Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator

The Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator is a vital tool for engineers and manufacturers working with sheet metal. It helps determine the exact amount of material required for a specific bend, taking into account factors such as thickness, bend angle, and radius. By using this calculator, users can avoid costly mistakes and ensure accurate production of complex sheet metal parts. This article will delve into the features and benefits of the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator, and how it can streamline the manufacturing process. Its importance in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated, saving time and resources effectively.
Understanding the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator
The Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator is a tool used to calculate the bend allowance of a sheet metal part, which is the amount of material that needs to be added to the length of the part to account for the bending process. This calculator takes!nto account the thickness of the sheet metal, the bend radius, and the bend angle to provide an accurate calculation of the bend allowance.
What is Bend Allowance?
Bend allowance refers to the amount of material that is added to the length of a sheet metal part to account for the bending process. This is necessary because when a sheet metal part is bent, the material on the outside of the bend is stretched, while the material on the inside of the bend is compressed. The bend allowance calculator takes into account the thickness of the sheet metal, the bend radius, and the bend angle to provide an accurate calculation of the bend allowance.
How to Use the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator
To use the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator, you need to input the thickness of the sheet metal, the bend radius, and the bend angle. The calculator will then provide the bend allowance in inches or millimeters, depending on the unit of measurement selected. The calculator can be used for various types of bends, including V-bends, hemming, and seaming.
Factors that Affect Bend Allowance
Several factors can affect the bend allowance of a sheet metal part, including the thickness of the sheet metal, the bend radius, and the bend angle. Other factors that can affect the bend allowance include the material properties of the sheet metal, such as its yield strength and ductility. The tooling used to bend the sheet metal can also affect the bend allowance, as different tools can produce different bend radii and bend angles.
Benefits of Using the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator
Using the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator can provide several benefits, including improved accuracy and increased efficiency. By accurately calculating the bend allowance, you can avoid errors and waste in the production process, which can save time and money. The calculator can also help you to optimize your production process by identifying the most efficient and cost-effective way to produce a sheet metal part.
Common Applications of the Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator
The Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator has a wide range of applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment. It is commonly used to calculate the bend allowance for complex and intricate sheet metal parts, such as aircraft components, car parts, and machine components. The calculator can also be used to calculate the bend allowance for simple sheet metal parts, such as brackets, clips, and fasteners.
| Material | Thickness | Bend Radius | Bend Angle | Bend Allowance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 0.1 inches | 0.5 inches | 90 degrees | 0.2 inches |
| Steel | 0.2 inches | 0.8 inches | 45 degrees | 0.3 inches |
| Copper | 0.05 inches | 0.2 inches | 180 degrees | 0.1 inches |
How do you calculate bend allowance for sheet metal?
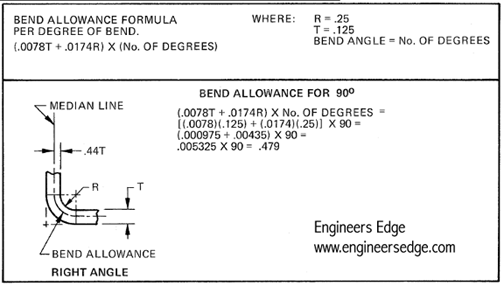
To calculate the bend allowance for sheet metal, you need to understand the concept of bend radius, bend angle, and material thickness. The bend allowance is the amount of material that is required to create a bend in the sheet metal, and it is typically measured in inches or millimeters. The calculation involves determining the neutral axis, which is the point at which the material is neither compressed nor stretched during the bending process.
Understanding Bend Allowance Formulas
The calculation of bend allowance involves using a formula that takes into account the bend radius, bend angle, and material thickness. The formula is: Bend Allowance = (π / 180) Bend Angle (Bend Radius + (Material Thickness / 2)). This formula provides an estimate of the bend allowance, but it may need to be adjusted based on the specific sheet metal being used.
- The bend radius is the radius of the bend, which is typically measured in inches or millimeters.
- The bend angle is the angle of the bend, which is typically measured in degrees.
- The material thickness is the thickness of the sheet metal, which is typically measured in inches or millimeters.
Factors Affecting Bend Allowance
Several factors can affect the bend allowance, including the type of material, thickness, and bend radius. For example, thicker materials require a larger bend allowance, while thinner materials require a smaller bend allowance. Additionally, sharp bends require a smaller bend allowance than large radius bends.
- Material type affects the bend allowance, with different materials having different yield strengths and elastic moduli.
- Material thickness affects the bend allowance, with thicker materials requiring a larger bend allowance.
- Bend radius affects the bend allowance, with sharper bends requiring a smaller bend allowance.
Calculating Bend Allowance for Different Materials
The bend allowance calculation can vary depending on the type of material being used. For example, aluminum and steel have different yield strengths and elastic moduli, which affect the bend allowance. Additionally, copper and brass have different properties that affect the bend allowance.
- Aluminum has a lower yield strength than steel, which affects the bend allowance.
- Steel has a higher yield strength than aluminum, which affects the bend allowance.
- Copper and brass have different properties that affect the bend allowance, such as ductility! and hardness.
Using Bend Allowance Charts and Tables
Bend allowance charts and tables can be used to simplify the calculation process. These charts and tables provide pre-calculated bend allowances for different materials, thicknesses, and bend radii. By using these charts and tables, you can quickly determine the bend allowance for a specific sheet metal part.
- Bend allowance charts provide a quick and easy way to determine the bend allowance for a specific material and thickness.
- Bend allowance tables provide a detailed list of bend allowances for different materials, thicknesses, and bend radii.
- Using bend allowance charts and tables can save time and reduce errors in the calculation process.
Applying Bend Allowance in Sheet Metal Design
The bend allowance is an important consideration in sheet metal design, as it affects the dimensional accuracy and structural integrity of the part. By accurately calculating the bend allowance, you can ensure that the part is manufactured correctly and functions as intended. Additionally, computer-aided design (CAD) software can be used to calculate the bend allowance and simulate the bending process.
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software can be used to calculate the bend allowance and simulate the bending process.
- Sheet metal design requires careful consideration of the bend allowance to ensure dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
- Manufacturing processes, such as laser cutting and punching, can be affected by the bend allowance, which must be taken into account during the design process.
What is the rule of thumb for bend allowance?

The rule of thumb for bend allowance is a guideline used to estimate the amount of material that will be required to create a bend in a piece of metal or other material. This guideline is used to calculate the length of the material needed to achieve a specific bend angle and radius. The bend allowance is typically calculated using a formula that takes into account the thickness of the material, the bend angle, and the bend radius.
Understanding Bend Allowance
To understand the rule of thumb for bend allowance, it is essential to know the factors that affect the bend allowance. These factors include the material type, thickness, bend angle, and bend radius. The bend allowance can be calculated using the following formula: Bend Allowance = (π/180) (Bend Angle) (Bend Radius + (0.5 Material Thickness)). Here are some key points to consider:
- The material type affects the bend allowance, with different materials having different elastic and plastic properties.
- The thickness of the material also affects the bend allowance, with thicker materials requiring more material to achieve the same bend angle.
- The bend angle and bend radius are also critical factors in determining the bend allowance, with larger angles and radii requiring more material.
Calculating Bend Allowance
Calculating the bend allowance involves using a formula that takes into account the material thickness, bend angle, and bend radius. The formula is: Bend Allowance = (π/180) (Bend Angle) (Bend Radius + (0.5 Material Thickness)). This formula provides a theoretical value for the bend allowance, which can be used to estimate the amount of material required. Here are some key points to consider:
- The formula assumes a uniform bend radius and angle, which may not always be the case in practice.
- The material thickness and bend angle are critical factors in determining the bend allowance, with larger angles and thicknesses requiring more material.
- The bend radius also affects the bend allowance, with smaller radii requiring less material.
Factors Affecting Bend Allowance
Several factors can affect the bend allowance, including the material type, thickness, bend angle, and bend radius. The material type can affect the bend allowance due to differences in elastic and plastic properties. Here are some key points to consider:
- The material type affects the bend allowance, with different materials having different elastic and plastic properties.
- The thickness of the material also affects the bend allowance, with thicker materials requiring more material to achieve the same bend angle.
- The bend angle and bend radius are also critical factors in determining the bend allowance, with larger angles and radii requiring more material.
Importance of Bend Allowance
The bend allowance is a critical factor in designing and manufacturing bent parts, as it determines the amount of material required to achieve a specific bend angle and radius. A correct bend allowance ensures that the part is dimensionally accurate and functional. Here are some key points to consider:
- A correct bend allowance is essential to ensure that the part is dimensionally accurate and functional.
- The bend allowance affects the cost and lead time of the part, as it determines the amount of material required.
- The bend allowance also affects the quality of the part, as it determines the smoothness and accuracy of the bend.
Best Practices for Bend Allowance
To ensure accurate and reliable bend allowance calculations, it is essential to follow best practices, including using verified formulas and material properties. Here are some key points to consider:
- Use verified formulas and material properties to ensure accurate calculations.
- Consider the material type, thickness, bend angle, and bend radius when calculating the bend allowance.
- Use computer-aided design (CAD) software to simulate and optimize the bend allowance calculation.
How to calculate bending load in sheet metal?

To calculate the bending load in sheet metal, you need to consider the material properties, sheet thickness, and bending radius. The bending load is the amount of force required to bend the sheet metal to a specific radius. The calculation involves using the bending moment and stress formulas to determine the required force.
Understanding Material Properties
The material properties of the sheet metal, such as its yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and young's modulus, play a crucial role in determining the bending load. These properties vary depending on the type of metal and its temper. To calculate the bending load, you need to know the material's elasticity and plasticity. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Yield strength: The stress at which the material begins to deform plastically.
- Ultimate tensile strength: The maximum stress the material can withstand before failing.
- Young's modulus: A measure of the material's elasticity and stiffness.
Determining Sheet Thickness and Bending Radius
The sheet thickness and bending radius are critical factors in calculating the bending load. A thicker sheet requires more force to bend, while a smaller bending radius requires more force than a larger radius. To calculate the bending load, you need to know the sheet's thickness and bending radius. Here are some key considerations:
- Sheet thickness: The thickness of the sheet metal, which affects its bending stiffness.
- Bending radius: The radius to which the sheet metal is bent, which affects the bending stress.
- Bending stiffness: The ability of the sheet metal to resist bending, which depends on its thickness and material properties.
Calculating Bending Moment and Stress
The bending moment and stress are calculated using the beam theory and material properties. The bending moment is the force required to bend the sheet metal, while the stress is the force per unit area. To calculate the bending load, you need to calculate the bending moment and stress. Here are some key steps:
- Bending moment calculation: The calculation involves using the beam theory and material properties to determine the required force.
- Stress calculation: The calculation involves using the material properties and bending moment to determine the stress in the sheet metal.
- Force calculation: The calculation involves using the bending moment and stress to determine the required force to bend the sheet metal.
Using Formulas and Equations
To calculate the bending load, you can use various formulas and equations. The most common formula is the bending stress equation, which calculates the stress in the sheet metal. You can also use the bending moment equation to calculate the force required to bend the sheet metal. Here are some key formulas:
- Bending stress equation: σ = (M y) / I, where σ is the stress, M is the bending moment, y is the distance from the neutral axis, and I is the moment of inertia.
- Bending moment equation: M = (F L) / 4, where M is the bending moment, F is the force, and L is the length of the sheet metal.
- Moment of inertia equation: I = (b t^3) / 12, where I is the moment of inertia, b is the width of the sheet metal, and t is the thickness of the sheet metal.
Considering Safety Factors and Tolerances
When calculating the bending load, it's essential to consider safety factors and tolerances. The safety factor is a multiplier that accounts for uncertainties and variations in the material properties and loading conditions. The tolerance is the allowable variation in the bending load. Here are some key considerations:
- Safety factor: A multiplier that accounts for uncertainties and variations in the material properties and loading conditions.
- Tolerance: The allowable variation in the bending load, which depends on the application and requirements.
- Load calculation: The calculation involves using the bending moment and stress to determine the required force, and then applying the safety factor and tolerance to ensure safe and reliable operation.
What is the bend rule for sheet metal?

The bend rule for sheet metal is a set of guidelines that helps to determine the minimum bend radius and bend allowance for a specific type of sheet metal. This rule is crucial in ensuring that the metal can be bent without cracking or tearing. The bend rule takes into account the thickness and type of sheet metal, as well as the bending process being used.
Understanding the Basics of Sheet Metal Bending
The bend rule for sheet metal is based on the properties of the metal, including its yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. To understand the bend rule, it's essential to know the basics of sheet metal bending, including the types of bends, such as V-bends, U-bends, and hemming.
- The bend angle is critical in determining the bend rule, as it affects the stress and strain on the metal.
- The bend radius is the minimum radius that the metal can be bent without cracking or tearing.
- The bend allowance is the amount of material that is stretched or compressed during the bending process.
Factors Affecting the Bend Rule
Several factors can affect the bend rule for sheet metal, including the type of metal, its thickness, and the bending process being used. For example, aluminum and steel have different properties that affect their bend rules.
- The thickness of the metal is a critical factor, as it affects the bend radius and bend allowance.
- The type of bending process, such as press braking or roll forming, can also impact the bend rule.
- The tools and equipment used in the bending process can also influence the bend rule.
Calculating the Bend Allowance
Calculating the bend allowance is a critical step in determining the bend rule for sheet metal. The bend allowance is typically calculated using a formula that takes into account the bend angle, bend radius, and thickness of the metal.
- The bend allowance can be calculated using a chart or table that provides the bend allowance for different bend angles and bend radii.
- The bend allowance can also be calculated using software or computer-aided design (CAD) programs.
- The bend allowance is essential in ensuring that the metal is bent accurately and precisely.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Sheet Metal Bending
Avoiding common mistakes in sheet metal bending is crucial in ensuring that the bend rule is followed correctly. One of the most common mistakes is over-bending or under-bending the metal, which can result in cracking or tearing.
- Over-bending can cause the metal to crack or tear, while under-bending can result in a loss of shape or dimension.
- Using the wrong tools or equipment can also lead to mistakes in the bending process.
- Lack of training or experience can also contribute to mistakes in sheet metal bending.
Applying the Bend Rule in Real-World Applications
The bend rule for sheet metal has numerous real-world applications, including in the manufacturing of automotive, aerospace, and construction products. By applying the bend rule, manufacturers can ensure that their products are strong, durable, and precise.
- The bend rule is essential in the design and development of sheet metal products.
- The bend rule can help manufacturers to optimize their production processes and reduce costs.
- The bend rule can also help to improve the quality and reliability of sheet metal products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator?
The Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator is a tool designed to help manufacturers and engineers calculate the bend allowance of sheet metal parts. The bend allowance is the amount of material that is required to create a bend in a sheet metal part, and it is an important factor in determining the accuracy and precision of the final product. By using a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator, users can quickly and easily calculate the bend allowance for their specific sheet metal parts, taking into account factors such as the material thickness, bend angle, and bend radius. This helps to ensure that the parts are manufactured to the correct dimensions and tolerances, and reduces the risk of errors and defects.
How does a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator work?
A Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator works by using a complex algorithm to calculate the bend allowance based on user-inputted values such as the material thickness, bend angle, and bend radius. The calculator takes into account the physical properties of the sheet metal, including its yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation, to determine the bend allowance. The calculator also considers the type of bend, such as a V-bend, U-bend, or hem, and the orientation of the bend. By using a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator, users can save time and reduce errors associated with manual calculations, and ensure that their sheet metal parts are manufactured to the correct dimensions and tolerances.
What are the benefits of using a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator?
The benefits of using a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator are numerous. One of the main benefits is increased accuracy, as the calculator can precisely calculate the bend allowance based on the user-inputted values. This helps to reduce errors and defects in the manufacturing process, and ensures that the parts are manufactured to the correct dimensions and tolerances. Another benefit is time savings, as the calculator can quickly and easily calculate the bend allowance, reducing the time spent on manual calculations. Additionally, a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator can help to improve communication between designers, engineers, and manufacturers, by providing a common language and standardized method for calculating bend allowances.
Can a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator be used for different types of sheet metal?
Yes, a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator can be used for different types of sheet metal, including steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. The calculator can be programmed to take into account the unique physical properties of each material, such as its yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation. This allows users to accurately calculate the bend allowance for their specific sheet metal parts, regardless of the type of material being used. Additionally, some Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculators may also be able to account for other factors that can affect the bend allowance, such as the surface finish, grain direction, and temper of the material. By using a Sheet Metal Bend Allowance Calculator that is capable of handling different types of sheet metal, users can ensure that their parts are manufactured to the correct dimensions and tolerances, and reduce the risk of errors and defects.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas