How should I push data between two SaaS services with REST API?
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, seamless data exchange between SaaS platforms is crucial for optimizing workflows and ensuring business efficiency. REST APIs have emerged as a powerful tool for enabling this communication, offering a standardized and flexible approach to data integration. However, pushing data between two SaaS services using REST APIs requires careful planning and execution to ensure reliability, security, and scalability. This article explores the key steps and best practices for effectively transferring data between SaaS platforms, from understanding API documentation to handling authentication, error management, and performance optimization. Whether you’re a developer or a business professional, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of API-driven data integration.
- How to Push Data Between Two SaaS Services Using REST API
- How to send data through REST API?
- How to integrate two applications using REST API?
- Which protocol does REST API use to transfer data between different applications?
- How to synchronize REST API?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the best way to authenticate when pushing data between two SaaS services using REST API?
- How can I handle rate limits when pushing data between SaaS services via REST API?
- What are the best practices for error handling when pushing data between SaaS services with REST API?
- How can I ensure data consistency when pushing data between two SaaS services using REST API?
How to Push Data Between Two SaaS Services Using REST API
To push data between two SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms using REST API, you need to understand the API documentation of both services, ensure proper authentication, and implement a reliable data transfer mechanism. REST APIs are widely used for their simplicity and compatibility, making them ideal for integrating SaaS platforms. Below, we break down the process into actionable steps.
Understanding REST API Basics
REST (Representational State Transfer) APIs are a set of rules for building web services. They use HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform operations on resources. To push data between SaaS services, you typically use the POST or PUT methods. Ensure both platforms support REST APIs and provide clear documentation for their endpoints.
| HTTP Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| GET | Retrieve data |
| POST | Create or send data |
| PUT | Update existing data |
| DELETE | Remove data |
Most SaaS platforms require authentication to access their APIs. Common methods include API keys, OAuth tokens, or Basic Authentication. Check the documentation of both services to determine the required authentication method. For example, if one service uses OAuth 2.0, you’ll need to obtain an access token before making API requests.
| Authentication Method | Description |
|---|---|
| API Key | A unique identifier passed in headers or URLs |
| OAuth 2.0 | Token-based authentication for secure access |
| Basic Authentication | Username and password encoded in Base64 |
Mapping Data Fields
Before pushing data, ensure the data fields in both SaaS platforms align. For example, if you’re sending customer information, map fields like name, email, and phone number between the two systems. Use JSON or XML formats to structure the data, as these are widely supported by REST APIs.
| Source Field | Target Field |
|---|---|
| first_name | firstName |
| email_address | |
| phone | contactNumber |
Handling API Rate Limits
SaaS platforms often impose rate limits to prevent abuse of their APIs. These limits restrict the number of requests you can make within a specific time frame. To avoid hitting these limits, implement retry mechanisms and throttling in your code. Monitor the API responses for headers like `X-RateLimit-Remaining` to track your usage.
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| X-RateLimit-Limit | Total allowed requests |
| X-RateLimit-Remaining | Remaining requests |
| Retry-After | Time to wait before retrying |
Error Handling and Logging
When pushing data, errors can occur due to network issues, invalid data, or API changes. Implement robust error handling to manage these scenarios. Log errors for debugging and use status codes like 400 (Bad Request) or 500 (Server Error) to identify issues. Additionally, set up notifications to alert you of critical failures.
| Status Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 200 | Success |
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 500 | Server Error |
How to send data through REST API?

Understanding REST API Basics
To send data through a REST API, you must first understand its fundamentals. REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to interact with resources. Here are the key steps:
- Identify the endpoint (URL) of the API where the data will be sent.
- Choose the appropriate HTTP method based on the action (e.g., POST for creating data).
- Format the data in a supported structure, such as JSON or XML.
Preparing the Data for Transmission
Before sending data, ensure it is properly formatted and structured. Most REST APIs use JSON as the data format due to its simplicity and readability. Follow these steps:
- Organize the data into key-value pairs or arrays as required by the API.
- Validate the data to ensure it meets the API's requirements (e.g., required fields, data types).
- Use tools like Postman or cURL to test the data structure before sending it.
Setting Up HTTP Headers
HTTP headers are crucial for sending additional information with your request. They help the server understand the type of data being sent and how to process it. Key headers include:
- Content-Type: Specifies the format of the data (e.g., application/json).
- Authorization: Includes authentication tokens or credentials if the API requires them.
- Accept: Indicates the response format the client can handle (e.g., application/json).
Making the API Request
Once the data and headers are ready, you can make the API request. Use tools or programming languages like Python, JavaScript, or Postman to send the request. Steps include:
- Construct the request with the appropriate HTTP method, endpoint, and headers.
- Include the formatted data in the request body (for POST or PUT requests).
- Send the request and wait for the server's response.
Handling the API Response
After sending the data, the server will respond with a status code and, optionally, a response body. Here's how to handle it:
- Check the status code (e.g., 200 for success, 400 for client errors) to determine if the request was successful.
- Parse the response body (if provided) to extract useful information or error messages.
- Log or display the response for debugging or user feedback purposes.
How to integrate two applications using REST API?
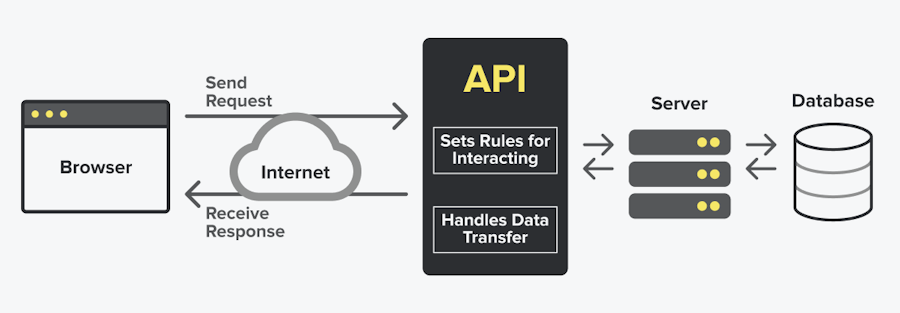
Understanding REST API Basics
To integrate two applications using REST API, it is essential to understand the basics of how REST APIs work. REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to interact with resources. Here are the key steps:
- Identify the endpoints: Determine the URLs provided by the API to access specific resources.
- Understand the data format: REST APIs typically use JSON or XML for data exchange.
- Authentication: Ensure you know the authentication method, such as API keys, OAuth, or Basic Auth.
Setting Up Authentication
Authentication is a critical step in integrating applications via REST API. Most APIs require some form of authentication to ensure secure access. Here’s how to handle it:
- Obtain API keys: Register your application with the API provider to get the necessary credentials.
- Use OAuth: For more secure integrations, implement OAuth to handle token-based authentication.
- Include headers: Add authentication tokens or keys to the HTTP headers of your API requests.
Defining API Endpoints and Methods
To integrate two applications, you need to define the API endpoints and the appropriate HTTP methods for each operation. Follow these steps:
- List available endpoints: Review the API documentation to identify the endpoints for the required resources.
- Choose the right method: Use GET for retrieving data, POST for creating resources, PUT for updating, and DELETE for removing resources.
- Test endpoints: Use tools like Postman or cURL to test the endpoints before integration.
Handling Data Exchange
Data exchange between applications is a core part of REST API integration. Ensure proper handling of data formats and responses:
- Parse JSON/XML: Use libraries in your programming language to parse and generate JSON or XML data.
- Validate responses: Check the status codes (e.g., 200 for success, 404 for not found) and handle errors gracefully.
- Map data fields: Align the data fields between the two applications to ensure seamless integration.
Testing and Debugging the Integration
Testing is crucial to ensure the integration works as expected. Follow these steps to test and debug your REST API integration:
- Use testing tools: Tools like Postman, SoapUI, or cURL can help simulate API requests and responses.
- Monitor logs: Check server logs and API logs to identify any issues or errors.
- Iterate and refine: Based on test results, refine your integration logic and retest until it works flawlessly.
Which protocol does REST API use to transfer data between different applications?

REST API primarily uses the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to transfer data between different applications. HTTP is the foundation of data communication on the web and is widely adopted due to its simplicity, scalability, and compatibility with various systems. REST APIs leverage HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources.
Why Does REST API Use HTTP?
REST APIs use HTTP because it is a standardized protocol that is universally supported across platforms and devices. HTTP provides a clear structure for communication, making it ideal for RESTful services. Here are some key reasons:
- Statelessness: HTTP is stateless, meaning each request from a client to a server must contain all the information needed to understand and process the request.
- Scalability: HTTP's stateless nature allows REST APIs to scale efficiently, as servers do not need to store session information between requests.
- Flexibility: HTTP supports various data formats, such as JSON, XML, and HTML, making it versatile for different use cases.
How Does REST API Utilize HTTP Methods?
REST APIs use HTTP methods to define the action to be performed on a resource. These methods align with CRUD operations:
- GET: Retrieves data from the server without modifying it.
- POST: Sends data to the server to create a new resource.
- PUT: Updates an existing resource or creates it if it does not exist.
- DELETE: Removes a resource from the server.
- PATCH: Partially updates an existing resource.
What Are the Advantages of Using HTTP in REST APIs?
Using HTTP in REST APIs offers several advantages:
- Interoperability: HTTP is supported by almost all programming languages and platforms, ensuring seamless integration.
- Simplicity: HTTP's straightforward request-response model makes it easy to implement and debug.
- Caching: HTTP supports caching mechanisms, which can improve performance by reducing server load.
What Data Formats Are Commonly Used in REST APIs?
REST APIs typically use lightweight data formats for communication:
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): The most popular format due to its simplicity and readability.
- XML (eXtensible Markup Language): Used in legacy systems or when more structured data is required.
- Plain Text: Occasionally used for simple responses or debugging purposes.
How Does REST API Ensure Security Over HTTP?
While HTTP itself is not secure, REST APIs can implement security measures:
- HTTPS: Encrypts data in transit using SSL/TLS, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
- Authentication: Methods like OAuth, API keys, or JWT (JSON Web Tokens) ensure only authorized users can access the API.
- Rate Limiting: Prevents abuse by limiting the number of requests a client can make within a specific timeframe.
How to synchronize REST API?
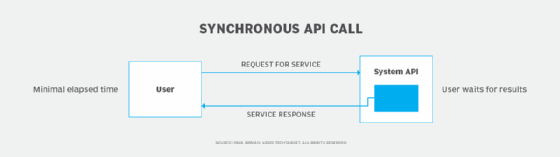
Understanding REST API Synchronization
Synchronizing a REST API involves ensuring that data and operations between the client and server are consistent and up-to-date. This process is crucial for maintaining data integrity and providing a seamless user experience. Below are key points to consider:
- Identify the data flow: Determine how data moves between the client and server, including which endpoints are involved.
- Use timestamps or versioning: Implement mechanisms like timestamps or version numbers to track changes and ensure the latest data is used.
- Handle conflicts: Develop strategies to resolve conflicts when the same data is modified simultaneously by different clients.
Implementing Polling for Synchronization
Polling is a technique where the client periodically requests updates from the server. While simple to implement, it can be inefficient. Here’s how to use polling effectively:
- Set a reasonable interval: Choose a polling frequency that balances responsiveness and server load.
- Optimize payload size: Minimize the amount of data sent in each response to reduce bandwidth usage.
- Use conditional requests: Implement headers like If-Modified-Since to avoid unnecessary data transfers.
Using Webhooks for Real-Time Synchronization
Webhooks provide a more efficient alternative to polling by allowing the server to notify the client of changes in real-time. Key considerations include:
- Set up a webhook endpoint: Create an endpoint on the client side to receive notifications from the server.
- Secure the webhook: Use authentication and encryption to ensure that only authorized parties can send and receive data.
- Handle retries and failures: Implement mechanisms to retry failed notifications and log errors for debugging.
ETags (Entity Tags) are HTTP headers used to validate cached resources. They help reduce unnecessary data transfers and improve synchronization efficiency:
- Generate unique ETags: Assign a unique identifier to each resource version to track changes.
- Use conditional requests: Include the If-None-Match header to check if the resource has changed since the last request.
- Optimize cache usage: Combine ETags with caching strategies to minimize redundant data transfers.
Handling Offline Synchronization
Offline synchronization ensures that data remains consistent even when the client is not connected to the server. This is particularly important for mobile and distributed applications:
- Use local storage: Store data locally on the client device to allow offline access and modifications.
- Track changes: Maintain a log of changes made offline to synchronize with the server once connectivity is restored.
- Resolve conflicts: Implement conflict resolution strategies to handle discrepancies between local and server data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best way to authenticate when pushing data between two SaaS services using REST API?
When pushing data between two SaaS services using REST API, authentication is crucial to ensure secure communication. The most common methods include OAuth 2.0, API keys, and Basic Authentication. OAuth 2.0 is widely recommended for its robust security features, allowing you to grant limited access without sharing credentials. API keys are simpler to implement but should be used with caution, as they can be less secure if not managed properly. Always ensure that your authentication method aligns with the security requirements of both services.
How can I handle rate limits when pushing data between SaaS services via REST API?
Rate limits are often imposed by SaaS providers to prevent abuse and ensure fair usage. To handle rate limits effectively, you should first check the API documentation of both services to understand their specific limits. Implement retry mechanisms with exponential backoff to handle temporary rate limit errors gracefully. Additionally, consider batching your requests or using webhooks to reduce the number of API calls. Monitoring your API usage and optimizing your code to minimize unnecessary requests can also help you stay within the allowed limits.
What are the best practices for error handling when pushing data between SaaS services with REST API?
Proper error handling is essential to ensure the reliability of data transfer between SaaS services. Always check for and handle common HTTP status codes such as 400 (Bad Request), 401 (Unauthorized), 429 (Too Many Requests), and 500 (Internal Server Error). Implement logging to track errors and retries, and use idempotent requests to avoid duplicate data in case of retries. Additionally, provide meaningful error messages to help diagnose issues quickly and consider setting up alerts for critical failures.
How can I ensure data consistency when pushing data between two SaaS services using REST API?
Ensuring data consistency is critical when transferring data between SaaS services. Use transactional mechanisms where possible to ensure that data is either fully transferred or not at all. Implement data validation checks before sending data to ensure it meets the required format and standards. Additionally, consider using webhooks or event-driven architectures to synchronize data in real-time and avoid discrepancies. Regularly monitor and reconcile data between the two services to catch and resolve inconsistencies early.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas