Which SaaS applications are heavily used by banks?

The banking industry has undergone a significant digital transformation in recent years, driven by the adoption of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications. These cloud-based solutions have become essential tools for financial institutions, enabling them to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. From customer relationship management (CRM) platforms to advanced analytics and cybersecurity tools, SaaS applications are revolutionizing how banks operate in an increasingly competitive and tech-driven landscape. This article explores the most widely used SaaS applications in the banking sector, highlighting their key features and the value they bring to financial institutions worldwide.
- Which SaaS Applications Are Heavily Used by Banks?
- Which software is mostly used at banks?
- What is an example of SaaS in banking?
- Which application is used in a bank?
- Which technology is widely used by banks?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What are the most commonly used SaaS applications in the banking industry?
- How do SaaS applications improve efficiency in banking operations?
- What role do SaaS applications play in ensuring regulatory compliance for banks?
- Which SaaS applications are preferred for enhancing customer experience in banking?
Which SaaS Applications Are Heavily Used by Banks?
Banks and financial institutions increasingly rely on Software as a Service (SaaS) applications to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. These applications provide scalable, cost-effective, and secure solutions tailored to the unique needs of the banking sector. Below, we explore the most widely used SaaS applications in the banking industry.
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Platforms
Banks use CRM platforms like Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics 365 to manage customer interactions, track leads, and improve customer retention. These tools help banks personalize services, analyze customer data, and automate marketing campaigns. For example, Salesforce's Financial Services Cloud is specifically designed for banking institutions, offering features like client onboarding, portfolio management, and regulatory compliance.
| CRM Platform | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Salesforce | Client onboarding, portfolio management, compliance tools |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Customer insights, marketing automation, AI-driven analytics |
2. Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems like Temenos T24 and Mambu are essential for managing daily banking operations. These SaaS platforms enable banks to handle transactions, account management, loan processing, and payment systems efficiently. Temenos T24, for instance, offers a cloud-based solution that supports multi-currency transactions and real-time processing, making it a popular choice for global banks.
| Core Banking System | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Temenos T24 | Multi-currency support, real-time processing, scalability |
| Mambu | Cloud-native, API-driven, flexible loan management |
3. Fraud Detection and Prevention Tools
Banks rely on fraud detection tools like SAS Fraud Management and Feedzai to identify and prevent fraudulent activities. These SaaS applications use machine learning and AI algorithms to analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies in real time. For example, Feedzai's platform integrates with existing banking systems to provide real-time alerts and risk scoring, helping banks mitigate fraud risks effectively.
| Fraud Detection Tool | Key Features |
|---|---|
| SAS Fraud Management | AI-driven analytics, real-time monitoring, predictive modeling |
| Feedzai | Real-time alerts, risk scoring, seamless integration |
4. Regulatory Compliance Solutions
Regulatory compliance is a critical concern for banks, and SaaS applications like ComplyAdvantage and Onfido help institutions meet these requirements. These platforms provide tools for anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC), and sanctions screening. ComplyAdvantage, for instance, uses AI-powered data to monitor global regulatory changes and ensure compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
| Compliance Solution | Key Features |
|---|---|
| ComplyAdvantage | AML monitoring, KYC verification, sanctions screening |
| Onfido | Identity verification, document checks, fraud prevention |
5. Digital Banking Platforms
Digital banking platforms like Backbase and NCR Digital Banking enable banks to offer omnichannel experiences to their customers. These SaaS solutions support mobile banking, online banking, and self-service portals, allowing customers to manage their accounts, transfer funds, and apply for loans seamlessly. Backbase, for example, provides a unified platform that integrates with existing systems to deliver a consistent user experience across all channels.
| Digital Banking Platform | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Backbase | Omnichannel support, unified platform, seamless integration |
| NCR Digital Banking | Mobile banking, self-service portals, real-time notifications |
Which software is mostly used at banks?
Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems are the backbone of banking operations, enabling banks to manage customer accounts, transactions, and other essential services. The most widely used core banking software includes:
- Finacle by Infosys: A popular choice for its scalability and ability to handle large volumes of transactions.
- Flexcube by Oracle: Known for its modular architecture, allowing banks to customize solutions based on their needs.
- Temenos T24: A global leader in core banking, offering real-time processing and multi-channel capabilities.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
Banks rely on CRM software to manage customer interactions, improve service, and drive sales. The most commonly used CRM systems in banking include:
- Salesforce Financial Services Cloud: Tailored for financial institutions, it helps banks manage customer data and streamline communication.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Offers robust tools for customer engagement and analytics.
- SAP CRM: Known for its integration capabilities with other SAP banking solutions.
Risk Management and Compliance Software
Risk management and compliance are critical for banks to adhere to regulations and mitigate risks. Popular software in this category includes:
- SAS Risk Management: Provides advanced analytics for risk assessment and regulatory compliance.
- Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications (OFSAA): Focuses on risk, finance, and compliance management.
- Moody's Analytics: Offers solutions for credit risk, liquidity risk, and regulatory reporting.
Payment Processing Software
Payment processing software is essential for handling transactions efficiently. Widely used solutions in banking include:
- ACI Worldwide: Specializes in real-time payment processing and fraud prevention.
- Fiserv: Offers a comprehensive suite for payment processing and digital banking.
- PayPal Braintree: Popular for its seamless integration with e-commerce platforms.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Software
AML software helps banks detect and prevent financial crimes. The most commonly used AML tools include:
- Actimize by NICE: A leader in financial crime prevention, offering advanced analytics and machine learning.
- FICO TONBELLER: Focuses on transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting.
- BAE Systems NetReveal: Provides solutions for fraud detection and anti-money laundering compliance.
What is an example of SaaS in banking?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Software-as-a-service-saas_final-5caef210a00b48f5ac5de4964f72a016.png)
What is SaaS in Banking?
Software as a Service (SaaS) in banking refers to cloud-based solutions that provide financial institutions with tools to manage operations, customer relationships, and data securely. An example of SaaS in banking is Mambu, a cloud-based core banking platform that enables banks to offer digital banking services, manage accounts, and process transactions efficiently.
Key Features of SaaS in Banking
SaaS platforms in banking offer several key features that enhance operational efficiency and customer experience:
- Scalability: Banks can easily scale their operations up or down based on demand without significant infrastructure changes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for expensive hardware and maintenance, as the software is hosted in the cloud.
- Security: Provides advanced security measures, including encryption and compliance with regulatory standards.
Benefits of SaaS for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions benefit significantly from adopting SaaS solutions:
- Faster Deployment: SaaS platforms can be deployed quickly, allowing banks to launch new services in a shorter time frame.
- Improved Customer Experience: Enables personalized and seamless banking experiences through advanced analytics and customer insights.
- Operational Flexibility: Supports remote access and integration with other systems, enhancing workflow efficiency.
Examples of SaaS Applications in Banking
Several SaaS applications are widely used in the banking sector:
- Core Banking Systems: Platforms like Mambu and Temenos provide end-to-end banking solutions.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tools like Salesforce Financial Services Cloud help banks manage customer interactions.
- Fraud Detection: Solutions like Feedzai use AI to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
Challenges of Implementing SaaS in Banking
While SaaS offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Data Privacy Concerns: Storing sensitive financial data in the cloud requires robust security measures.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating SaaS solutions with legacy systems can be technically challenging.
- Regulatory Compliance: Banks must ensure that SaaS providers comply with industry regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS.
Which application is used in a bank?
Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems are the backbone of any bank's operations. These applications handle the primary functions of a bank, including account management, transaction processing, and customer data management. They are essential for ensuring that all banking operations run smoothly and securely.
- Account Management: Allows banks to create, modify, and manage customer accounts efficiently.
- Transaction Processing: Facilitates the processing of deposits, withdrawals, and transfers in real-time.
- Customer Data Management: Stores and manages customer information securely, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Loan Management Systems
Loan management systems are specialized applications used by banks to manage the entire lifecycle of loans. These systems help in loan origination, disbursement, and repayment tracking, ensuring that the bank can manage its loan portfolio effectively.
- Loan Origination: Streamlines the process of applying for and approving loans.
- Disbursement: Manages the distribution of loan funds to borrowers.
- Repayment Tracking: Monitors and tracks loan repayments, including interest and principal amounts.
Payment Processing Systems
Payment processing systems are crucial for handling various types of transactions, including credit card payments, wire transfers, and online payments. These systems ensure that transactions are processed quickly and securely, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Credit Card Payments: Processes payments made through credit cards, including authorization and settlement.
- Wire Transfers: Facilitates the transfer of funds between banks and financial institutions.
- Online Payments: Enables customers to make payments through internet banking platforms.
Risk Management Systems
Risk management systems are used by banks to identify, assess, and mitigate various types of risks, including credit risk, market risk, and operational risk. These systems help banks maintain financial stability and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Credit Risk: Assesses the risk of default by borrowers and manages credit exposure.
- Market Risk: Monitors and manages risks associated with market fluctuations.
- Operational Risk: Identifies and mitigates risks related to internal processes, systems, and people.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are used by banks to manage interactions with current and potential customers. These systems help in customer acquisition, retention, and service improvement, ensuring a positive customer experience.
- Customer Acquisition: Tracks and manages leads to convert them into customers.
- Customer Retention: Analyzes customer behavior to improve retention rates.
- Service Improvement: Uses customer feedback to enhance service quality and satisfaction.
Which technology is widely used by banks?
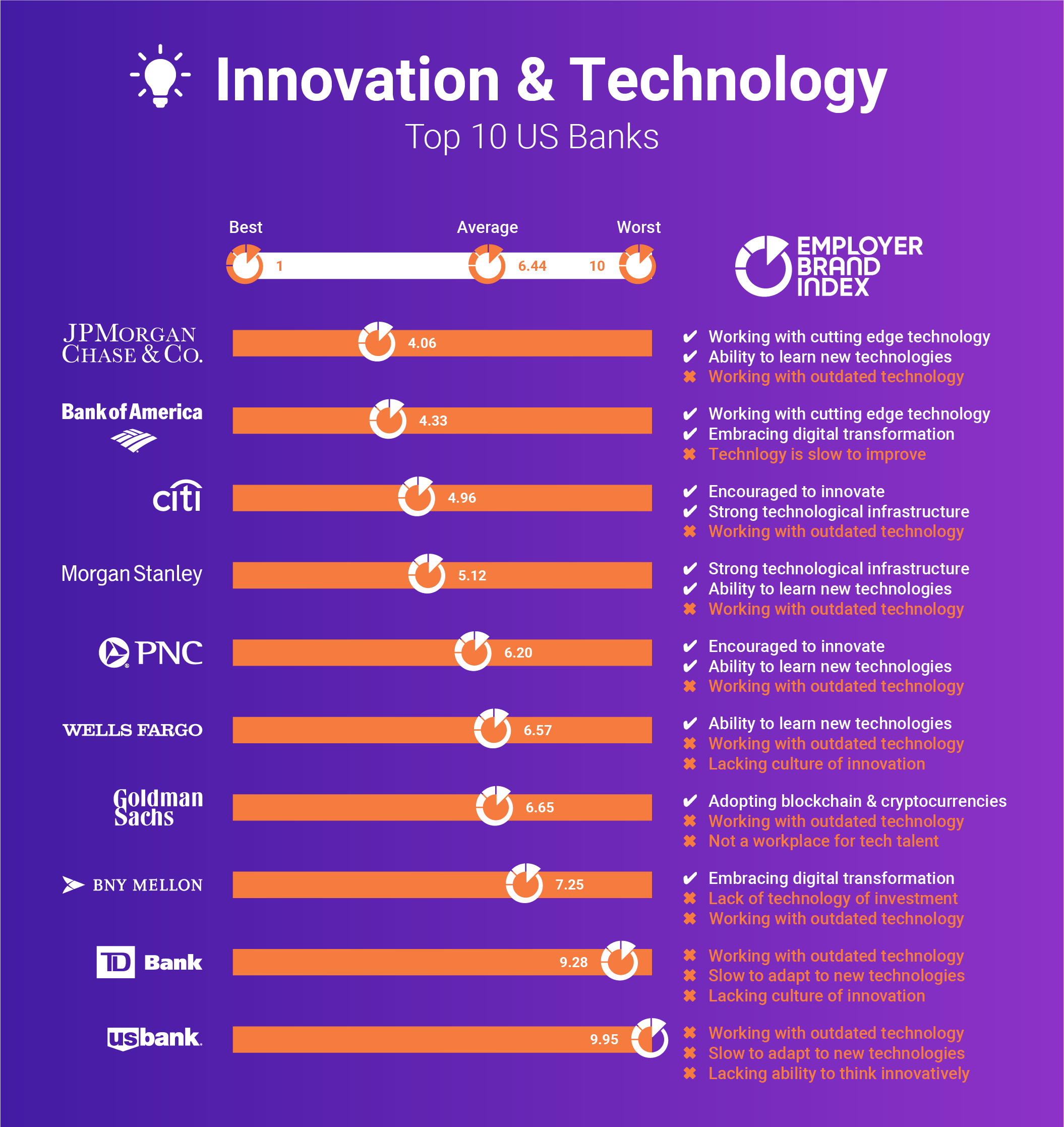
Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems are the backbone of modern banking operations. These systems enable banks to manage customer accounts, process transactions, and provide a centralized platform for various banking services. Key features include:
- Real-time transaction processing for seamless customer experiences.
- Centralized database management to ensure data consistency across branches.
- Scalability to handle growing customer demands and transaction volumes.
Mobile Banking Applications
Mobile banking apps have become a cornerstone of customer interaction for banks. These applications allow customers to access their accounts, transfer funds, and perform other banking activities from their smartphones. Key aspects include:
- User-friendly interfaces to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Secure authentication methods like biometrics and two-factor authentication.
- Integration with other financial services such as digital wallets and payment gateways.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is increasingly being adopted by banks for its ability to enhance security and transparency. It is particularly useful for cross-border payments and fraud prevention. Key benefits include:
- Decentralized ledger systems that reduce the risk of data tampering.
- Faster and cheaper international transactions compared to traditional methods.
- Smart contracts that automate and enforce agreements without intermediaries.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing the banking sector by enabling personalized services and improving operational efficiency. Applications include:
- Fraud detection systems that analyze transaction patterns in real-time.
- Chatbots and virtual assistants for customer support and query resolution.
- Predictive analytics for credit scoring and risk management.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is widely used by banks to enhance flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. It allows banks to store and process data on remote servers, reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure. Key advantages include:
- On-demand resource allocation to handle peak transaction loads.
- Enhanced disaster recovery capabilities through data redundancy.
- Cost savings by eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the most commonly used SaaS applications in the banking industry?
Banks heavily rely on SaaS applications to streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and ensure compliance. Some of the most commonly used applications include Salesforce for customer relationship management, Microsoft Azure for cloud infrastructure, Workday for human resources and financial management, and ServiceNow for IT service management. These platforms help banks manage large volumes of data, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
How do SaaS applications improve efficiency in banking operations?
SaaS applications significantly improve efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors, and enabling real-time data access. For example, Oracle Financial Services helps banks manage financial data and reporting, while Zendesk enhances customer support through ticketing systems and live chat. By leveraging these tools, banks can focus on strategic initiatives rather than operational bottlenecks.
What role do SaaS applications play in ensuring regulatory compliance for banks?
Regulatory compliance is a critical concern for banks, and SaaS applications like ComplyAdvantage and OneTrust are designed to address this need. These platforms provide tools for monitoring transactions, detecting fraud, and ensuring adherence to global regulations such as GDPR and AML (Anti-Money Laundering). By using these applications, banks can minimize risks and avoid hefty fines.
Which SaaS applications are preferred for enhancing customer experience in banking?
To enhance customer experience, banks often use SaaS applications like Adobe Experience Cloud for personalized marketing, HubSpot for customer engagement, and Zoho CRM for managing client interactions. These tools enable banks to deliver tailored services, improve communication, and build stronger relationships with their customers, ultimately driving loyalty and satisfaction.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas