Solar Position Details Calculator
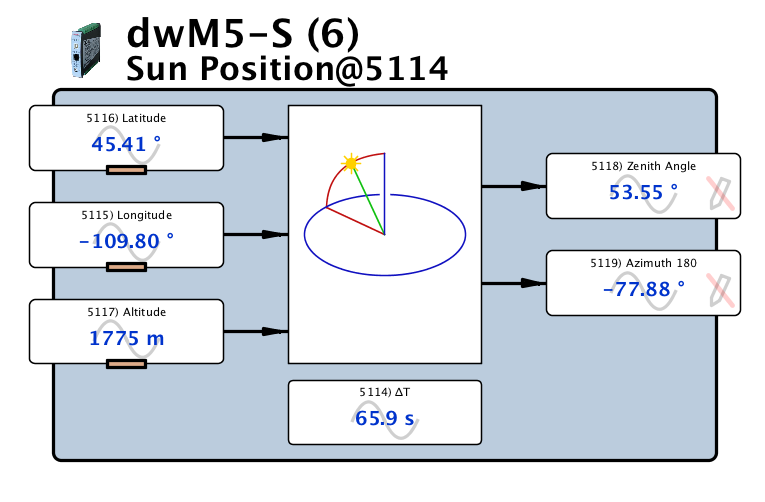
The Solar Position Details Calculator is a valuable tool for determining the precise location of the sun in the sky at any given time and location. This calculator provides critical information for solar panel installation, architecture, and engineering applications. By inputting the date, time, and geographical coordinates, users can obtain detailed calculations of the sun's altitude, azimuth, and hour angle. This data is essential for optimizing solar energy systems and designing buildings that maximize natural light and heat. The calculator's accuracy and reliability make it an indispensable resource for professionals and individuals alike. Its user-friendly interface simplifies complex calculations.
Solar Position Details Calculator: Understanding the Basics
The Solar Position Details Calculator is a tool used to calculate the position of the sun in the sky at a given location and time. This calculator takes into account the latitude, longitude, and time zone of the location, as well as the date and time, to provide accurate calculations of the sun's altitude, azimuth, and other relevant parameters. The calculator is commonly used in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and renewable energy to determine the solar irradiance and shading patterns on buildings and surfaces.
Introduction to Solar Position Calculations
Solar position calculations involve determining the position of the sun in the sky at a given location and time. This requires taking into account the Earth's rotation, axial tilt, and elliptical orbit around the sun. The calculator uses complex algorithms and mathematical formulas to provide accurate calculations of the sun's position, including its declination, hour angle, and equation of time. These calculations are essential for determining the solar radiation and energy yield of solar panels and other renewable energy systems.
Key Parameters in Solar Position Calculations
The Solar Position Details Calculator takes into account several key parameters to provide accurate calculations, including:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Latitude | The angular distance of a location north or south of the equator |
| Longitude | The angular distance of a location east or west of the prime meridian |
| Time Zone | The time zone of the location, which affects the solar time and calculations |
| Date and Time | The specific date and time for which the solar position is being calculated |
These parameters are crucial in determining the solar altitude and azimuth angles, which are used to calculate the solar irradiance and shadowing effects on surfaces.
Applications of Solar Position Details Calculator
The Solar Position Details Calculator has various applications in different fields, including:
Architecture: to determine the solar radiation and shading patterns on buildings and surfaces
Engineering: to design and optimize solar panels and other renewable energy systems
Renewable Energy: to determine the energy yield and performance of solar panels and other renewable energy systems
Agriculture: to determine the solar radiation and photoperiod effects on crops and plant growth
The calculator is an essential tool for professionals and researchers working in these fields to make informed decisions and optimize their designs and systems.
Benefits of Using Solar Position Details Calculator
Using the Solar Position Details Calculator offers several benefits, including:
Accurate calculations: the calculator provides accurate calculations of the sun's position and solar radiation
Time-saving: the calculator automates the calculation process, saving time and effort
Improved design: the calculator helps professionals and researchers to design and optimize their systems and surfaces for maximum energy efficiency and performance
Cost-effective: the calculator is a cost-effective tool compared to manual calculations or other software programs
The calculator is a valuable resource for anyone working with solar energy and radiation, providing fast and accurate calculations to inform their decisions and designs.
Limitations and Future Developments of Solar Position Details Calculator
While the Solar Position Details Calculator is a powerful tool, it has some limitations, including:
Atmospheric conditions: the calculator does not account for atmospheric conditions such as air pollution, cloud cover, and aerosol Optical depth
Topography: the calculator does not account for topographical features such as hills, valleys, and mountains
Future developments of the calculator may include incorporating these factors to provide even more accurate calculations and real-time data. Additionally, the calculator may be integrated with other tools and software programs to provide a more comprehensive solar energy and radiation analysis.
What is the formula for the position of the sun?

The formula for the position of the sun is based on the solar declination and the equation of time. The solar declination is the angle between the sun's position in the sky and the celestial equator, while the equation of time is the difference between the mean solar time and the apparent solar time.
Understanding Solar Declination
The solar declination is calculated using the latitude of the location and the time of year. The formula for solar declination is: δ = 23.45° sin(360° (284 + n) / 365), where δ is the solar declination, n is the day of the year, and 23.45° is the axial tilt of the Earth. The key factors that affect the solar declination are:
- The latitude of the location, which affects the angle of incidence of the sun's rays
- The time of year, which affects the position of the sun in the sky
- The axial tilt of the Earth, which affects the amount of solar radiation received by the location
Equation of Time
The equation of time is the difference between the mean solar time and the apparent solar time. The equation of time is calculated using the solar declination and the hour angle of the sun. The formula for the equation of time is: EqT = 229.2° (0.000075 + 0.001868 cos(360° (n - 2) / 365) - 0.032077 sin(360° (n - 2) / 365)), where EqT is the equation of time, n is the day of the year, and 229.2° is a constant. The key factors that affect the equation of time are:
- The solar declination, which affects the position of the sun in the sky
- The hour angle of the sun, which affects the time of day
- The day of the year, which affects the position of the sun in the sky
Calculating the Position of the Sun
To calculate the position of the sun, we need to use the solar declination and the equation of time. The formula for the position of the sun is: azimuth = arctan((sin(δ) sin(φ)) / (cos(δ) sin(φ) sin(ω) - cos(ω) cos(φ))), where azimuth is the azimuth angle of the sun, δ is the solar declination, φ is the latitude of the location, and ω is the hour angle of the sun. The key factors that affect the position of the sun are:
- The solar declination, which affects the position of the sun in the sky
- The latitude of the location, which affects the angle of incidence of the sun's rays
- The hour angle of the sun, which affects the time of day
Factors Affecting the Position of the Sun
There are several factors that affect the position of the sun, including:
- The latitude of the location, which affects the angle of incidence of the sun's rays
- The time of year, which affects the position of the sun in the sky
- The time of day, which affects the hour angle of the sun
These factors can be used to calculate the position of the sun at any given time and location.
Applications of the Formula
The formula for the position of the sun has several applications, including:
- Solar energy systems, which rely on the position of the sun to generate electricity
- Navigation systems, which use the position of the sun to determine direction and location
- Agriculture and architecture, which use the position of the sun to optimize building design and crop growth
These applications rely on the accuracy of the formula for the position of the sun, which is critical for solar energy systems and navigation systems.
What is the current solar declination?
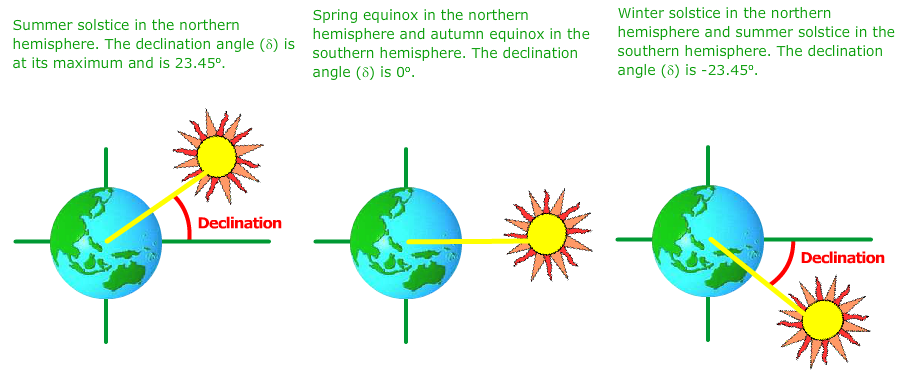
The current solar declination is the angle between the sun's rays and the Earth's equatorial plane. This angle varies throughout the year due to the Earth's tilt on its axis, which is approximately 23.5 degrees. The solar declination changes daily, with the sun's position shifting slightly each day. This shift affects the amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, resulting in changes in temperature and seasonal patterns.
Understanding Solar Declination
The solar declination is an essential factor in determining the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth's surface. It is calculated using the sun's position and the Earth's tilt. The solar declination angle is used in various applications, including architecture, engineering, and agriculture. Some key points to consider when understanding solar declination include:
- The solar declination angle varies between -23.5 degrees and 23.5 degrees throughout the year.
- The sun's position is affected by the Earth's elliptical orbit, resulting in a slightly variable solar declination.
- Solar declination tables or calculators are used to determine the exact angle for a given date and location.
Calculating Solar Declination
Calculating the solar declination involves using astronomical algorithms and mathematical models. These calculations take into account the Earth's tilt, the sun's position, and the time of year. The solar declination can be calculated using various methods, including:
- Using solar declination tables or charts, which provide pre-calculated values for specific dates and locations.
- Employing astronomical software or online calculators that use algorithms to calculate the solar declination.
- Utilizing mathematical formulas, such as the solar declination equation, to calculate the angle manually.
Applications of Solar Declination
The solar declination has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: designing buildings that maximize natural lighting and heating or cooling efficiency.
- Engineering: developing solar panels and renewable energy systems that optimize energy production.
- Agriculture: determining the best planting times and crop management strategies based on solar radiation patterns.
Effects of Solar Declination on Climate
The solar declination plays a significant role in shaping the Earth's climate and weather patterns. The angle of the sun's rays affects the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth's surface, resulting in changes in:
- Temperature: the solar declination influences the global temperature patterns, with variations in seasonal temperatures.
- Precipitation: the solar declination affects the atmospheric circulation patterns, which in turn influence precipitation and weather patterns.
- Seasonal patterns: the solar declination drives the changes in seasons, with the sun's position determining the length of days and amount of sunlight.
Importance of Accurate Solar Declination Data
Accurate solar declination data is crucial for various applications, including renewable energy systems, agriculture, and climate modeling. High-quality solar declination data is necessary to:
- Optimize solar panel performance and energy production.
- Determine the best crop management strategies and planting times.
- Improve climate models and weather forecasting accuracy.
Is there a solar calculator?

Yes, there is a solar calculator that can help you estimate the cost and benefits of installing solar panels on your home or business. This type of calculator takes into account various factors, including the amount of sunlight your location receives, the size and efficiency of the solar panels, and the local electricity rates. By using a solar calculator, you can get a better understanding of how much you can save on your energy bills and how long it will take for the solar panels to pay for themselves.
How to Use a Solar Calculator
To use a solar calculator, you will need to input some basic information, such as your location, the size of your home or business, and your current energy usage. The calculator will then use this information to estimate the amount of solar energy you can generate and the cost of installing the solar panels. Here are the steps to follow:
- Enter your location to determine the amount of sunlight you receive
- Input the size of your home or business to determine the size of the solar panel system needed
- Enter your current energy usage to determine how much energy you can save with solar panels
Benefits of Using a Solar Calculator
Using a solar calculator can help you make a more informed decision about whether or not to install solar panels on your home or business. Some of the benefits of using a solar calculator include:
- Estimating the cost savings of installing solar panels
- Determining the return on investment of the solar panels
- Identifying the environmental benefits of using renewable energy
The solar calculator can also help you understand the incentives and tax credits available for installing solar panels, which can help offset the upfront cost.
Factors That Affect the Accuracy of a Solar Calculator
The accuracy of a solar calculator depends on various factors, including the quality of the data used to estimate the amount of sunlight your location receives. Other factors that can affect the accuracy of the calculator include:
- The angle and orientation of the solar panels
- The shading of the solar panels from trees or other objects
- The temperature and weather patterns in your location
It's essential to consider these factors when using a solar calculator to get a more accurate estimate of the benefits and costs of installing solar panels.
Types of Solar Calculators Available
There are different types of solar calculators available, including online calculators and software programs. Some solar calculators are specifically designed for residential use, while others are designed for commercial use. Here are some examples:
- Web-based calculators that can be accessed from any device with an internet connection
- Mobile apps that can be downloaded on your smartphone or tablet
- Specialized software that can be installed on your computer
Each type of solar calculator has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it's essential to choose the one that best suits your needs.
Limitations of Solar Calculators
While solar calculators can be a useful tool for estimating the benefits and costs of installing solar panels, they do have some limitations. Some of the limitations include:
- Assumptions about the amount of sunlight your location receives
- Simplifications of the complex factors that affect the performance of solar panels
- Lack of personalization to your specific situation
It's essential to understand these limitations and use the solar calculator as a rough estimate rather than a definitive prediction of the benefits and costs of installing solar panels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Solar Position Details Calculator and how does it work?
The Solar Position Details Calculator is a tool designed to calculate the position of the sun in the sky at a given location and time. This calculator takes into account various astronomical and geographical parameters, such as the latitude and longitude of! the location, the date and time of the calculation, and the timezone of the location. By using these parameters, the calculator can determine the altitude and azimuth of the sun, as well as other relevant details such as the solar declination and the equation of time. The calculator uses complex algorithms and mathematical models to perform these calculations, ensuring a high degree of accuracy and reliability. The results provided by the calculator can be used for a variety of applications, including solar energy systems design, architecture, and agriculture.
What are the inputs required to use the Solar Position Details Calculator?
To use the Solar Position Details Calculator, several inputs are required, including the latitude and longitude of the location, the date and time of the calculation, and the timezone of the location. The latitude and longitude are used to determine the position of the location on the Earth's surface, while the date and time are used to calculate the position of the sun in the sky. The timezone is used to ensure that the calculation is performed in the correct time zone, taking into account daylight saving time if applicable. Additional inputs may also be required, such as the altitude of the location above sea level, to further refine the calculations. All of these inputs are used by the calculator to provide accurate and reliable results, and are typically entered into the calculator through a user-friendly interface.
What are the typical outputs of the Solar Position Details Calculator?
The Solar Position Details Calculator provides a range of outputs, including the altitude and azimuth of the sun, the solar declination, and the equation of time. The altitude of the sun is the angle between the sun and the horizon, while the azimuth is the compass direction of the sun. The solar declination is the angle between the sun's position and the celestial equator, and is used to calculate the position of the sun throughout the year. The equation of time is a correction factor that takes into account the elliptical shape of the Earth's orbit around the sun, and is used to ensure that the calculation is accurate. These outputs can be used for a variety of applications, including solar energy systems design, architecture, and agriculture, and are typically provided in a user-friendly format, such as a table or graph.
How accurate are the results provided by the Solar Position Details Calculator?
The Solar Position Details Calculator is designed to provide highly accurate results, using complex algorithms and mathematical models to calculate the position of the sun in the sky. The calculator takes into account a range of factors, including the latitude and longitude of the location, the date and time of the calculation, and the timezone of the location, to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable. The calculator is also designed to account for variations in the angle of the sun, including the solar declination and the equation of time, to provide precise results. However, the accuracy of the results can be affected by a range of factors, including the quality of the inputs and the complexity of the calculation. To ensure the highest level of accuracy, it is recommended that the calculator is used with high-quality inputs and that the results are verified through other means, such as on-site measurements or consultation with a professional.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas