Spur Gear Calculator Generator
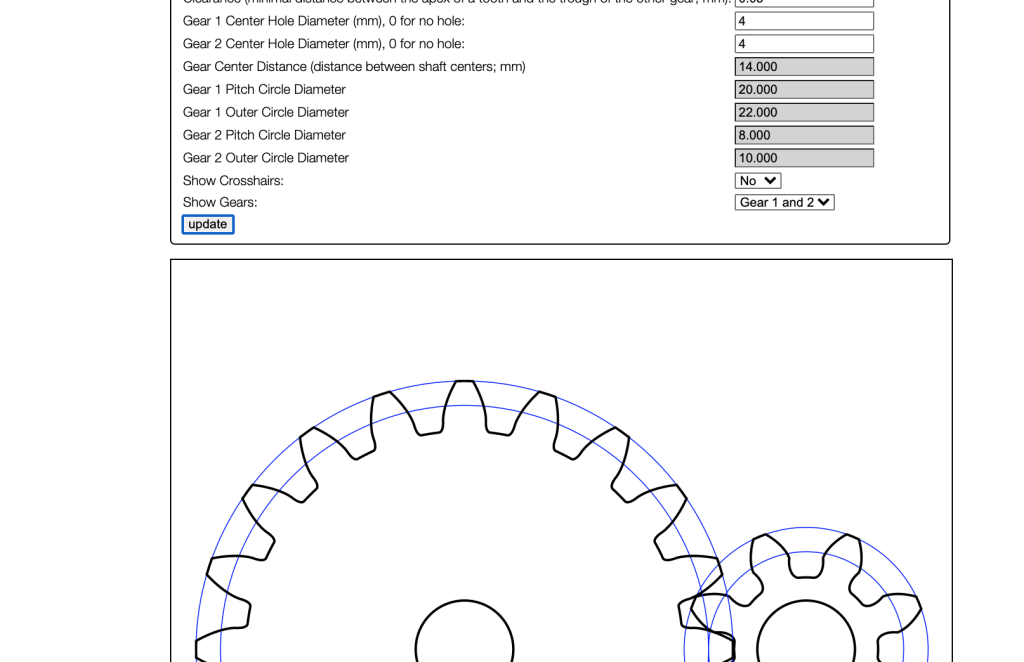
The Spur Gear Calculator Generator is a valuable tool for engineers and designers, enabling them to efficiently calculate and generate spur gear designs. This calculator takes into account various parameters such as pitch diameter, number of teeth, and pressure angle to produce accurate results. With its user-friendly interface, users can easily input their specifications and generate detailed reports, including gear ratios, tooth profiles, and other essential design elements. This generator simplifies the design process, saving time and reducing errors, making it an indispensable resource for the engineering community. It streamlines gear design and optimization.
Understanding the Spur Gear Calculator Generator
The Spur Gear Calculator Generator is a tool designed to simplify the process of calculating and designing spur gears, which are a type of gear used in mechanical systems to transmit power between two or more shafts. This calculator generator provides a user-friendly interface for inputting parameters such as gear ratio, pitch diameter, and number of teeth, and then generates the necessary calculations for designing and manufacturing the gears.
Introduction to Spur Gears
Spur gears are a fundamental component in many mechanical systems, including gearboxes, transmissions, and machinery. They are used to transmit power between two or more shafts, and are characterized by their simple design and high efficiency. The Spur Gear Calculator Generator is an essential tool for engineers and designers who need to create and optimize spur gear systems.
Key Parameters in Spur Gear Design
The design of a spur gear system involves several key parameters, including gear ratio, pitch diameter, number of teeth, and pressure angle. The Spur Gear Calculator Generator allows users to input these parameters and generate the necessary calculations for designing and manufacturing the gears. The calculator also takes into account factors such as material properties and tolerances to ensure that the gears are designed to meet specific performance requirements.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Gear Ratio | The ratio of the number of teeth on the driven gear to the number of teeth on the drive gear |
| Pitch Diameter | The diameter of the gear at the pitch circle, where the teeth are evenly spaced |
| Number of Teeth | The number of teeth on each gear |
| Pressure Angle | The angle between the line of action and the tangent to the pitch circle |
Benefits of Using a Spur Gear Calculator Generator
The Spur Gear Calculator Generator offers several benefits, including increased accuracy, reduced design time, and improved performance. By using this tool, users can quickly and easily generate the necessary calculations for designing and manufacturing spur gears, without having to resort to manual calculations or trial-and-error methods. The calculator generator also allows users to optimize their gear designs, taking into account factors such as efficiency, noise reduction, and cost savings.
Applications of Spur Gear Calculator Generators
Spur Gear Calculator Generators have a wide range of applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and consumer products. They are used to design and manufacture gearboxes, transmissions, and other mechanical systems that require precise and efficient gear operation. The calculator generator is also useful for educational purposes, allowing students and engineers to learn about gear design and analysis in a practical and interactive way.
Future Developments in Spur Gear Technology
The field of spur gear technology is constantly evolving, with new materials, new manufacturing techniques, and new design methods being developed and implemented. The Spur Gear Calculator Generator is expected to play a key role in these developments, by providing a powerful tool for engineers and designers to create and optimize spur gear systems. Future developments in spur gear technology are likely to focus on improving efficiency, reducing noise and vibration, and increasing reliability and lifetime of the gears.
How do you calculate spur gear?
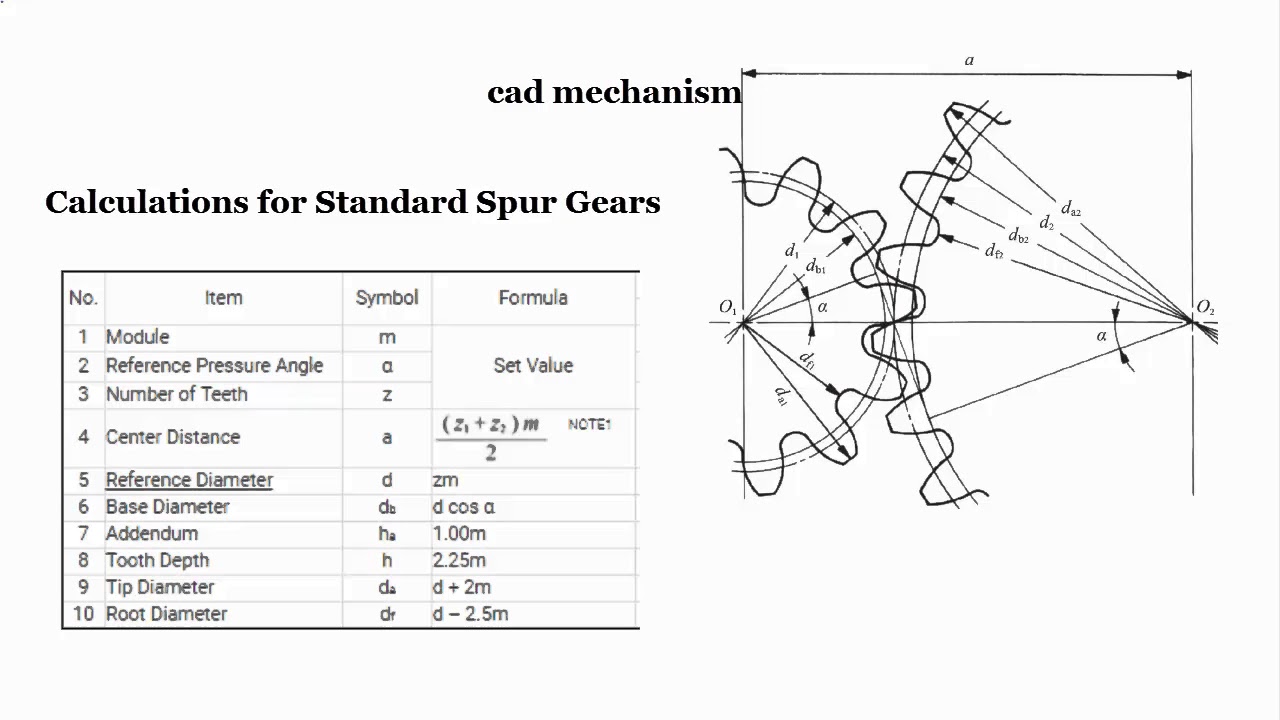
To calculate spur gear, you need to consider several factors, including the gear ratio, tooth number, pitch diameter, and pressure angle. The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the pinion and the gear, and it is calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the gear by the number of teeth on the pinion. The pitch diameter is the diameter of the circle that passes through the centers of the teeth, and it is used to calculate the spur gear dimensions. The pressure angle is the angle between the tooth profile and the pitch circle, and it affects the gear efficiency and noise level.
Spur Gear Design
The spur gear design involves calculating the gear dimensions, including the pitch diameter, tooth width, and tooth height. To design a spur gear, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine the gear ratio and the number of teeth on the pinion and the gear.
- Calculate the pitch diameter using the gear ratio and the number of teeth.
- Choose a standard pitch and calculate the tooth width and tooth height.
The spur gear design is critical to ensure proper meshing and smooth operation of the gear set.
Spur Gear Calculation
The spur gear calculation involves calculating the gear dimensions and tooth profile. To calculate the spur gear, you need to consider the gear ratio, tooth number, pitch diameter, and pressure angle. The calculation involves the following steps:
- Calculate the pitch diameter using the gear ratio and the number of teeth.
- Calculate the tooth width and tooth height using the standard pitch.
- Determine the tooth profile and calculate the addendum and dedendum.
The spur gear calculation is essential to ensure accurate gear manufacturing and proper gear operation.
Spur Gear Ratio
The spur gear ratio is the ratio of the number of teeth on the gear to the number of teeth on the pinion. The gear ratio is calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the gear by the number of teeth on the pinion. The gear ratio affects the torque and speed of the output shaft. To determine the gear ratio, you need to consider the required torque and speed of the output shaft. The gear ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
- Determine the required torque and speed of the output shaft.
- Calculate the gear ratio using the torque and speed requirements.
- Choose a standard gear ratio and calculate the number of teeth on the pinion and the gear.
The spur gear ratio is critical to ensure proper gear operation and required output.
Spur Gear Efficiency
The spur gear efficiency is affected by the gear ratio, tooth profile, and pressure angle. The gear efficiency is calculated by dividing the output power by the input power. The gear efficiency can be improved by optimizing the tooth profile and pressure angle. To improve the gear efficiency, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine the required efficiency and calculate the output power.
- Calculate the gear efficiency using the output power and input power.
- Optimize the tooth profile and pressure angle to improve the gear efficiency.
The spur gear efficiency is essential to ensure smooth operation and minimum power loss.
Spur Gear Manufacturing
The spur gear manufacturing involves cutting, grinding, and finishing the gear teeth. To manufacture a spur gear, you need to follow these steps:
- Cut the gear blank using a lathe or milling machine.
- Grind the gear teeth using a grinder or hobbing machine.
- Finish the gear teeth using a finishing machine or lapping process.
The spur gear manufacturing is critical to ensure accurate gear dimensions and smooth operation. The manufacturing process can be optimized by using advanced machinery and quality control measures.
How do you size a spur gear?
To size a spur gear, you need to consider several factors, including the torque and speed requirements of the application, as well as the material and manufacturing constraints. The sizing process typically involves calculating the pitch diameter and tooth width of the gear, as well as selecting the appropriate pitch and pressure angle. This information can be used to determine the gear ratio and efficiency of the gear set.
Understanding Gear Terminology
When sizing a spur gear, it's essential to understand the terminology used in the industry. Key terms include pitch circle, addendum, and dedendum, which refer to the distance from the center of the gear to the outer edge of the teeth, the height of the teeth above the pitch circle, and the depth of the teeth below the pitch circle, respectively. To size a gear, you'll need to consider the following factors:
- Torque: The amount of rotational force required to drive the gear
- Speed: The rate at which the gear rotates, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM)
- Material: The type of material used to manufacture the gear, such as steel or plastic
Calculating Gear Dimensions
To calculate the dimensions of a spur gear, you'll need to use formulas and equations that take into account the pitch diameter, tooth width, and gear ratio. The pitch diameter is the distance from the center of the gear to the pitch circle, while the tooth width is the distance from the pitch circle to the outer edge of the teeth. The gear ratio is the ratio of the pitch diameter of the driven gear to the pitch diameter of the driving gear. Key calculations include:
- Pitch diameter: Calculated using the formula D = N / P, where D is the pitch diameter, N is the number of teeth, and P is the pitch
- Tooth width: Calculated using the formula W = D sin(P), where W is the tooth width, D is the pitch diameter, and P is the pressure angle
- Gear ratio: Calculated using the formula G = D2 / D1, where G is the gear ratio, D2 is the pitch diameter of the driven gear, and D1 is the pitch diameter of the driving gear
Selecting Gear Materials
When selecting a material for a spur gear, you'll need to consider the strength, durability, and wear resistance of the material. Strong materials like steel and titanium are suitable for high-torque applications, while lightweight materials like aluminum and plastic are suitable for low-torque applications. Additionally, you'll need to consider the manufacturing process and the surface finish of the material. Key considerations include:
- Strength: The ability of the material to withstand stress and strain
- Durability: The ability of the material to withstand wear and tear
- Wear resistance: The ability of the material to withstand friction and abrasion
Determining Gear Efficiency
The efficiency of a spur gear is determined by the gear ratio, tooth profile, and lubrication. A high-efficiency gear set can transmit power and torque with minimal loss, while a low-efficiency gear set can result in energy loss and heat generation. Key factors that affect gear efficiency include:
- Gear ratio: The ratio of the pitch diameter of the driven gear to the pitch diameter of the driving gear
- Tooth profile: The shape and geometry of the teeth, including the addendum and dedendum
- Lubrication: The type and amount of lubricant used to reduce friction and wear
Considering Manufacturing Constraints
When sizing a spur gear, you'll need to consider the manufacturing constraints, including the machining process, tooling, and tolerances. The machining process can affect the surface finish and accuracy of the gear, while the tooling and tolerances can affect the cost and lead time of production. Key considerations include:
- Machining: The process used to cut and shape the gear, including milling, grinding, and hobbing
- Tooling: The cutting tools and fixtures used to manufacture the gear
- Tolerances: The allowable variations in dimension and position of the gear
What is the maximum gear ratio for a spur?

The maximum gear ratio for a spur gear is typically determined by the diameter and tooth count of the gears. In general, the maximum gear ratio is limited by the speed and torque requirements of the application. For example, a high gear ratio may be required for a low-speed application, but it may not be suitable for a high-speed application due to the increased risk of vibration and noise.
Design Considerations for Spur Gears
When designing spur gears, there are several factors to consider, including the gear ratio, tooth profile, and material selection. The gear ratio is critical in determining the speed and torque of the output shaft. A high gear ratio can provide a high torque output, but it may also increase the noise and vibration of the system. Some key considerations include:
- Gear ratio: The ratio of the output speed to the input speed, which determines the torque and speed of the output shaft.
- Tooth profile: The shape and size of the teeth, which affects the efficiency and noise of the gear.
- Material selection: The type of material used for the gear, which affects the strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of the gear.
Factors Affecting Gear Ratio
The gear ratio is affected by several factors, including the diameter and tooth count of the gears. A larger diameter and higher tooth count can provide a higher gear ratio, but it may also increase the size and weight of the gear. Other factors that can affect the gear ratio include the speed and torque requirements of the application, as well as the efficiency and noise considerations. Some key factors include:
- Diameter: The size of the gear, which affects the gear ratio and torque output.
- Tooth count: The number of teeth on the gear, which affects the gear ratio and efficiency of the gear.
- Speed: The speed of the input shaft, which affects the gear ratio and torque output.
Gear Ratio Limits
The gear ratio is limited by several factors, including the diameter and tooth count of the gears, as well as the speed and torque requirements of the application. In general, the maximum gear ratio is limited by the size and weight of the gear, as well as the efficiency and noise considerations. Some key limits include:
- Diameter limit: The maximum diameter of the gear, which affects the gear ratio and torque output.
- Tooth count limit: The maximum tooth count of the gear, which affects the gear ratio and efficiency of the gear.
- Speed limit: The maximum speed of the input shaft, which affects the gear ratio and torque output.
Applications of High Gear Ratios
High gear ratios are often required in low-speed applications, such as industrial machinery and automotive transmissions. In these applications, a high gear ratio can provide a high torque output, which is necessary for heavy-duty operations. Some key applications include:
- Industrial machinery: High gear ratios are often required in industrial machinery, such as pumps and conveyors.
- Automotive transmissions: High gear ratios are often required in automotive transmissions, such as manual transmissions and automatic transmissions.
- Aerospace applications: High gear ratios are often required in aerospace applications, such as aircraft engines and helicopter transmissions.
Challenges of High Gear Ratios
High gear ratios can pose several challenges, including noise and vibration, as well as efficiency and durability considerations. In general, high gear ratios can increase the noise and vibration of the system, which can lead to reduced efficiency and increased wear. Some key challenges include:
- Noise and vibration: High gear ratios can increase the noise and vibration of the system, which can lead to reduced efficiency and increased wear.
- Efficiency considerations: High gear ratios can reduce the efficiency of the system, which can lead to increased energy consumption and reduced performance.
- Durability considerations: High gear ratios can reduce the durability of the system, which can lead to increased maintenance and reduced lifespan.
What is the formula for calculating gears?

The formula for calculating gears is a mathematical equation that determines the relationship between the rotational speed and torque of two or more gears in a gear system. The formula is:
i = (N2 / (N1 (d2 / d1)))
where i is the gear ratio, N1 and N2 are the number of teeth on the input and output gears, and d1 and d2 are the diameters of the input and output gears.
Understanding Gear Ratios
To understand gear ratios, it's essential to know that the gear ratio is the ratio of the output speed to the input speed. A gear ratio can be calculated using the formula:
gear ratio = (number of teeth on output gear) / (number of teeth on input gear).
Here are the key points to consider:
- The gear ratio determines the output speed and torque of the gear system.
- A higher gear ratio results in a lower output speed and a higher output torque.
- A lower gear ratio results in a higher output speed and a lower output torque.
Calculating Gear Speed
To calculate the output speed of a gear system, you need to know the input speed and the gear ratio. The formula for calculating the output speed is:
output speed = (input speed) / (gear ratio).
Here are the key points to consider:
- The input speed is the speed at which the input gear rotates.
- The gear ratio determines the output speed and torque of the gear system.
- A higher gear ratio results in a lower output speed and a higher output torque.
Understanding Torque and Gear Ratio
Torque is a measure of the rotational force of a gear system. The gear ratio determines the output torque of the gear system. A higher gear ratio results in a higher output torque, while a lower gear ratio results in a lower output torque.
Here are the key points to consider:
- The gear ratio determines the output torque of the gear system.
- A higher gear ratio results in a higher output torque.
- A lower gear ratio results in a lower output torque.
Designing Gear Systems
When designing a gear system, it's essential to consider the input speed, output speed, and torque requirements of the system. The gear ratio must be carefully selected to ensure that the output speed and torque meet the requirements of the system.
Here are the key points to consider:
- The input speed and output speed requirements of the system must be considered.
- The torque requirements of the system must be considered.
- The gear ratio must be carefully selected to ensure that the output speed and torque meet the requirements of the system.
Applications of Gear Systems
Gear systems are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. The gear ratio and torque requirements of the system depend on the specific application.
Here are the key points to consider:
- The gear ratio and torque requirements of the system depend on the specific application.
- Automotive applications require a high gear ratio to achieve high output torque.
- Aerospace applications require a low gear ratio to achieve high output speed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of a Spur Gear Calculator Generator?
The Spur Gear Calculator Generator is a software tool designed to help engineers and designers calculate and generate the dimensions and specifications of spur gears. Spur gears are a type of gear that has teeth cut parallel to the axis of rotation, and are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including mechanical systems, robotics, and automotive systems. The calculator generator uses mathematical formulas and algorithms to calculate the optimal gear dimensions, taking into account factors such as teeth number, pitch diameter, and pressure angle. This allows designers to quickly and easily generate accurate gear specifications, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
How does the Spur Gear Calculator Generator work?
The Spur Gear Calculator Generator works by using a combination of mathematical equations and geometric calculations to determine the optimal gear dimensions. The user inputs the required design parameters, such as the number of teeth, pitch diameter, and material properties, and the calculator generator uses these inputs to calculate the corresponding gear dimensions, including the tooth width, tooth height, and pitch circle diameter. The calculator generator also takes into account constraints such as interference and undercutting, to ensure that the generated gear design is feasible and manufacturable. The resulting gear design can then be exported to a CAD system or other design software for further analysis and refinement.
What are the benefits of using a Spur Gear Calculator Generator?
Using a Spur Gear Calculator Generator offers several benefits, including increased accuracy and reduced design time. By automating the gear design process, the calculator generator eliminates the need for manual calculations and trial-and-error approaches, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies. Additionally, the calculator generator allows designers to optimize their gear designs for specific performance criteria, such as torque, speed, and efficiency. This can lead to improved system performance, increased reliability, and reduced maintenance costs. Furthermore, the calculator generator can also help designers to explore different design options and compare alternative gear designs, allowing them to make informed decisions about their design.
Can the Spur Gear Calculator Generator be used for complex gear designs?
Yes, the Spur Gear Calculator Generator can be used for complex gear designs, including multi-stage gearboxes, planetary gears, and helical gears. The calculator generator has the capability to handle non-standard gear designs and custom gear geometries, allowing designers to create unique and innovative gear designs. Additionally, the calculator generator can also be used to analyze and optimize existing gear designs, allowing designers to refine and improve their designs. The calculator generator's advanced algorithms and mathematical models enable it to handle complex gear design problems, including non-linear and dynamic analysis. This makes it an essential tool for engineers and designers working on challenging and high-performance gear design projects.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas