Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area Equation and Calculator

The frustrum of a cone is a geometric shape formed by cutting a cone with a plane parallel to its base, resulting in a smaller cone being removed from the top. Calculating the volume and area of this shape is crucial in various engineering and mathematical applications. The volume and area equations for the frustrum of a cone involve the radii of the top and bottom circles, as well as the height of the shape. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these equations and offers a calculator to simplify the calculation process. The formulas are derived from basic principles.
- Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area Equation and Calculator
- What is the formula for the volume of a frustum cone?
- What is the formula for the area of the frustum of a cone?
- What is the formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone?
- What is the surface area of a conical cylinder?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area Equation and Calculator
The Frustrum of a Cone is a three-dimensional shape that is formed by cutting a cone with a plane parallel to its base. The resulting shape has a circular base and a circular top, with a curved lateral surface. The volume and area of a Frustrum of a Cone can be calculated using mathematical equations, which are essential in engineering and architecture applications.
Introduction to Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area
The volume of a Frustrum of a Cone can be calculated using the formula: V = (1/3)πh(R^2 + r^2 + Rr), where V is the volume, π is a mathematical constant, h is the height of the Frustrum, R is the radius of the base, and r is the radius of the top. The area of the Frustrum can be calculated using the formula: A = π(R + r)√(h^2 + (R - r)^2), where A is the area.
Frustrum of Cone Volume Equation
The volume equation of a Frustrum of a Cone is a complex equation that involves the height and radii of the base and top. The equation is: V = (1/3)πh(R^2 + r^2 + Rr), where V is the volume, π is a mathematical constant, h is the height of the Frustrum, R is the radius of the base, and r is the radius of the top. This equation is essential in calculating the volume of a Frustrum of a Cone.
Frustrum of Cone Area Equation
The area equation of a Frustrum of a Cone is a complex equation that involves the height and radii of the base and top. The equation is: A = π(R + r)√(h^2 + (R - r)^2), where A is the area, π is a mathematical constant, h is the height of the Frustrum, R is the radius of the base, and r is the radius of the top. This equation is essential in calculating the area of a Frustrum of a Cone.
Calculator for Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area
A calculator can be used to calculate the volume and area of a Frustrum of a Cone. The input values are the height and radii of the base and top, and the output values are the volume and area. The calculator uses the equations mentioned earlier to calculate the volume and area.
Applications of Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area
The applications of Frustrum of Cone volume and area are varied and numerous. They are used in engineering and architecture to design and calculate the volume and area of structures and objects. They are also used in mathematics to calculate the volume and area of three-dimensional shapes.
Table of Frustrum of Cone Volume and Area
| Height | Radius of Base | Radius of Top | Volume | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 3 | 196.35 | 141.37 |
| 15 | 7 | 5 | 394.79 | 235.19 |
| 20 | 10 | 8 | 707.96 | 376.99 |
The values in the table are calculated using the equations mentioned earlier. The height, radius of base, and radius of top are the input values, and the volume and area are the output values. The values are rounded to two decimal places for simplicity.
What is the formula for the volume of a frustum cone?

The formula for the volume of a frustum cone is given by V = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2), where h is the height of the frustum, and R1 and R2 are the radii of the larger and smaller bases, respectively.
Understanding the Formula
The formula for the volume of a frustum cone is derived from the integration of the area of the circular cross-sections with respect to the height of the frustum. This involves calculating the area of each circular cross-section, which is given by A = πr^2, where r is the radius of the cross-section. The formula can be broken down into the following steps:
- Calculate the area of the larger base: A1 = πR1^2
- Calculate the area of the smaller base: A2 = πR2^2
- Calculate the volume of the frustum using the formula: V = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2)
Key Components of the Formula
The formula for the volume of a frustum cone involves several key components, including the height of the frustum, the radii of the larger and smaller bases, and the constant π. These components are combined using algebraic operations to produce the final formula. The key components can be broken down into the following:
- The height of the frustum: h
- The radii of the larger and smaller bases: R1 and R2
- The constant π: π = 3.14159
Applying the Formula in Real-World Scenarios
The formula for the volume of a frustum cone has numerous practical applications in engineering, architecture, and design. For example, it can be used to calculate the volume of a frustum-shaped container, such as a bucket or a tank. The formula can also be used to determine the volume of a frustum-shaped structure, such as a building or a monument. The applications can be broken down into the following:
- Calculating the volume of a frustum-shaped container
- Determining the volume of a frustum-shaped structure
- Designing frustum-shaped objects or structures
Derivation of the Formula
The formula for the volume of a frustum cone can be derived using integration and calculus. The derivation involves setting up an integral that represents the volume of the frustum, and then evaluating the integral to produce the final formula. The derivation can be broken down into the following steps:
- Setting up the integral: ∫πr^2 dh
- Evaluating the integral: V = ∫πr^2 dh = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2)
- Simplifying the formula: V = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2)
Calculating the Volume of a Frustum Cone with Different Shapes
The formula for the volume of a frustum cone can be used to calculate the volume of a frustum with different shapes, such as a right circular frustum or an oblique frustum. The formula can also be used to calculate the volume of a frustum with non-circular bases, such as an elliptical frustum or a rectangular frustum. The calculations can be broken down into the following:
- Calculating the volume of a right circular frustum
- Calculating the volume of an oblique frustum
- Calculating the volume of a frustum with non-circular bases
What is the formula for the area of the frustum of a cone?

The formula for the area of the frustum of a cone is given by the equation: A = π (R + r) √(h^2 + (R - r)^2), where R is the radius of the larger base, r is the radius of the smaller base, and h is the height of the frustum.
Understanding the Frustum of a Cone
The frustum of a cone is a three-dimensional shape that is formed by removing the top portion of a cone, resulting in a shape that has a larger base and a smaller base. To calculate the area of the frustum, we need to consider the radii of the two bases and the height of the shape. The formula for the area of the frustum takes into account these parameters, providing a precise calculation of the area.
- The frustum is a three-dimensional shape with two circular bases.
- The radii of the two bases are used to calculate the area of the frustum.
- The height of the frustum is also a critical parameter in calculating its area.
Calculating the Area of the Frustum
To calculate the area of the frustum, we use the formula A = π (R + r) √(h^2 + (R - r)^2). This formula involves the radii of the two bases and the height of the shape. By substituting the values of R, r, and h into the formula, we can calculate the exact area of the frustum.
- The formula for the area of the frustum involves the pi constant (π).
- The radii of the two bases are used in the formula to calculate the area.
- The height of the frustum is also used in the formula to calculate the area.
Parameters Involved in the Formula
The formula for the area of the frustum involves several parameters, including the radii of the two bases (R and r) and the height of the shape (h). These parameters are critical in calculating the accurate area of the frustum.
- The radius of the larger base (R) is a critical parameter.
- The radius of the smaller base (r) is also a critical parameter.
- The height of the frustum (h) is a key parameter in calculating its area.
Significance of the Frustum Formula
The formula for the area of the frustum is essential in various mathematical and engineering applications, including the calculation of volumes and surface areas of three-dimensional shapes. The precise calculation of the area of the frustum is critical in these applications.
- The frustum formula is used in mathematical modeling and simulation.
- The formula is also used in engineering design and optimization.
- The accurate calculation of the area of the frustum is critical in these applications.
Applications of the Frustum Formula
The formula for the area of the frustum has various practical applications in engineering, architecture, and design. The precise calculation of the area of the frustum is essential in these applications, where accurate calculations are critical.
- The frustum formula is used in building design and construction.
- The formula is also used in mechanical engineering and manufacturing.
- The accurate calculation of the area of the frustum is critical in these applications.
What is the formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone?
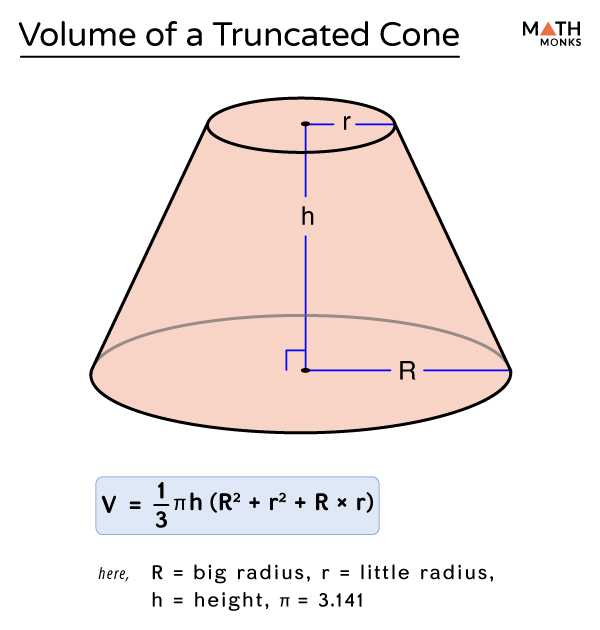
The formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone is given by V = (1/3) π h (R^2 + r^2 + R r), where h is the height of the cone, R is the radius of the larger base, and r is the radius of the smaller base. This formula is derived from the integration of the area of the trapezoidal cross-sections with respect to the height of the cone.
Derivation of the Formula
The derivation of the formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone involves integrating the area of the trapezoidal cross-sections with respect to the height of the cone. The area of each trapezoidal cross-section is given by A = (1/2) (R + r) h, where h is the height of the cross-section. The volume of the cone is then obtained by integrating this area with respect to the height of the cone. The resulting formula is V = (1/3) π h (R^2 + r^2 + R r). Some key points to consider when deriving this formula include:
- The height of the cone is an important parameter in the derivation of the formula.
- The radii of the larger and smaller bases are also crucial in determining the volume of the cone.
- The integration process involves finding the area of the trapezoidal cross-sections and then integrating this area with respect to the height of the cone.
Application of the Formula
The formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone has numerous applications in engineering and architecture. For example, it can be used to calculate the volume of a trapezoidal tank or a conical structure with a trapezoidal base. The formula is also useful in designing and optimizing the shape of trapezoidal cones to achieve specific structural or aerodynamic properties. Some key considerations when applying this formula include:
- The accuracy of the measurements of the height and radii of the cone is crucial in obtaining accurate results.
- The units of measurement must be consistent to avoid errors in calculation.
- The limitations of the formula must be understood, such as its assumption of a trapezoidal cross-section.
Comparison with Other Formulas
The formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone is similar to the formula for the volume of a cylindrical cone, which is given by V = (1/3) π h R^2. However, the trapezoidal cone formula takes into account the tapering of the cone, which is not present in the cylindrical cone. The formula is also related to the formula for the volume of a sphere, which is given by V = (4/3) π R^3. Some key differences between these formulas include:
- The shape of the cone, whether it is trapezoidal, cylindrical, or spherical.
- The parameters used in the formula, such as the height and radii of the cone.
- The applications of the formula, such as in engineering or architecture.
Limitations of the Formula
The formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone has several limitations, including its assumption of a trapezoidal cross-section and its simplifying assumptions about the shape of the cone. The formula is also sensitive to the accuracy of the measurements of the height and radii of the cone. Additionally, the formula does not take into account real-world factors such as friction or material properties. Some key limitations to consider include:
- The assumptions made in the derivation of the formula, such as the trapezoidal cross-section.
- The simplifications made in the formula, such as the neglect of friction or material properties.
- The sensitivity of the formula to the accuracy of the measurements.
Real-World Applications
The formula for the volume of a trapezoidal cone has numerous real-world applications, including in engineering and architecture. For example! it can be used to calculate the volume of a trapezoidal tank or a conical structure with a trapezoidal base. The formula is also useful in designing and optimizing the shape of trapezoidal cones to achieve specific structural or aerodynamic properties. Some key applications include:
- The design of trapezoidal tanks or conical structures.
- The optimization of the shape of trapezoidal cones for specific structural or aerodynamic properties.
- The calculation of the volume of trapezoidal cones for engineering or architectural purposes.
What is the surface area of a conical cylinder?

The surface area of a conical cylinder, also known as a conical frustum, is a complex calculation that involves finding the area of the two bases and the lateral surface area. The formula for the surface area of a conical cylinder is given by: $A = pi r_1^2 + pi r_2^2 + pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$, where $r_1$ and $r_2$ are the radii of the two bases and $h$ is the height of the cylinder.
Understanding the Formula
The formula for the surface area of a conical cylinder involves several key components, including the radii of the two bases, the height of the cylinder, and the lateral surface area. To calculate the surface area, we need to find the area of the two bases and add it to the lateral surface area. The formula can be broken down into the following steps:
- Calculate the area of the two bases using the formula $pi r_1^2 + pi r_2^2$
- Calculate the lateral surface area using the formula $pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$
- Add the area of the two bases and the lateral surface area to find the total surface area
Calculating the Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area of a conical cylinder is a critical component of the overall surface area calculation. To calculate the lateral surface area, we need to use the formula $pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$. This formula involves the slant height of the cylinder, which is the distance from the center of one base to the center of the other base. The slant height can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. The steps to calculate the lateral surface area are:
- Calculate the slant height using the formula $sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$
- Calculate the lateral surface area using the formula $pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$
- Add the lateral surface area to the area of the two bases to find the total surface area
Applications of Conical Cylinders
Conical cylinders have several practical applications in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and design. Some examples of conical cylinders include rocket nozzles, satellite dishes, and architectural features. The surface area of a conical cylinder is an important consideration in these applications, as it can affect the aerodynamics, structural integrity, and thermal performance of the object. The key factors to consider when designing a conical cylinder are:
- The materials used to construct the cylinder
- The dimensions of the cylinder, including the radii and height
- The environmental conditions in which the cylinder will be used
Surface Area of a Conical Cylinder with Different Radii
When the radii of the two bases are different, the surface area calculation becomes more complex. In this case, we need to use the formula $A = pi r_1^2 + pi r_2^2 + pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$, where $r_1$ and $r_2$ are the radii of the two bases. The steps to calculate the surface area are:
- Calculate the area of the two bases using the formula $pi r_1^2 + pi r_2^2$
- Calculate the lateral surface area using the formula $pi (r_1 + r_2) sqrt{h^2 + (r_1 - r_2)^2}$
- Add the area of the two bases and the lateral surface area to find the total surface area
Calculating the Surface Area of a Conical Cylinder with a Large Height
When the height of the conical cylinder is large compared to the radii of the bases, the surface area calculation can be simplified. In this case, we can use the formula $A = pi r_1^2 + pi r_2^2 + pi (r_1 + r_2) h$, where $h$ is the height of the cylinder. The key factors to consider when calculating the surface area are:
- The accuracy of the calculation, which can be affected by the magnitude of the height
- The computational method, which can be affected by the complexity of the calculation
- The interpretation of the results, which can be affected by the context of the problem
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Frustrum of a Cone and How is it Used in Calculations?
The frustrum of a cone is a geometric shape that is formed by cutting a cone with a plane parallel to its base. This shape is also known as a conical frustum or a truncated cone. The frustrum of a cone is used in various calculations, including volume and surface area calculations. To calculate the volume of a frustrum of a cone, you need to know the radius of the top and bottom bases, as well as the height of the frustum. The volume of a frustrum of a cone can be calculated using the formula: V = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2), where V is the volume, π is a mathematical constant, h is the height, and R1 and R2 are the radii of the top and bottom bases.
How do You Calculate the Volume of a Frustrum of a Cone?
To calculate the volume of a frustrum of a cone, you can use the formula: V = (1/3)πh(R1^2 + R2^2 + R1R2). This formula requires you to know the height of the frustum, as well as the radii of the top and bottom bases. You can also use an online calculator to calculate the volume of a frustrum of a cone. These calculators usually require you to input the height and radii of the frustum, and then they will calculate the volume for you. It's also important to note that the volume of a frustrum of a cone is always less than the volume of a full cone with the same height and radius. This is because the frustrum is a truncated version of the full cone.
What is the Surface Area of a Frustrum of a Cone and How is it Calculated?
The surface area of a frustrum of a cone is the total area of its curved surface and its two bases. The curved surface of a frustrum of a cone is the area of the cone that is not part of the bases. To calculate the surface area of a frustrum of a cone, you need to know the radii of the top and bottom bases, as well as the slant height of the frustum. The slant height is the distance from the center of the top base to the center of the bottom base. The surface area of a frustrum of a cone can be calculated using the formula: A = π(R1 + R2)√(h^2 + (R2 - R1)^2) + πR1^2 + πR2^2, where A is the surface area, π is a mathematical constant, R1 and R2 are the radii of the top and bottom bases, and h is the height of the frustum.
How do You Use a Calculator to Find the Volume and Surface Area of a Frustrum of a Cone?
There are many online calculators that can be used to find the volume and surface area of a frustrum of a cone. These calculators usually require you to input the height and radii of the frustum, and then they will calculate the volume and surface area for you. Some calculators may also require you to input the slant height of the frustum, which is the distance from the center of the top base to the center of the bottom base. To use a calculator, simply enter the required values and click the calculate button. The calculator will then display the volume and surface area of the frustrum of a cone. It's also important to note that you should always check your input values to make sure they are accurate, as small errors can result in large differences in the calculated values. Additionally, you can also use mathematical software or programming languages to write your own code to calculate the volume and surface area of a frustrum of a cone.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas