to handle the desired flow rate while minimizing pressure losses and energy consumption. By using this calculator, users can accurately determine the required pipe diameter, which is critical in the design and installation of piping systems for various applications, including water supply, gas distribution, and industrial processes. The calculator takes into account key factors such as the type of fluid, flow velocity, and pipe material to provide an accurate calculation of the required pipe diameter.
How does the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator work?
The Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator uses a complex algorithm that takes into account various input parameters such as flow rate, pressure drop, fluid density, and viscosity. The calculator then applies empirical formulas and mathematical models to determine the required pipe diameter. The calculation process involves iterative calculations to ensure that the resulting diameter meets the specified conditions. The calculator also considers pipe roughness, bends, and valves to provide a realistic calculation of the required pipe diameter. By using this calculator, users can easily determine the required pipe diameter without having to perform complex calculations or consult multiple references. The calculator is user-friendly and provides quick and accurate results, making it an essential tool for engineers and plumbing professionals.
What are the benefits of using the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
The Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator offers several benefits to engineers and plumbing professionals. One of the primary benefits is the ability to accurately determine the required pipe diameter, which helps to minimize errors and reduce costs associated with pipe installation and maintenance. The calculator also saves time by providing quick and accurate results, allowing users to focus on other aspects of the design and installation process. Additionally, the calculator helps to optimize pipe sizing, which can lead to energy savings and reduced environmental impact. The calculator is also easy to use, even for users who are not familiar with complex calculations. By using this calculator, users can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, which is essential for safe and efficient piping systems.
What are the limitations of the Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator?
The Pipe Diameter Required Based on Factor Calculator has some limitations that users should be aware of. One of the main limitations is that the calculator is based on simplified models and assumptions, which may not accurately reflect the complexities of real-world piping systems. The calculator also requires accurate input data, which can be difficult to obtain in some cases. Additionally, the calculator is limited to specific types of fluids and pipe materials, and may not be applicable to all piping systems. Users should also be aware that the calculator is not a substitute for professional judgment and expertise, and should be used in conjunction with other design tools and consultation with experts. By understanding the limitations of the calculator, users can use it effectively and make informed decisions about pipe sizing and installation.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas