Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator

When working with countersink spot drills, determining the correct depth is crucial to achieve a precise and safe operation. The countersink spot drill depth formula provides a reliable method to calculate the required depth, taking into account the drill bit angle and hole diameter. This calculator is designed to simplify the process, allowing users to input the necessary parameters and obtain the optimal depth. By utilizing the countersink spot drill depth formula and calculator, machinists and engineers can ensure accurate and efficient drilling operations, reducing errors and improving overall productivity. Accurate calculations are essential for success.
-
Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula
- Benefits of Using a Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator
- Applications of the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator
- Table of Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formulas and Calculators
- Importance of Accurate Countersink Hole Depth Calculation
- How do you calculate spot drill depth?
- What is the formula for countersink depth?
- How deep to drill a countersink?
- What is the rule for countersinks?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and how does it work?
- How do I use the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator to determine the optimal depth of my countersink holes?
- What are the benefits of using the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator in my manufacturing process?
- Can I use the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator for a variety of different materials and applications?
Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator are essential tools in the field of engineering and manufacturing, particularly in the process of drilling and countersinking holes in various materials. The formula and calculator are used to determine the correct depth of a countersink hole, ensuring that the screw or fastener is properly seated and the material is not damaged. In this section, we will delve into the details of the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator, exploring their applications, benefits, and usage.
Understanding the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula is a mathematical equation that calculates the required depth of a countersink hole based on the diameter of the screw or fastener, the angle of the countersink, and the thickness of the material. The formula takes into account the geometry of the countersink and the material properties, ensuring that the hole is drilled to the correct depth and the screw or fastener is properly seated. The formula is typically expressed as: depth = (diameter sin(angle)) / 2, where diameter is the diameter of the screw or fastener, angle is the angle of the countersink, and depth is the required depth of the hole.
Benefits of Using a Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator
A Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator is a software tool or online application that simplifies the process of calculating the required depth of a countersink hole. The calculator takes into account the input parameters, such as the diameter of the screw or fastener, the angle of the countersink, and the thickness of the material, and provides an accurate calculation of the required depth. The benefits of using a Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator include increased accuracy, reduced errors, and improved efficiency in the drilling and countersinking process.
Applications of the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator have a wide range of applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and manufacturing. The formula and calculator are used to drill and countersink holes in various materials, such as metals, plastics, and composites. The correct calculation of the countersink hole depth is critical in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of the final product.
Table of Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formulas and Calculators
| Formula/Calculator | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula | Calculates the required depth of a countersink hole based on the diameter of the screw or fastener, the angle of the countersink, and the thickness of the material | Aerospace, Automotive, Construction, and Manufacturing |
| Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator | Simplifies the process of calculating the required depth of a countersink hole using a software tool or online application | Metals, Plastics, and Composites |
Importance of Accurate Countersink Hole Depth Calculation
Accurate calculation of the countersink hole depth is critical in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of the final product. A miscalculation or inaccurate measurement can result in a weak joint, material failure, or safety hazards. The use of the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator ensures that the hole is drilled to the correct depth, providing a strong and secure joint. The accuracy and reliability of the formula and calculator make them essential tools in the drilling and countersinking process.
How do you calculate spot drill depth?

To calculate spot drill depth, you need to consider several factors, including the type of material being drilled, the size and type of drill bit, and the desired depth of the hole. The spot drill depth is typically calculated by adding the depth of the hole to be drilled to the length of the drill point, which is the angled or tapered portion of the drill bit that initiates the hole. This calculation ensures that the drill bit penetrates the material to the desired depth without over-drilling or under-drilling.
Understanding Drill Bit Geometry
The geometry of the drill bit plays a crucial role in calculating spot drill depth. The drill bit's point angle, lip angle, and flute length all impact the drilling process. To calculate spot drill depth, you need to understand how these factors interact with the material being drilled. For example, a drill bit with a shallow point angle may require a deeper spot drill depth to achieve the desired hole depth, while a drill bit with a steep point angle may require a shallower spot drill depth.
- The point angle of the drill bit affects the rate of penetration and the accuracy of the hole.
- The lip angle of the drill bit influences the drilling forces and the tool life.
- The flute length of the drill bit determines the maximum drilling depth and the stability of the drilling process.
Material Properties and Drill Depth
The properties of the material being drilled, such as its hardness, toughness, and density, also impact the calculation of spot drill depth. Softer materials, like aluminum or copper, may require a shallower spot drill depth due to their lower hardness, while harder materials, like steel or titanium, may require a deeper spot drill depth due to their higher hardness.
- The hardness of the material affects the drilling forces and the tool wear.
- The toughness of the material influences the drilling stability and the hole quality.
- The density of the material determines the drilling speed and the feed rate.
Drill Bit Size and Type
The size and type of drill bit used also play a significant role in calculating spot drill depth. Smaller drill bits typically require a shallower spot drill depth due to their lower drilling forces, while larger drill bits may require a deeper spot drill depth due to their higher drilling forces. Additionally, precision drill bits may require a more accurate calculation of spot drill depth to achieve the desired hole tolerance.
- The drill bit diameter affects the drilling forces and the hole size.
- The drill bit material influences the tool life and the drilling speed.
- The drill bit coating determines the friction and the wear resistance.
Calculating Spot Drill Depth
To calculate spot drill depth, you can use a formula that takes into account the drill bit geometry, material properties, and desired hole depth. The formula typically involves adding the drill point length to the desired hole depth, while also considering the material properties and drill bit size.
- The formula for calculating spot drill depth is: Spot Drill Depth = Desired Hole Depth + Drill Point Length.
- The drill point length is typically 0.1-0.5 times the drill bit diameter.
- The desired hole depth is the final depth of the hole, taking into account the material thickness and the desired hole tolerance.
Best Practices for Spot Drilling
To ensure accurate and efficient spot drilling, follow best practices such as using the correct drill bit size and type, maintaining proper drilling parameters, and monitoring the drilling process. Additionally, consider using spot drilling techniques, such as pilot drilling or peck drilling, to improve hole accuracy and reduce drill bit wear.
- Use the correct drill bit size and type for the specific material and application.
- Maintain proper drilling parameters, such as drilling speed and feed rate, to ensure optimal drill bit performance.
- Monitor the drilling process to detect any issues or anomalies that may affect the hole quality.
What is the formula for countersink depth?
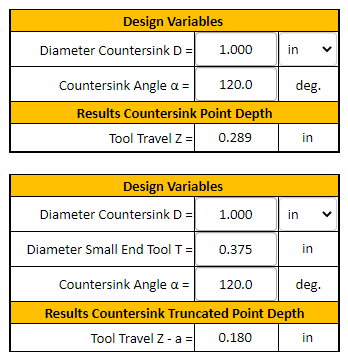
The formula for countersink depth is determined by the type of countersink being used and the thickness of the material it is being applied to. The general formula is: countersink depth (d) = screw head diameter / 2 + material thickness. This formula provides a basic guideline for calculating the countersink depth, but it may need to be adjusted depending on the specific application and requirements.
Understanding Countersink Depth
To calculate the countersink depth, it is essential to understand the geometry of the countersink and the screw head. The countersink depth is typically measured from the surface of the material to the bottom of the countersink. The formula takes into account the diameter of the screw head and the thickness of the material to ensure a proper fit. Here are some key considerations:
- The countersink angle can affect the depth calculation, with steeper angles requiring less depth.
- The material type and density can also impact the countersink depth, with harder materials requiring less depth.
- The screw head type and size can also influence the countersink depth, with larger screw heads requiring more depth.
Countersink Types and Depths
There are different types of countersinks, each with its own characteristics and requirements. The most common types of countersinks are 90-degree countersinks, 120-degree countersinks, and 130-degree countersinks. Each type of countersink has its own depth calculation, taking into account the screw head diameter and material thickness. Here are some key differences:
- 90-degree countersinks are the most common and are used for general-purpose applications.
- 120-degree countersinks are used for deeper applications and require a larger screw head diameter.
- 130-degree countersinks are used for shallow applications and require a smaller screw head diameter.
Calculating Countersink Depth for Specific Materials
The material thickness and type can significantly impact the countersink depth calculation. For example, aluminum and steel have different densities and properties, which can affect the countersink depth. Here are some key considerations:
- Soft materials like aluminum and copper require a shallower countersink depth.
- Hard materials like steel and titanium require a deeper countersink depth.
- Composite materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass require a customized countersink depth calculation.
Factors Affecting Countersink Depth
Several factors can affect the countersink depth, including the screw head type, material thickness, and countersink angle. Here are some key factors to consider:
- The screw head type and size can influence the countersink depth, with larger screw heads requiring more depth.
- The material thickness and type can impact the countersink depth, with thicker materials requiring more depth.
- The countersink angle can affect the depth calculation, with steeper angles requiring less depth.
Applications of Countersink Depth Calculations
The countersink depth calculation is essential in various applications, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. Here are some key applications:
- Aerospace applications require precise countersink depth calculations to ensure structural integrity.
- Automotive applications require customized countersink depth calculations to ensure proper fit and functionality.
- Construction applications require standardized countersink depth calculations to ensure safety and durability.
How deep to drill a countersink?

To determine how deep to drill a countersink, it's essential to consider the type of material being worked with, the size of the screw or fastener, and the desired finish. The countersink depth will depend on the angle of the countersink and the thickness of the material. A general rule of thumb is to drill the countersink to a depth that allows the screw head to sit flush with the surface of the material.
Understanding Countersink Depths
The depth of a countersink is critical to ensure a secure and flush fit. To achieve this, consider the following factors:
- Material thickness: The thickness of the material will determine the maximum depth of the countersink.
- Screw size: The size of the screw or fastener will influence the depth of the countersink.
- Countersink angle: The angle of the countersink will affect the depth required to achieve a flush fit.
Measuring Countersink Depths
Measuring the depth of a countersink can be done using a depth gauge or a caliper. It's essential to measure the depth accurately to avoid over-drilling or under-drilling. Consider the following:
- Use a depth gauge: A depth gauge can provide an accurate measurement of the countersink depth.
- Check the screw head: Verify that the screw head sits flush with the surface of the material.
- Adjust the countersink: If necessary, adjust the countersink depth to achieve the desired finish.
Factors Affecting Countersink Depths
Several factors can affect the depth of a countersink, including the type of material, the size of the screw, and the desired finish. Consider the following:
- Material type: Different materials may require different countersink depths.
- Screw type: The type of screw or fastener can influence the countersink depth.
- Finish requirements: The desired finish will determine the depth of the countersink.
Drilling Countersinks Safely
Drilling countersinks requires caution to avoid accidents and ensure a safe working environment. Consider the following:
- Use proper safety equipment: Wear safety glasses and a dust mask when drilling countersinks.
- Choose the right drill bit: Select a drill bit that is suitable for the material and countersink depth.
- Drill slowly and carefully: Drill slowly and carefully to avoid over-drilling or under-drilling.
Common Mistakes When Drilling Countersinks
Common mistakes when drilling countersinks include over-drilling, under-drilling, and using the wrong drill bit. Consider the following:
- Over-drilling: Drilling too deep can result in a weak or unstable joint.
- Under-drilling: Drilling too shallow can result in a loose or insecure fit.
- Using the wrong drill bit: Using the wrong drill bit can result in a poor finish or damage to the material.
What is the rule for countersinks?
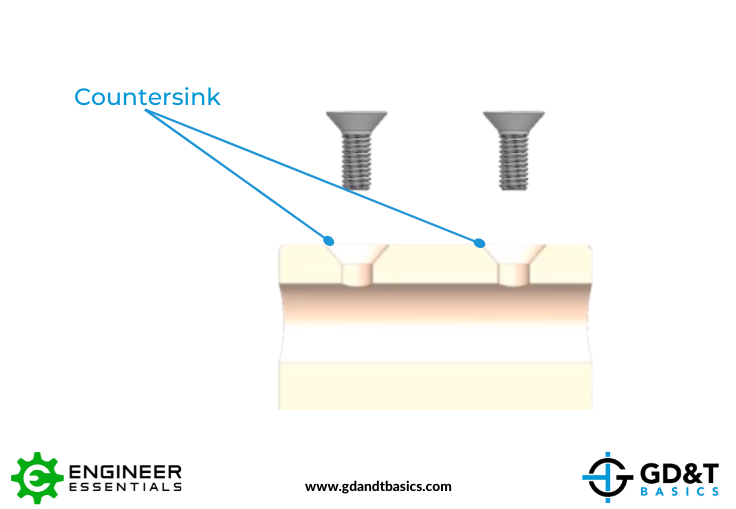
The rule for countersinks is to create a conical hole in a material, typically metal or wood, to allow a screw or fastener to sit flush with the surface. This is achieved by using a countersink bit, which is a type of drill bit specifically designed for this purpose. The countersink hole is typically larger in diameter than the screw or fastener, and is used to provide a secure and stable connection.
Understanding Countersink Angles
The angle of the countersink is critical, as it determines the strength and stability of the connection. A shallow angle can result in a weak connection, while a steep angle can cause the screw or fastener to strip or break. The most common countersink angles are:
- 82 degrees: This is a standard angle for most countersinks, and is suitable for most applications.
- 90 degrees: This angle is used for flush mounts, where the screw or fastener needs to sit perfectly level with the surface.
- 100 degrees: This angle is used for heavy-duty applications, where a stronger connection is required.
Choosing the Right Countersink Bit
The right countersink bit is essential for creating a smooth and accurate countersink hole. The bit should be made of a high-quality material, such as high-speed steel or tungsten carbide, and should be sharpened regularly to maintain its effectiveness. Some key factors to consider when choosing a countersink bit include:
- Bit size: The bit should be the correct size for the screw or fastener being used.
- Bit material: The bit should be made of a durable material that can withstand the rigors of drilling.
- Bit type: There are several types of countersink bits available, including straight, tapered, and combination bits.
Countersink Depths and Diameters
The depth and diameter of the countersink hole are critical factors in determining the strength and stability of the connection. The depth of the hole should be sufficient to allow the screw or fastener to sit flush with the surface, while the diameter should be large enough to provide a secure connection. Some key considerations when determining countersink depths and diameters include:
- Material thickness: The thickness of the material being drilled should be taken into account when determining the depth of the countersink hole.
- Screw or fastener size: The size of the screw or fastener being used should be taken into account when determining the diameter of the countersink hole.
- Application requirements: The specific requirements of the application should be taken into account when determining the depth and diameter of the countersink hole.
Countersink Safety Precautions
When working with countersinks, it is essential to take safety precautions to avoid injury or damage. Some key safety considerations include:
- Wear protective gear: Safety glasses, ear protection, and a dust mask should be worn when drilling or countersinking.
- Use proper drilling techniques: The drill should be held firmly and straight, and the bit should be advanced slowly and steadily.
- Avoid over-tightening: The screw or fastener should not be over-tightened, as this can cause the material to split or crack.
Common Countersink Applications
Countersinks are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Woodworking: Countersinks are commonly used in woodworking to create smooth and flush connections between wooden components.
- Metalworking: Countersinks are also used in metalworking to create strong and secure connections between metal components.
- Construction: Countersinks are used in construction to create secure and stable connections between building components, such as beams and joists.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and how does it work?
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula is a mathematical equation used to calculate the optimal depth of a countersink hole in a workpiece. This formula takes into account the angle of the countersink, the diameter of the hole, and the thickness of the material being drilled. By using this formula, users can ensure that their countersink holes are precisely controlled, which is critical in many applications, such as aerospace engineering, automotive manufacturing, and construction. The formula is typically expressed as a simple equation, where the depth of the countersink hole is calculated as a function of the tangent of the countersink angle and the radius of the hole. This allows users to quickly and easily determine the optimal depth of their countersink holes, which is essential for achieving high-quality finishes and precise fits.
How do I use the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator to determine the optimal depth of my countersink holes?
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Calculator is a user-friendly tool that allows users to quickly and easily calculate the optimal depth of their countersink holes. To use the calculator, users simply need to input the relevant parameters, such as the angle of the countersink, the diameter of the hole, and the thickness of the material being drilled. The calculator then uses the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula to calculate the optimal depth of the countersink hole, taking into account the specific requirements of the user's application. The calculator is typically web-based, making it easily accessible from any computer or mobile device with an internet connection. This allows users to quickly and easily determine the optimal depth of their countersink holes, without the need for complex calculations or expensive software.
What are the benefits of using the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator in my manufacturing process?
The Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator offer a number of significant benefits to users, including improved accuracy, increased efficiency, and enhanced quality control. By using the formula and calculator, users can ensure that their countersink holes are precisely controlled, which is critical in many applications where tight tolerances and high-quality finishes are required. Additionally, the formula and calculator can help users to reduce waste and minimize errors, by providing a quick and easy way to calculate the optimal depth of countersink holes. This can be especially beneficial in high-volume manufacturing applications, where small errors can quickly add up to significant costs. Furthermore, the formula and calculator can also help users to improve their productivity, by allowing them to quickly and easily determine the optimal depth of their countersink holes, without the need for complex calculations or expensive software.
Can I use the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator for a variety of different materials and applications?
Yes, the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator can be used for a wide range of materials and applications, including metals, plastics, and composites. The formula and calculator are material-agnostic, meaning that they can be used with any type of material that requires countersink holes. Additionally, the formula and calculator can be used in a variety of applications, including aerospace engineering, automotive manufacturing, construction, and electronics manufacturing. The formula and calculator are also highly customizable, allowing users to input specific parameters and requirements for their particular application. This makes the formula and calculator a versatile tool that can be used in a wide range of situations, from simple DIY projects to complex industrial manufacturing applications. By using the Countersink Spot Drill Depth Formula and Calculator, users can ensure that their countersink holes are precisely controlled, regardless of the material or application.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas