Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement Applied Equations and Calculator

The concept of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement involves the application of rotational motion to objects, where the angular displacement is concentrated around a fixed axis. This type of displacement is crucial in various engineering and physics applications, including robotics, mechanics, and structural analysis. To accurately calculate and analyze such displacements, specific equations and calculators are employed, taking into account parameters such as rotational velocity, torque, and moment of inertia. These tools enable precise predictions and simulations of real-world systems, facilitating informed decision-making and design optimization. Mathematical models and computational methods are used to derive and apply these equations.
-
Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement Applied Equations and Calculator
- Introduction to Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
- Applied Equations for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
- Calculator for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
- Applications of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
- Limitations and Assumptions of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
- How do you calculate angular displacement?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement and its significance in engineering calculations?
- How do I apply the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement equations to solve real-world problems?
- What are the key differences between Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement and other types of angular displacement?
- Can I use online calculators and software tools to calculate Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement, and what are their advantages?
Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement Applied Equations and Calculator
The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is a complex concept in physics and engineering that deals with the calculation of angular displacement and its application in various fields. To understand this concept, we need to delve into the world of rotational motion and torque. The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is used to calculate the angular displacement of an object when a concentrated force is applied to it. This concept is crucial in designing and analyzing mechanical systems, such as gears, shafts, and bearings.
Introduction to Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is a theoretical concept that is used to calculate the angular displacement of an object when a concentrated force is applied to it. This concept is based on the principle of conservation of angular momentum, which states that the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant over time. The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is calculated using the equation of motion, which takes into account the applied force, moment of inertia, and angular velocity of the object.
Applied Equations for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
The applied equations for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement are based on the equation of motion, which is given by:
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| θ = (F r) / (I ω) | Angular displacement (θ) is calculated using the applied force (F), radius (r), moment of inertia (I), and angular velocity (ω) |
| ω = (F r) / (I θ) | Angular velocity (ω) is calculated using the applied force (F), radius (r), moment of inertia (I), and angular displacement (θ) |
Calculator for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
A calculator for Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is a software tool that is used to calculate the angular displacement and angular velocity of an object when a concentrated force is applied to it. The calculator uses the applied equations to calculate the angular displacement and angular velocity, and it provides a graphical representation of the results. The calculator is useful for engineers and physicists who need to design and analyze mechanical systems.
Applications of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
The applications of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement are diverse and include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Robotics | The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is used to calculate the angular displacement and angular velocity of robotic arms and joints |
| Aerospace engineering | The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is used to calculate the angular displacement and angular velocity of satellites and spacecraft |
Limitations and Assumptions of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement
The limitations and assumptions of Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement include:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Assumes a rigid body | The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement assumes that the object is a rigid body, which means that it does not deform under the applied force |
| Assumes a constant force | The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement assumes that the applied force is constant, which means that it does not change over time |
How do you calculate angular displacement?
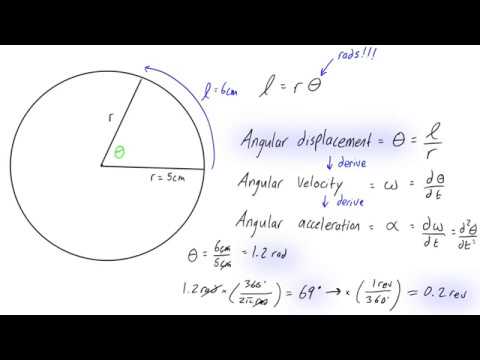
To calculate angular displacement, you need to understand the concept of rotation and angular motion. Angular displacement is the measure of the change in the angular position of an object as it rotates around a fixed axis. It is typically measured in radians or degrees and can be calculated using the following formula: θ = Δθ = θf - θi, where θ is the angular displacement, θf is the final angular position, and θi is the initial angular position.
Understanding Angular Displacement
Angular displacement is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of the angular displacement is the amount of rotation, while the direction is the axis of rotation. To calculate angular displacement, you need to know the initial and final angular positions of the object. The initial angular position is the position of the object before it starts rotating, and the final angular position is the position of the object after it has rotated. The calculation of angular displacement involves subtracting the initial angular position from the final angular position:
- Identify the initial and final angular positions of the object.
- Calculate the difference between the final and initial angular positions.
- Express the result in radians or degrees.
Calculating Angular Displacement using Radians
When calculating angular displacement using radians, you need to use the following formula: θ = r / L, where θ is the angular displacement, r is the radius of the circle, and L is the arc length. The radian is a unit of angular measurement that is defined as the ratio of the arc length to the radius of the circle. The calculation of angular displacement in radians involves multiplying the arc length by the radius of the circle and then dividing by the radius squared:
- Measure the arc length of the circle.
- Measure the radius of the circle.
- Calculate the angular displacement using the formula θ = r / L.
Calculating Angular Displacement using Degrees
When calculating angular displacement using degrees, you need to use the following formula: θ = (360° / 2π) (r / L), where θ is the angular displacement, r is the radius of the circle, and L is the arc length. The degree is a unit of angular measurement that is defined as 1/360 of a full rotation. The calculation of angular displacement in degrees involves multiplying the arc length by the radius of the circle and then dividing by the radius squared, and then multiplying by 360° / 2π:
- Measure the arc length of the circle.
- Measure the radius of the circle.
- Calculate the angular displacement using the formula θ = (360° / 2π) (r / L).
Applications of Angular Displacement
Angular displacement has many practical applications in physics and engineering, including the design of gears, motors, and generators. It is also used in the calculation of torque and rotational kinetic energy. The calculation of angular displacement is essential in understanding the motion of objects that rotate around a fixed axis. The applications of angular displacement involve the use of mathematical models to describe the behavior of rotating systems:
- Design of gears and transmissions.
- Calculation of torque and rotational kinetic energy.
- Analysis of rotating systems.
Importance of Angular Displacement in Physics
Angular displacement is a fundamental concept in physics that is used to describe the motion of objects that rotate around a fixed axis. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction, and it is essential in understanding the behavior of rotating systems. The calculation of angular displacement is crucial in the design of machines and mechanisms that involve rotation, and it has many practical applications in engineering and technology:
- Understanding the motion of objects that rotate around a fixed axis.
- Design of machines and mechanisms that involve rotation.
- Calculation of torque and rotational kinetic energy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement and its significance in engineering calculations?
The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is a fundamental concept in the field of engineering mechanics, particularly in the study of rotational motion and angular displacement. It refers to the angular displacement of an object or a system about a fixed axis, where the displacement is concentrated at a single point or axis. This concept is crucial in understanding the behavior of mechanical systems, such as gears, cams, and linkages, which are commonly used in machinery and mechanical devices. The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is often used to analyze and design these systems, ensuring that they operate efficiently and effectively. By applying the relevant equations and formulas, engineers can predict and optimize the performance of these systems, taking into account factors such as torque, speed, and acceleration.
How do I apply the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement equations to solve real-world problems?
To apply the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement equations to solve real-world problems, you need to have a solid understanding of the underlying mathematical concepts and physical principles. First, you need to identify the given parameters and unknown quantities in the problem, such as the angular displacement, torque, and moment of inertia. Then, you can select the appropriate equations and formulas to use, depending on the specific problem and constraints. For example, you may need to use the equation of motion for an object under constant torque or the equation for angular momentum. By plugging in the given values and solving for the unknown quantities, you can determine the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement and other relevant parameters. Additionally, you can use calculators and software tools to streamline the calculation process and visualize the results.
What are the key differences between Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement and other types of angular displacement?
The Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is distinct from other types of angular displacement, such as left vertical concentrated angular displacement and horizontal angular displacement. The main difference lies in the direction and orientation of the angular displacement, which affects the sign and magnitude of the displacement. For example, right vertical concentrated angular displacement is typically positive when measured in a clockwise direction, while left vertical concentrated angular displacement is negative. Furthermore, the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement is often used in specific contexts, such as gear trains and cam mechanisms, where the direction and magnitude of the displacement are critical. In contrast, other types of angular displacement may be used in different applications, such as robotics and aerospace engineering.
Can I use online calculators and software tools to calculate Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement, and what are their advantages?
Yes, you can use online calculators and software tools to calculate the Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement, which can simplify and accelerate the calculation process. These tools can perform complex calculations and provide accurate results, eliminating the need for manual calculations and reducing errors. Additionally, many online calculators and software tools offer user-friendly interfaces and interactive visualizations, making it easier to input parameters and interpret results. Some popular tools for calculating Right Vertical Concentrated Angular Displacement include mathematical software like MATLAB and Mathematica, as well as engineering simulation software like ANSYS and Autodesk Simulation. The advantages of using these tools include increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and enhanced collaboration, as you can share results and work together with colleagues and peers.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas