Bloom Filter Calculator
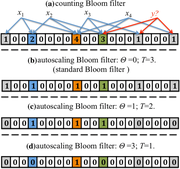
A Bloom filter is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure used to test whether an element is a member of a set. The Bloom Filter Calculator is a tool designed to help users determine the optimal parameters for their Bloom filter, such as the size of the filter and the number of hash functions. This calculator takes into account the expected number of elements and the desired false positive probability, providing a convenient way to balance memory usage and accuracy. By using the calculator, developers can efficiently implement Bloom filters in their applications. It simplifies the process of configuring the filter.
Bloom Filter Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
A Bloom Filter Calculator is a tool used to calculate the optimal parameters for a Bloom filter, which is a space-efficient data structure used to test whether an element is a member of a set. The calculator takes into account the size of the set, the desired error rate, and the hash functions used to determine the optimal size of the filter and number of hash functions.
Introduction to Bloom Filters
Bloom filters are probabilistic data structures that are used to test whether an element is a member of a set. They are space-efficient and fast, making them ideal for use in large-scale applications. The filter consists of a bit array and a set of hash functions that are used to map elements to the array. When an element is added to the filter, the corresponding bits in the array are set to 1. To test whether an element is in the filter, the hash functions are used to map the element to the array, and if all the corresponding bits are 1, the element is likely to be in the set.
How Bloom Filter Calculators Work
A Bloom filter calculator works by taking into account the size of the set, the desired error rate, and the hash functions used. The calculator uses these parameters to determine the optimal size of the filter and number of hash functions. The calculator typically uses the following formulas to calculate the optimal parameters:
| Parameter | Formula |
|---|---|
| Size of the filter | m = -(n ln(p)) / (ln(2)^2) |
| Number of hash functions | k = (m/n) ln(2) |
Advantages of Using a Bloom Filter Calculator
Using a Bloom filter calculator has several advantages, including:
Optimal parameter selection: The calculator ensures that the size of the filter and number of hash functions are optimized for the specific use case, resulting in better performance and lower error rates.
Time savings: The calculator saves time and effort by automating the process of calculating the optimal parameters, which can be complex and error-prone if done manually.
Improved accuracy: The calculator ensures that the desired error rate is achieved, resulting in more accurate results.
Common Applications of Bloom Filter Calculators
Bloom filter calculators are used in a variety of applications, including:
Data storage and retrieval: Bloom filters are used to cache frequently accessed data, reducing the load on the storage system.
Network security: Bloom filters are used to detect and prevent malicious activity, such as DDoS attacks.
Bioinformatics: Bloom filters are used to search for patterns in large datasets, such as genomic data.
Best Practices for Using a Bloom Filter Calculator
When using a Bloom filter calculator, it's essential to follow best practices, including:
Selecting the right hash functions: The hash functions used should be independent and uniform, ensuring that the bits in the filter are randomly distributed.
Choosing the optimal size of the filter: The size of the filter should be large enough to minimize the error rate, but small enough to minimize memory usage.
Monitoring and adjusting the filter: The filter should be monitored and adjusted as needed to ensure that the desired error rate is maintained.
How to choose the size of a Bloom filter?
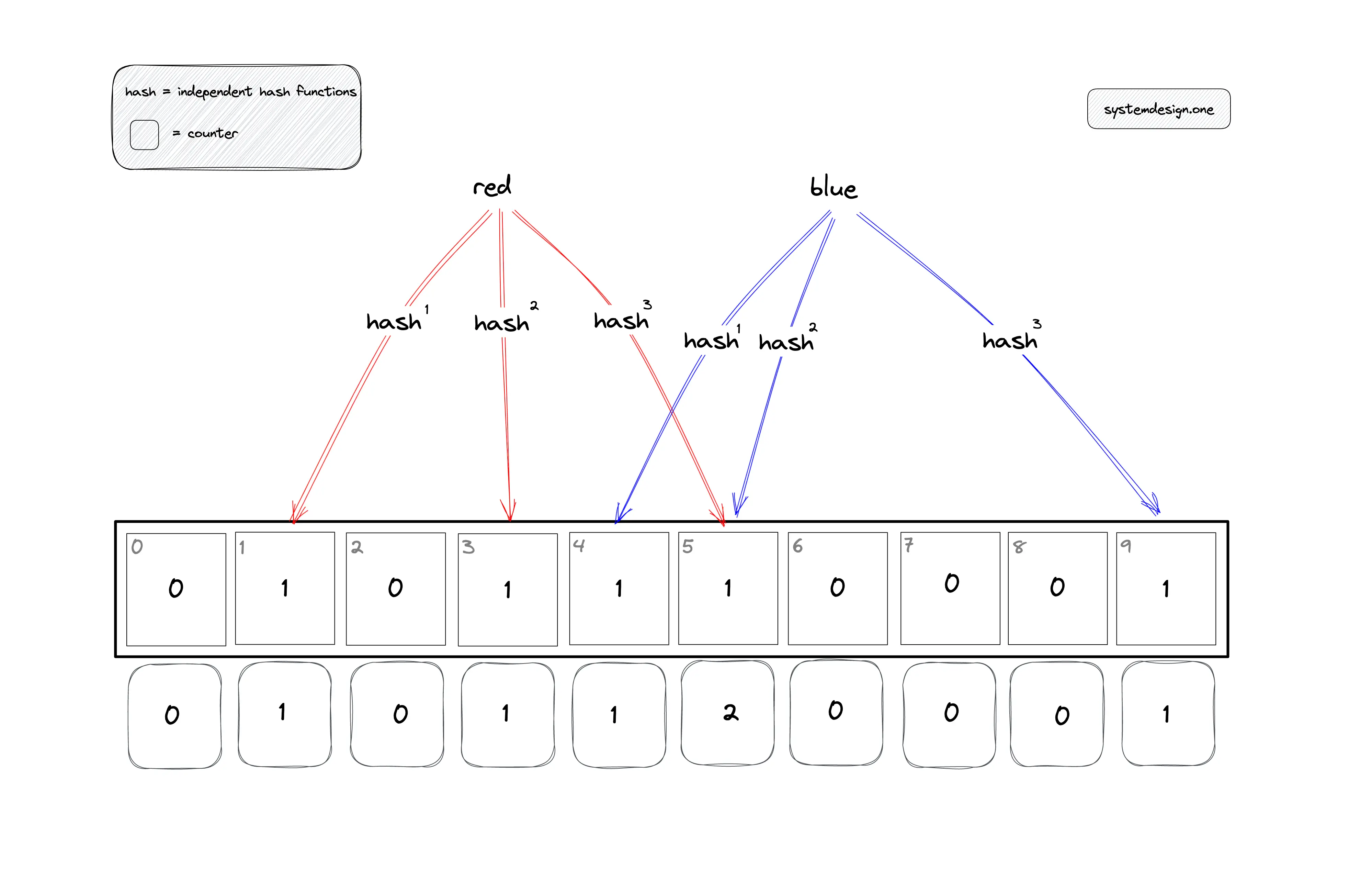
To choose the size of a Bloom filter, you need to consider several factors, including the expected number of elements, the desired false positive rate, and the available memory. The size of the Bloom filter is typically determined by the number of bits required to store the filter, which is a function of the number of elements and the desired false positive rate. A larger Bloom filter will have a lower false positive rate, but will also require more memory.
Understanding the Basics of Bloom Filters
To choose the size of a Bloom filter, you need to understand the basics of how Bloom filters work. A Bloom filter is a probabilistic data structure that uses a bit array to store the presence or absence of elements in a set. The filter uses hash functions to map elements to indices in the bit array. When an element is added to the filter, the corresponding bits in the array are set to 1. To check if an element is in the filter, the same hash functions are used to map the element to indices in the array, and if any of the corresponding bits are 0, the element is not in the filter. The key factors to consider when choosing the size of a Bloom filter are:
- Expected number of elements
- Desired false positive rate
- Available memory
Calculating the Optimal Size of a Bloom Filter
To calculate the optimal size of a Bloom filter, you can use the following formula: m = -(n ln(p)) / (ln(2)^2), where m is the size of the filter in bits, n is the expected number of elements, p is the desired false positive rate, and ln is the natural logarithm. This formula provides a good estimate of the required size of the filter, but it assumes that the hash functions are uniformly distributed and that the filter is fully populated. In practice, the actual size of the filter may need to be adjusted based on the specific use case and the characteristics of the data.
- Expected number of elements (n)
- Desired false positive rate (p)
- Number of hash functions (k)
Choosing the Number of Hash Functions
The number of hash functions used in a Bloom filter also affects its size and false positive rate. Using more hash functions will reduce the false positive rate, but will also increase the computational overhead of adding elements to the filter and checking membership. The optimal number of hash functions can be calculated using the following formula: k = (m/n) ln(2), where k is the number of hash functions, m is the size of the filter in bits, and n is the expected number of elements. The key considerations when choosing the number of hash functions are:
- Computational overhead
- False positive rate
- Memory usage
Memory Considerations for Bloom Filters
The memory usage of a Bloom filter is an important consideration when choosing its size. Bloom filters are typically used in applications where memory is limited, such as in embedded systems or mobile devices. To minimize memory usage, the size of the filter should be chosen to balance the false positive rate and the available memory. The key factors to consider when evaluating memory usage are:
- Available memory
- False positive rate
- Computational overhead
Trade-Offs between False Positive Rate and Memory Usage
There is a fundamental trade-off between the false positive rate and memory usage in Bloom filters. A smaller filter will have a higher false positive rate, but will also require less memory. Conversely, a larger filter will have a lower false positive rate, but will also require more memory. The key considerations when evaluating this trade-off are:
- False positive rate
- Memory usage
- Computational overhead
What is the formula for the Bloom filter?

The formula for the Bloom filter is a probabilistic data structure that is used to test whether an element is a member of a set. The formula is based on the use of hash functions to map elements to a bit array. The size of the bit array and the number of hash functions used are critical parameters in determining the Brenden (probability of false positives) of the Bloom filter.
Introduction to Bloom Filter Formula
The Bloom filter formula is based on the use of multiple hash functions to map elements to a bit array. The formula is as follows: m = -(n ln(p)) / (ln(2)^2), where m is the size of the bit array, n is the number of elements, p is the desired false positive probability, and ln is the natural logarithm. The number of hash functions used is typically determined by the formula: k = (m/n) ln(2), where k is the number of hash functions.
- The size of the bit array (m) is a critical parameter in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
- The number of hash functions (k) used is also critical in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
- The false positive probability (p) is a key parameter in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
Bloom Filter False Positive Probability
The false positive probability of a Bloom filter is the probability that the filter returns a false positive, which means that it indicates that an element is a member of the set when it is not. The false positive probability is determined by the formula: p = (1 - e^(-kn/m))^k, where p is the false positive probability, n is the number of elements, m is the size of the bit array, and k is the number of hash functions.
- The false positive probability (p) is a key parameter in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
- The size of the bit array (m) is a critical parameter in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
- The number of hash functions (k) used is also critical in determining the performance of the Bloom filter.
Optimizing Bloom Filter Performance
The performance of a Bloom filter can be optimized by adjusting the size of the bit array and the number of hash functions used. The optimal values for these parameters depend on the desired false positive probability and the number of elements in the set.
- The size of the bit array (m) should be chosen to minimize the false positive probability.
- The number of hash functions (k) should be chosen to minimize the false positive probability.
- The desired false positive probability (p) should be chosen based on the requirements of the application.
Bloom Filter Applications
Bloom filters have a wide range of applications, including data compression, caching, and network routing. They are particularly useful in situations where fast lookup times are required and false positives are acceptable.
- Data compression is a key application of Bloom filters.
- Caching is another key application of Bloom filters.
- Network routing is also a key application of Bloom filters.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bloom Filters
Bloom filters have several advantages, including fast lookup times and low memory usage. However, they also have some disadvantages, including false positives and limited scalability.
- Fast lookup times are a key advantage of Bloom filters.
- Low memory usage is another key advantage of Bloom filters.
- False positives are a key disadvantage of Bloom filters.
When not to use Bloom filter?
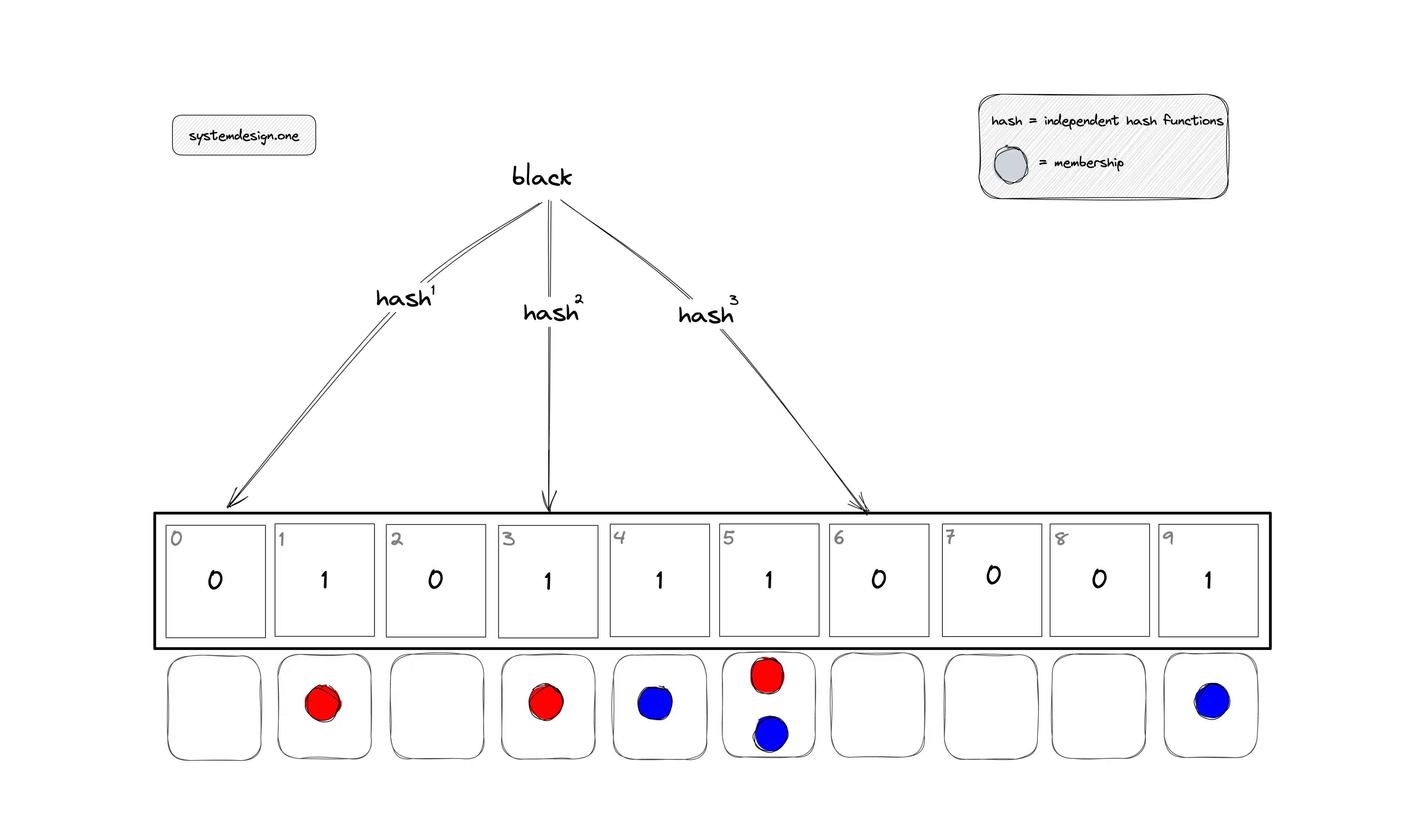
When not to use Bloom filter is a crucial consideration in data structure and algorithm design. Bloom filters are probabilistic data structures that are used to test whether an element is a member of a set. However, there are certain scenarios where using a Bloom filter may not be the best approach.
High False Positive Rates
In situations where false positives are unacceptable, Bloom filters may not be the best choice. This is because Bloom filters are designed to return false positives with a certain probability, which can be a problem in applications where accuracy is critical. For example, in security applications, a false positive can lead to incorrect identification of a threat. Some key points to consider when evaluating the use of Bloom filters in such scenarios include:
- Error rates: The probability of false positives and false negatives in the Bloom filter.
- Data quality: The accuracy and completeness of the data being stored in the Bloom filter.
- Application requirements: The level of accuracy and reliability required by the application.
Large Dataset Sizes
Bloom filters can become inefficient when dealing with very large dataset sizes. This is because the size of the Bloom filter grows exponentially with the size of the dataset, which can lead to high memory usage and slow lookup times. In such cases, other data structures like hash tables or trees may be more suitable. Some key considerations when evaluating the use of Bloom filters for large datasets include:
- Memory constraints: The available memory for storing the Bloom filter.
- Performance requirements: The required lookup and insertion times for the application.
- Data distribution: The distribution of the data in the dataset and its impact on the Bloom filter.
Frequent Insertions and Deletions
Bloom filters are not designed to handle frequent insertions and deletions. This is because the probability of false positives and false negatives can become unpredictable when the underlying data is constantly changing. In such scenarios, other data structures like dynamic arrays or linked lists may be more suitable. Some key points to consider when evaluating the use of Bloom filters in such scenarios include:
- Update frequency: The frequency of insertions and deletions in the dataset.
- Data volatility: The rate of change of the data in the dataset.
- Application requirements: The level of accuracy and reliability required by the application.
Real-Time Applications
Bloom filters may not be the best choice for real-time applications where predictable performance is critical. This is because the lookup time in a Bloom filter can be variable, depending on the size of the filter and the number of hash functions used. In such cases, other data structures like arrays or queues may be more suitable. Some key considerations when evaluating the use of Bloom filters for real-time applications include:
- Performance requirements: The required lookup and insertion times for the application.
- Latency constraints: The maximum allowed latency for the application.
- Throughput requirements: The required throughput for the application.
Multi-Threading and Concurrency
Bloom filters can be challenging to implement in multi-threaded and concurrent environments. This is because the insertion and lookup operations in a Bloom filter are not atomic, which can lead to race conditions and inconsistent results. In such cases, other data structures like locks or semaphores may be more suitable. Some key points to consider when evaluating the use of Bloom filters in such scenarios include:
- Thread safety: The ability of the Bloom filter to handle concurrent access.
- Concurrency control: The mechanisms used to control concurrent access to the Bloom filter.
- Performance overhead: The performance overhead of using concurrency control mechanisms.
How many bits is a Bloom filter?

A Bloom filter is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure that is used to test whether an element is a member of a set. The size of a Bloom filter is typically measured in bits, and it is designed to be highly compact and efficient. The number of bits in a Bloom filter depends on the size of the set and the desired false positive rate.
Introduction to Bloom Filter Size
The size of a Bloom filter is determined by the number of bits required to represent the set. A larger set requires a larger Bloom filter, which increases the number of bits needed. The size of the Bloom filter can be calculated using the following formula: m = -(n ln(p)) / (ln(2)^2), where m is the size of the Bloom filter, n is the size of the set, and p is the desired false positive rate.
- The false positive rate is the probability that an element is reported as present in the set when it is not.
- The size of the set is the number of elements in the set.
- The number of bits is the size of the Bloom filter in bits.
Calculating the Number of Bits
To calculate the number of bits in a Bloom filter, we need to know the size of the set and the desired false positive rate. We can use the formula mentioned earlier to calculate the size of the Bloom filter. For example, if we have a set of 1000 elements and we want a false positive rate of 1%, we can calculate the size of the Bloom filter as follows: m = -(1000 ln(0.01)) / (ln(2)^2). This gives us a Bloom filter size of approximately 9585 bits.
- The formula is used to calculate the size of the Bloom filter.
- The size of the set is used to calculate the number of bits.
- The desired false positive rate is used to calculate the number of bits.
Optimizing Bloom Filter Size
To optimize the size of a Bloom filter, we can use hash functions to reduce the number of bits required. A hash function maps an element to a bit in the Bloom filter. By using multiple hash functions, we can reduce the number of bits required to represent the set.
- Hash functions are used to map elements to bits.
- Multiple hash functions can be used to reduce the number of bits.
- Optimization is used to reduce the size of the Bloom filter.
Bloom Filter Applications
Bloom filters have many applications in computer science, including data storage, networking, and cryptography. They are particularly useful in distributed systems where space efficiency is critical.
- Data storage is an application of Bloom filters.
- Networking is an application of Bloom filters.
- Cryptography is an application of Bloom filters.
Bloom Filter Advantages
The main advantages of Bloom filters are their space efficiency and fast lookup times. They are particularly useful in real-time systems where speed is critical.
- Space efficiency is an advantage of Bloom filters.
- Fast lookup times are an advantage of Bloom filters.
- Real-time systems can benefit from the advantages of Bloom filters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Bloom Filter Calculator and how does it work?
A Bloom Filter Calculator is a tool used to calculate the optimal parameters for a Bloom filter, which is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure used to test whether an element is a member of a set. The calculator takes into account the expected number of elements to be stored in the filter, the desired false positive rate, and the available memory. It then calculates the optimal size of the filter and the number of hash functions required to achieve the desired false positive rate. This is done using the mathematical formulas that govern the behavior of Bloom filters, which involve probability theory and information theory. By using a Bloom Filter Calculator, developers can easily determine the optimal parameters for their specific use case, ensuring that their Bloom filter is efficient and effective.
What are the advantages of using a Bloom Filter Calculator?
Using a Bloom Filter Calculator has several advantages. Firstly, it saves time and effort by automating the process of calculating the optimal parameters for a Bloom filter. This is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets or complex systems, where manual calculations can be error-prone and time-consuming. Secondly, a Bloom Filter Calculator ensures that the calculated parameters are optimal, which means that the Bloom filter will have the best possible performance in terms of false positive rate and memory usage. This is critical in real-time systems or high-performance applications, where efficiency and accuracy are crucial. Finally, a Bloom Filter Calculator provides flexibility and customizability, allowing developers to experiment with different parameters and trade-offs to find the best solution for their specific use case.
How does a Bloom Filter Calculator handle false positives?
A Bloom Filter Calculator takes into account the desired false positive rate when calculating the optimal parameters for a Bloom filter. The calculator uses mathematical models to predict the probability of false positives based on the size of the filter, the number of hash functions, and the expected number of elements. By adjusting these parameters, the calculator can minimize the false positive rate to a desired level, ensuring that the Bloom filter is reliable and trustworthy. However, it's important to note that false positives are an inherent property of Bloom filters, and cannot be eliminated completely. Therefore, the calculator provides a trade-off between false positive rate and memory usage, allowing developers to choose the best balance for their specific use case. By using a Bloom Filter Calculator, developers can optimize their Bloom filter to achieve the best possible performance in terms of false positive rate and memory efficiency.
Can a Bloom Filter Calculator be used for other types of probabilistic data structures?
While a Bloom Filter Calculator is specifically designed for Bloom filters, the underlying mathematical principles and algorithms can be applied to other types of probabilistic data structures, such as Cuckoo filters or HyperLogLog counters. These data structures share similar properties and characteristics with Bloom filters, such as probabilistic membership testing and space-efficient storage. By modifying the calculator to account for the specific parameters and formulas of these data structures, developers can use the calculator to optimize their performance and efficiency. However, this would require a deep understanding of the underlying mathematics and algorithms, as well as extensive testing and validation to ensure that the calculator produces accurate and reliable results. Therefore, while a Bloom Filter Calculator can be adapted for other types of probabilistic data structures, it's essential to exercise caution and care when doing so.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas