Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator

The hydraulic diameter of rectangular ducts is a crucial parameter in fluid dynamics, particularly in the design and optimization of ventilation, heating, and cooling systems. It is used to calculate the friction factor, pressure drop, and flow rate of fluids in rectangular ducts. This calculator is designed to simplify the process of determining the hydraulic diameter of rectangular ducts, providing a quick and accurate solution for engineers and technicians. With this tool, users can easily input the dimensions of the duct and obtain the hydraulic diameter, saving time and effort in their calculations. It is a valuable resource.
- Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator
- What is the formula for the hydraulic diameter of a rectangle?
- What is the formula for the hydraulic radius of a rectangular duct?
- What is the formula for the equivalent diameter of a rectangular duct?
- What is the hydraulic diameter for a rectangular duct having 10m width and 6m depth?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator and its purpose?
- How does the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator work?
- What are the benefits of using the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator?
- What are the limitations and potential sources of error of the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator?
Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator is a tool used to calculate the hydraulic diameter of rectangular ducts, which is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics and engineering applications. The hydraulic diameter is used to determine the flow characteristics of fluids in rectangular ducts, such as the velocity, pressure drop, and flow rate. This calculator is essential for engineers and designers who work with rectangular ducts in various industries, including HVAC, chemical processing, and power generation.
What is Hydraulic Diameter?
The hydraulic diameter is a measure of the size of a rectangular duct that takes into account the duct's width and height. It is defined as the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the duct to its perimeter. The hydraulic diameter is used to calculate the Reynolds number, which is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the nature of fluid flow in the duct. The Reynolds number is used to determine whether the flow is laminar or turbulent, and it is essential for designing and optimizing fluid flow systems.
How to Calculate Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter of a rectangular duct can be calculated using the following formula: Dh = (2 width height) / (width + height). This formula is based on the definition of hydraulic diameter and is widely used in engineering applications. To use the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator, simply enter the width and height of the duct, and the calculator will output the hydraulic diameter.
Importance of Hydraulic Diameter in Fluid Dynamics
The hydraulic diameter is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics because it affects the flow characteristics of fluids in rectangular ducts. The hydraulic diameter is used to calculate the friction factor, which is a measure of the resistance to fluid flow in the duct. The friction factor is used to determine the pressure drop in the duct, which is essential for designing and optimizing fluid flow systems. The hydraulic diameter is also used to calculate the flow rate and velocity of fluids in the duct.
Applications of Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| HVAC | Designing and optimizing air ducts for heating and cooling systems |
| Chemical Processing | Designing and optimizing fluid flow systems for chemical processing applications |
| Power Generation | Designing and optimizing fluid flow systems for power generation applications |
The calculator is also used in other industries, such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Benefits of Using Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator offers several benefits, including:
Accurate calculations: The calculator provides accurate calculations of the hydraulic diameter, which is essential for designing and optimizing fluid flow systems.
Time-saving: The calculator saves time and effort by providing quick and easy calculations of the hydraulic diameter.
Improved design: The calculator helps engineers and designers to improve the design of fluid flow systems by providing accurate calculations of the hydraulic diameter.
Increased efficiency: The calculator helps to increase the efficiency of fluid flow systems by providing accurate calculations of the hydraulic diameter, which is used to determine the flow rate and velocity of fluids in the duct. The calculator also helps to reduce the pressure drop in the duct, which can lead to energy savings and cost savings.
What is the formula for the hydraulic diameter of a rectangle?

The formula for the hydraulic diameter of a rectangle is given by: D = 4A/P, where A is the cross-sectional area of the rectangle and P is the perimeter of the rectangle. This formula is used to calculate the hydraulic diameter of a rectangular pipe or channel.
Importance of Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter is an important parameter in fluid mechanics and is used to calculate the Reynolds number, which is a measure of the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces in a fluid. The hydraulic diameter is also used to calculate the friction factor and the pressure drop in a pipe or channel. Some key points to consider when calculating the hydraulic diameter are:
- The cross-sectional area of the rectangle must be known in order to calculate the hydraulic diameter.
- The perimeter of the rectangle must also be known in order to calculate the hydraulic diameter.
- The hydraulic diameter is only applicable to rectangular pipes or channels and not to circular or elliptical pipes or channels.
Calculation of Hydraulic Diameter
To calculate the hydraulic diameter, the cross-sectional area and perimeter of the rectangle must be known. The cross-sectional area can be calculated as the product of the width and height of the rectangle, while the perimeter can be calculated as the sum of the lengths of all four sides of the rectangle. Some key steps to follow when calculating the hydraulic diameter are:
- Calculate the cross-sectional area of the rectangle using the formula A = width x height.
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle using the formula P = 2(width + height).
- Use the formula D = 4A/P to calculate the hydraulic diameter.
Applications of Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter has a number of practical applications in engineering and physics. Some examples of these applications include:
- Calculating the pressure drop in a pipe or channel.
- Calculating the friction factor in a pipe or channel.
- Designing pipework and channel systems for fluid flow applications.
Limitations of Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter is not without its limitations. Some of the limitations of the hydraulic diameter include:
- It is only applicable to rectangular pipes or channels and not to circular or elliptical pipes or channels.
- It assumes a fully developed flow in the pipe or channel, which may not always be the case.
- It does not take into account turbulence or non-Newtonian fluids.
Alternatives to Hydraulic Diameter
There are a number of alternative methods for calculating the hydraulic diameter, including:
- Using the equivalent diameter, which is the diameter of a circular pipe or channel that has the same cross-sectional area as the rectangular pipe or channel.
- Using the hydraulic radius, which is the ratio of the cross-sectional area to the perimeter of the pipe or channel.
- Using numerical methods, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), to simulate the fluid flow in the pipe or channel.
What is the formula for the hydraulic radius of a rectangular duct?
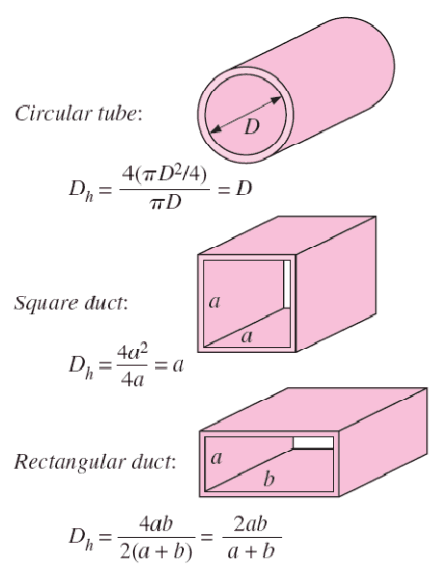
The formula for the hydraulic radius of a rectangular duct is given by the equation: R = (b h) / (2 (b + h)), where R is the hydraulic radius, b is the width of the duct, and h is the height of the duct. This formula is used to calculate the hydraulic radius of a rectangular duct in fluid dynamics and hydraulics.
Introduction to Hydraulic Radius
The hydraulic radius is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics and hydraulics. It is used to describe the flow characteristics of a fluid in a channel or duct. The hydraulic radius is defined as the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the flow to the wasted perimeter of the channel or duct. Some key points to consider when calculating the hydraulic radius include:
- The width and height of the duct must be known to calculate the hydraulic radius.
- The hydraulic radius is used to calculate the flow velocity and flow rate of a fluid in a channel or duct.
- The hydraulic radius is an important factor in determining the pressure drop and energy loss in a fluid flow system.
Calculation of Hydraulic Radius
The calculation of the hydraulic radius is a straightforward process that involves using the formula: R = (b h) / (2 (b + h)). To calculate the hydraulic radius, you need to know the width and height of the duct. Some key steps to follow when calculating the hydraulic radius include:
- Measure the width and height of the duct.
- Plug the values into the formula: R = (b h) / (2 (b + h)).
- Solve for R, the hydraulic radius.
Importance of Hydraulic Radius in Fluid Dynamics
The hydraulic radius is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics and hydraulics. It is used to calculate the flow characteristics of a fluid in a channel or duct. The hydraulic radius is also used to determine the pressure drop and energy loss in a fluid flow system. Some key points to consider when evaluating the importance of the hydraulic radius include:
- The hydraulic radius affects the flow velocity and flow rate of a fluid in a channel or duct.
- The hydraulic radius is used to calculate the head loss and pressure drop in a fluid flow system.
- The hydraulic radius is an important factor in designing pipelines and channels.
Applications of Hydraulic Radius
The hydraulic radius has a wide range of applications in engineering and science. It is used in the design of pipelines, channels, and fluid flow systems. The hydraulic radius is also used to calculate the flow characteristics of a fluid in a channel or duct. Some key applications of the hydraulic radius include:
- Design of pipelines and channels.
- Calculation of flow velocity and flow rate of a fluid in a channel or duct.
- Determination of pressure drop and energy loss in a fluid flow system.
Limitations of Hydraulic Radius
The hydraulic radius has some limitations that must be considered when using it to calculate the flow characteristics of a fluid in a channel or duct. The hydraulic radius assumes a steady-state flow and does not account for turbulence or unsteady flow. Some key limitations of the hydraulic radius include:
- The hydraulic radius assumes a steady-state flow.
- The hydraulic radius does not account for turbulence or unsteady flow.
- The hydraulic radius is only applicable to fully developed flow.
What is the formula for the equivalent diameter of a rectangular duct?

The formula for the equivalent diameter of a rectangular duct is D = 1.30 (a b) ^ 0.625 / (a + b) ^ 0.25, where D is the equivalent diameter, a and b are the dimensions of the rectangular duct. This formula is used to calculate the equivalent diameter of a rectangular duct, which is a crucial parameter in fluid dynamics and aerodynamics.
Importance of Equivalent Diameter in Duct Design
The equivalent diameter is a critical parameter in duct design as it affects the flow rate, pressure drop, and energy losses in the duct. A correct calculation of the equivalent diameter is essential to ensure that the duct is designed to meet the required performance criteria. The formula for the equivalent diameter takes into account the dimensions of the rectangular duct and provides a consistent and accurate way to calculate the equivalent diameter.
- The equivalent diameter is used to calculate the flow rate of fluids in the duct.
- The equivalent diameter affects the pressure drop in the duct, which is critical in pump selection and system design.
- The equivalent diameter is also used to calculate energy losses in the duct, which is essential in energy efficiency and cost savings.
Applications of Equivalent Diameter in Engineering
The equivalent diameter has numerous applications in engineering, including aerospace engineering, chemical engineering, and mechanical engineering. The formula for the equivalent diameter is used in the design of aircraft, chemical processing plants, and power generation systems.
- The equivalent diameter is used in the design of aircraft to calculate the thrust and efficiency of jet engines.
- The equivalent diameter is used in chemical processing plants to calculate the flow rate and pressure drop of chemicals.
- The equivalent diameter is used in power generation systems to calculate the energy losses and efficiency of turbines.
Limitations of the Equivalent Diameter Formula
The formula for the equivalent diameter has some limitations, including assumptions about the flow regime and duct geometry. The formula assumes a turbulent flow regime and a rectangular duct geometry, which may not be applicable in all cases.
- The formula assumes a turbulent flow regime, which may not be applicable in laminar flow regimes.
- The formula assumes a rectangular duct geometry, which may not be applicable in circular or elliptical ducts.
- The formula may not account for flow disturbances and duct irregularities.
Comparison with Other Duct equivalent Formulas
The formula for the equivalent diameter is compared with other formulas and methods to calculate the equivalent diameter. Other formulas include the hydraulic diameter and the equivalent circular diameter.
- The hydraulic diameter formula is used to calculate the equivalent diameter of circular ducts.
- The equivalent circular diameter formula is used to calculate the equivalent diameter of rectangular ducts.
- The formula for the equivalent diameter is compared with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to validate its accuracy.
Future Research Directions in Equivalent Diameter Formulas
Future research directions in equivalent diameter formulas include improving the accuracy and applicability of the formula. Researchers are exploring new methods and techniques to calculate the equivalent diameter, including machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- Researchers are exploring new methods to calculate the equivalent diameter, including machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- The formula for the equivalent diameter is being validated and verified using experimental data and CFD simulations.
- Future research directions include extending the formula to complex duct geometries and multiphase flows.
What is the hydraulic diameter for a rectangular duct having 10m width and 6m depth?

The hydraulic diameter for a rectangular duct can be calculated using the formula: D = (4 A) / P, where A is the cross-sectional area of the duct and P is the perimeter of the duct. For a rectangular duct with a width of 10m and a depth of 6m, the cross-sectional area A is 10m 6m = 60m². The perimeter P of the duct is 2 (10m + 6m) = 32m. Therefore, the hydraulic diameter D = (4 60m²) / 32m = 7.5m.
Introduction to Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter is an important parameter in fluid dynamics, used to calculate the pressure drop and flow rate in pipes and ducts. It is defined as the diameter of a circular pipe that has the same hydraulic properties as the non-circular pipe or duct. The hydraulic diameter is used in various engineering applications, including pipe flow, heat transfer, and mass transfer. Some key points to consider when calculating the hydraulic diameter include:
- The cross-sectional area of the duct or pipe must be known.
- The perimeter of the duct or pipe must be known.
- The hydraulic diameter is calculated using the formula D = (4 A) / P.
Calculating the Hydraulic Diameter
To calculate the hydraulic diameter, we need to know the cross-sectional area and perimeter of the duct or pipe. For a rectangular duct, the cross-sectional area A is calculated as the product of the width and depth, while the perimeter P is calculated as twice the sum of the width and depth. The hydraulic diameter is then calculated using the formula D = (4 A) / P. Some key steps to follow when calculating the hydraulic diameter include:
- Measure the width and depth of the duct or pipe.
- Calculate the cross-sectional area A using the formula A = width depth.
- Calculate the perimeter P using the formula P = 2 (width + depth).
Application of Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter has various applications in engineering, including pipe flow, heat transfer, and mass transfer. It is used to calculate the pressure drop and flow rate in pipes and ducts, and to design pipelines and ductwork systems. The hydraulic diameter is also used in the calculation of the Reynolds number, which is used to determine the nature of the flow in a pipe or duct. Some key applications of the hydraulic diameter include:
- Pipe flow: calculating the pressure drop and flow rate in pipes.
- Heat transfer: calculating the heat transfer coefficient in pipes and ducts.
- Mass transfer: calculating the mass transfer coefficient in pipes and ducts.
Importance of Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics, as it affects the pressure drop and flow rate in pipes and ducts. A accurate calculation of the hydraulic diameter is essential to ensure that the pipeline or ductwork system operates efficiently and safely. The hydraulic diameter is also used to calculate the friction factor, which is used to determine the pressure drop in pipes and ducts. Some key reasons why the hydraulic diameter is important include:
- Accurate calculation: ensures that the pipeline or ductwork system operates efficiently and safely.
- Pressure drop: affects the pressure drop in pipes and ducts.
- Flow rate: affects the flow rate in pipes and ducts.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Hydraulic Diameter
When calculating the hydraulic diameter, there are several common mistakes that can be made, including using the wrong formula or not accounting for the perimeter of the duct or pipe. It is also important to ensure that the cross-sectional area and perimeter are calculated accurately. Some key mistakes to avoid when calculating the hydraulic diameter include:
- Using the wrong formula to calculate the hydraulic diameter.
- Not accounting for the perimeter of the duct or pipe.
- Not ensuring that the cross-sectional area and perimeter are calculated accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator and its purpose?
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator is an online tool used to calculate the hydraulic diameter of a rectangular duct. The hydraulic diameter is a critical parameter in the design and analysis of fluid flow systems, such as air conditioning, heating, and ventilation systems. It is defined as the equivalent diameter of a circular duct that has the same flow characteristics as the rectangular duct. The calculator takes into account the dimensions of the rectangular duct, including its width and height, to calculate the hydraulic diameter. This parameter is essential in determining the pressure drop, flow rate, and energy efficiency of the fluid flow system.
How does the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator work?
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator uses a mathematical formula to calculate the hydraulic diameter of a rectangular duct. The formula takes into account the aspect ratio of the duct, which is the ratio of the width to the height. The calculator also considers the units of measurement used for the dimensions of the duct, such as inches, feet, or meters. To use the calculator, simply enter the dimensions of the rectangular duct, select the units of measurement, and click the calculate button. The calculator will then display the calculated hydraulic diameter, which can be used in further calculations or design of the fluid flow system. The accuracy of the calculator depends on the accuracy of the input values and the complexity of the fluid flow system.
What are the benefits of using the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator?
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator offers several benefits to users, including engineers, designers, and researchers. One of the main advantages is that it saves time and reduces errors associated with manual calculations. The calculator is also easy to use and intuitive, requiring minimal input and setup. Additionally, the calculator provides accurate and reliable results, which are essential in the design and analysis of fluid flow systems. The calculator can also be used to optimize the design of rectangular ducts, by minimizing the pressure drop and maximizing the flow rate. Overall, the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator is a valuable tool for anyone working with fluid flow systems, and can help to improve the efficiency and performance of these systems.
What are the limitations and potential sources of error of the Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator?
The Hydraulic Diameter of Rectangular Ducts Calculator is a useful tool, but it also has some limitations and potential sources of error. One of the main limitations is that it assumes a fully developed flow in the rectangular duct, which may not always be the case in real-world applications. Additionally, the calculator does not take into account other factors that can affect the flow characteristics, such as turbulence, roughness, and obstructions. The calculator also relies on the accuracy of the input values, and any errors or uncertainties in these values can propagate to the calculated hydraulic diameter. Furthermore, the calculator is based on empirical formulas and correlations, which may not be exact or universal. Therefore, it is essential to validate the results of the calculator with experimental data or other sources to ensure their accuracy and reliability.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas