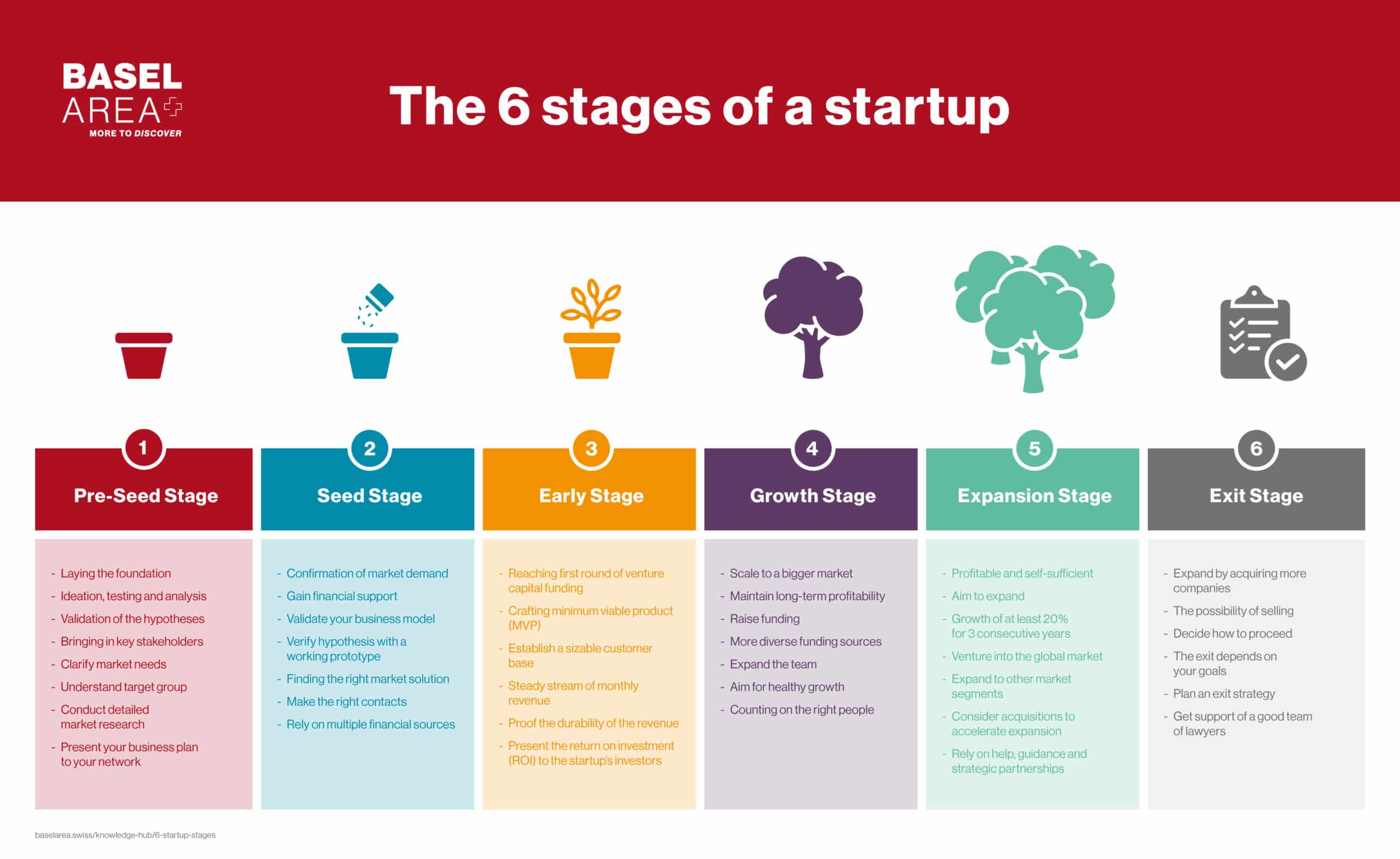
What are the expectations of an early stage SaaS pro forma for an angel or seed investor?

When seeking angel or seed funding for an early-stage SaaS startup, a well-crafted pro forma is essential to demonstrate the company’s potential and align with investor expectations. This financial model serves as a roadmap, projecting revenue, expenses, and growth over a defined period. Investors typically look for realistic assumptions, clear market validation, and a path to profitability. Key elements include customer acquisition costs, lifetime value, churn rates, and scalability. A compelling pro forma not only highlights the startup’s financial viability but also showcases the team’s ability to execute the business plan, making it a critical tool for securing early-stage investment.
- What Are the Expectations of an Early Stage SaaS Pro Forma for an Angel or Seed Investor?
- What are the expectations of an angel investor?
- What is the early stage of seed funding?
- What is the pre-seed valuation for SaaS?
- What is the difference between seed and early stage investment?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What financial metrics should be included in an early-stage SaaS pro forma for angel or seed investors?
- How detailed should the revenue projections be in a SaaS pro forma for early-stage investors?
- What assumptions should be clearly outlined in a SaaS pro forma for angel or seed investors?
- How important is the break-even analysis in an early-stage SaaS pro forma for investors?
What Are the Expectations of an Early Stage SaaS Pro Forma for an Angel or Seed Investor?
When presenting a SaaS pro forma to angel or seed investors, it is crucial to understand their expectations. These investors are primarily focused on the growth potential, scalability, and financial viability of the business. A well-prepared pro forma should clearly outline the revenue projections, customer acquisition costs, churn rates, and cash flow forecasts. Investors want to see a realistic yet ambitious plan that demonstrates how the company will achieve product-market fit and scale efficiently. Below, we break down the key elements that investors typically expect in an early-stage SaaS pro forma.
1. Revenue Projections and Growth Trajectory
Investors expect to see revenue projections that are both realistic and ambitious. The pro forma should include monthly or quarterly revenue forecasts for at least the next 3-5 years. These projections should be based on historical data (if available) or market research and assumptions about customer acquisition and pricing strategies. Highlight the growth trajectory and explain how the company plans to achieve it.
| Year | Revenue | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $500,000 | 100% |
| Year 2 | $1,200,000 | 140% |
| Year 3 | $2,500,000 | 108% |
2. Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a critical metric for SaaS businesses. Investors want to see a detailed breakdown of how much it costs to acquire a new customer. This includes marketing expenses, sales team costs, and any other related expenditures. The pro forma should also show how the company plans to optimize CAC over time through scaling efforts and efficiency improvements.
| Metric | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAC | $500 | $400 | $300 |
3. Churn Rates and Customer Retention
Churn rate is another key metric that investors closely examine. A high churn rate can indicate issues with product-market fit or customer satisfaction. The pro forma should include monthly or annual churn rates and explain the strategies in place to reduce churn and improve customer retention. Investors want to see a clear plan for maintaining a low churn rate as the business scales.
| Metric | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Churn Rate | 5% | 4% | 3% |
4. Cash Flow Forecasts
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any early-stage SaaS company. Investors want to see a detailed cash flow forecast that outlines when the company will reach breakeven and how much capital will be required to get there. The pro forma should include monthly cash flow projections and highlight any potential cash crunches or funding needs.
| Month | Cash Flow | Cumulative Cash Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | -$50,000 | -$50,000 |
| Month 6 | -$20,000 | -$150,000 |
| Month 12 | $10,000 | -$50,000 |
5. Key Metrics and Milestones
Investors expect the pro forma to include key metrics and milestones that demonstrate progress and traction. These could include monthly recurring revenue (MRR), annual recurring revenue (ARR), customer count, and product development milestones. Clearly outline the timeline for achieving these milestones and how they align with the overall business strategy.
| Metric | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRR | $50,000 | $150,000 | $300,000 |
| Customer Count | 100 | 500 | 1,200 |
What are the expectations of an angel investor?

What Are the Key Expectations of an Angel Investor?
Angel investors typically have specific expectations when investing in startups or early-stage companies. These expectations revolve around financial returns, growth potential, and strategic involvement. Below are the key expectations:
- High Return on Investment (ROI): Angel investors seek significant financial returns, often aiming for a 10x or higher return on their investment within 5-7 years.
- Scalable Business Model: They look for businesses with the potential to scale rapidly and achieve substantial market penetration.
- Clear Exit Strategy: Investors expect a well-defined exit plan, such as an acquisition or IPO, to realize their returns.
What Role Does Risk Play in Angel Investing?
Angel investors are aware of the high-risk nature of investing in startups. Their expectations include:
- Risk Mitigation: They often diversify their portfolio to spread risk across multiple investments.
- Due Diligence: Investors conduct thorough research to assess the viability and potential of the startup.
- Alignment with Founders: They expect founders to share the risk and demonstrate commitment to the business.
How Important Is the Team for Angel Investors?
The founding team is a critical factor for angel investors. Their expectations include:
- Strong Leadership: Investors look for founders with vision, resilience, and the ability to execute.
- Relevant Experience: A team with industry expertise and a track record of success is highly valued.
- Complementary Skills: A balanced team with diverse skills increases the likelihood of success.
What Financial Metrics Do Angel Investors Focus On?
Angel investors pay close attention to specific financial metrics to evaluate potential investments. These include:
- Revenue Growth: Consistent and rapid revenue growth is a key indicator of success.
- Burn Rate: Investors monitor how quickly the startup is spending its capital.
- Profit Margins: High margins suggest a sustainable and scalable business model.
How Do Angel Investors Evaluate Market Potential?
Market potential is a crucial factor for angel investors. Their expectations include:
- Large Addressable Market: Investors prefer startups targeting large or rapidly growing markets.
- Unique Value Proposition: The product or service should solve a significant problem or meet a clear market need.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong differentiator that sets the startup apart from competitors is essential.
What is the early stage of seed funding?
What is Seed Funding?
Seed funding is the initial capital raised by a startup to develop its business idea, build a prototype, or conduct market research. It is typically the first official round of funding and is used to prove the concept before seeking larger investments. Key characteristics include:
- Early-stage investment: Provided when the company is in its infancy.
- High risk: Investors take a chance on unproven ideas.
- Equity or convertible notes: Often exchanged for ownership stakes or future equity.
Who Provides Seed Funding?
Seed funding can come from various sources, each with its own motivations and expectations. Common providers include:
- Angel investors: High-net-worth individuals investing personal funds.
- Venture capital firms: Specialized firms focusing on early-stage startups.
- Accelerators and incubators: Programs offering funding, mentorship, and resources.
How is Seed Funding Used?
Startups utilize seed funding to achieve critical milestones that validate their business model. Typical uses include:
- Product development: Building a minimum viable product (MVP).
- Market research: Understanding customer needs and market demand.
- Team building: Hiring key personnel to execute the vision.
What are the Challenges of Seed Funding?
Securing seed funding is often challenging due to the high level of uncertainty and competition. Common obstacles include:
- Proving viability: Convincing investors of the idea's potential.
- Valuation disputes: Agreeing on the startup's worth.
- Limited resources: Managing funds efficiently to achieve milestones.
What are the Benefits of Seed Funding?
Despite the challenges, seed funding offers significant advantages for startups. These include:
- Validation: Gaining credibility and attracting further investment.
- Flexibility: Using funds to pivot or refine the business model.
- Networking: Access to investors' expertise and connections.
What is the pre-seed valuation for SaaS?
What is Pre-Seed Valuation in SaaS?
Pre-seed valuation in SaaS refers to the estimated worth of a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company during its earliest stage of development, typically before it has generated significant revenue or secured substantial funding. At this stage, the valuation is often based on factors such as the team's expertise, the market potential, the product's uniqueness, and the traction achieved through early prototypes or customer interest. Pre-seed valuations are generally lower compared to later funding rounds, as the company is still in the idea validation phase.
- Team Expertise: Investors often value the experience and skills of the founding team highly.
- Market Potential: The size and growth potential of the target market play a significant role in determining valuation.
- Product Uniqueness: A unique or innovative product can command a higher valuation.
- Traction: Early signs of customer interest or prototype usage can positively influence valuation.
- Idea Validation: The extent to which the business idea has been tested and validated impacts the valuation.
How is Pre-Seed Valuation Calculated for SaaS Startups?
Pre-seed valuation for SaaS startups is typically calculated using a combination of qualitative and quantitative factors. Since these companies often lack significant financial data, investors rely on metrics such as the problem being solved, the scalability of the solution, and the competitive landscape. Additionally, comparable company analysis and discounted cash flow (DCF) methods may be used, albeit with adjustments for the early-stage nature of the business.
- Problem Being Solved: The importance and urgency of the problem addressed by the SaaS product.
- Scalability: The potential for the solution to scale across markets or industries.
- Competitive Landscape: The level of competition and the startup's differentiation.
- Comparable Company Analysis: Benchmarking against similar startups in the same industry.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): Projecting future cash flows and discounting them to present value.
Key Factors Influencing Pre-Seed Valuation in SaaS
Several key factors influence the pre-seed valuation of SaaS startups, including the founders' track record, the size of the addressable market, and the stage of product development. Investors also consider the potential for recurring revenue, which is a hallmark of SaaS businesses, as well as the strength of the intellectual property or proprietary technology.
- Founders' Track Record: Previous successes or relevant experience can boost valuation.
- Addressable Market Size: A larger market opportunity can justify a higher valuation.
- Product Development Stage: A more developed product or prototype can increase valuation.
- Recurring Revenue Potential: The ability to generate consistent revenue over time.
- Intellectual Property: Patents or proprietary technology can add significant value.
Common Challenges in Determining Pre-Seed Valuation for SaaS
Determining pre-seed valuation for SaaS startups can be challenging due to the lack of historical data, uncertainty about market fit, and difficulty in forecasting future performance. Additionally, the subjective nature of early-stage valuations and the variability in investor expectations can lead to wide discrepancies in valuation estimates.
- Lack of Historical Data: Limited financial or operational data makes valuation difficult.
- Market Fit Uncertainty: Unproven demand for the product adds risk.
- Forecasting Challenges: Difficulty in predicting future revenue or growth.
- Subjective Valuations: Early-stage valuations often rely on investor judgment.
- Investor Expectations: Different investors may have varying valuation criteria.
Why is Pre-Seed Valuation Important for SaaS Startups?
Pre-seed valuation is crucial for SaaS startups as it sets the foundation for future funding rounds, determines the equity stake given to investors, and influences the company's perceived value in the market. A fair and realistic valuation can attract the right investors and provide the necessary capital to achieve key milestones, such as product development and market entry.
- Future Funding Rounds: A strong pre-seed valuation can pave the way for higher valuations in subsequent rounds.
- Equity Stake: Determines how much ownership is diluted in exchange for funding.
- Perceived Value: A higher valuation can enhance the startup's reputation and credibility.
- Investor Attraction: A fair valuation can attract experienced and supportive investors.
- Milestone Achievement: Provides the capital needed to reach critical business goals.
What is the difference between seed and early stage investment?

What is Seed Investment?
Seed investment refers to the initial capital raised by a startup to develop its idea, build a prototype, or conduct market research. This stage typically occurs when the company is in its infancy and has little to no revenue. Investors at this stage are often taking a significant risk, as the business model is unproven. Key characteristics of seed investment include:
- Small funding amounts: Seed rounds usually range from $10,000 to $2 million, depending on the startup's needs and potential.
- High risk: Investors are betting on the idea and the team, as there is often no tangible product or revenue.
- Equity exchange: In return for funding, investors receive equity or convertible notes in the startup.
What is Early Stage Investment?
Early stage investment occurs after the seed stage, when the startup has a working prototype, some market traction, or initial revenue. This stage is often referred to as Series A funding. Investors at this stage are still taking risks, but the company has demonstrated some level of viability. Key characteristics of early stage investment include:
- Larger funding amounts: Early stage rounds typically range from $2 million to $15 million, depending on the startup's growth potential.
- Proven concept: The startup has a functional product, some customer base, or early revenue streams.
- Focus on scaling: Funds are used to expand operations, hire talent, and increase market reach.
Key Differences in Funding Amounts
The funding amounts between seed and early stage investments differ significantly. Seed funding is generally smaller, as it is used to validate the idea and build a prototype. Early stage funding, on the other hand, is larger and aimed at scaling the business. Key points include:
- Seed funding: Typically ranges from $10,000 to $2 million.
- Early stage funding: Usually ranges from $2 million to $15 million.
- Purpose: Seed funding is for idea validation, while early stage funding is for growth and expansion.
Risk Levels for Investors
The risk levels for investors vary between seed and early stage investments. Seed investors face higher risks due to the unproven nature of the startup, while early stage investors have more data to assess the company's potential. Key points include:
- Seed investment: High risk, as the startup may not have a product or revenue.
- Early stage investment: Moderate risk, as the startup has some traction or revenue.
- Investor expectations: Seed investors expect higher returns to compensate for the risk, while early stage investors seek steady growth.
Equity and Ownership
The equity and ownership structure differs between seed and early stage investments. Seed investors often receive a larger percentage of equity due to the higher risk, while early stage investors may negotiate for a smaller but more secure stake. Key points include:
- Seed investment: Investors may receive 10-25% equity, depending on the valuation.
- Early stage investment: Investors typically receive 5-15% equity, as the company's valuation increases.
- Valuation: Seed rounds have lower valuations, while early stage rounds have higher valuations due to proven traction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What financial metrics should be included in an early-stage SaaS pro forma for angel or seed investors?
An early-stage SaaS pro forma for angel or seed investors should include key financial metrics such as Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), and gross margins. These metrics provide a clear picture of the company's growth potential, profitability, and scalability. Additionally, investors will expect to see projections for cash flow, burn rate, and runway, as these indicate how long the company can operate before needing additional funding.
How detailed should the revenue projections be in a SaaS pro forma for early-stage investors?
Revenue projections in a SaaS pro forma for early-stage investors should be realistic and well-supported by assumptions. While it’s important to show ambitious growth, the projections must also reflect the current market conditions, customer acquisition strategies, and historical data (if available). Break down revenue by customer segments, geographic regions, or product lines to demonstrate a clear understanding of the business model. Avoid overly optimistic or vague projections, as investors will scrutinize the assumptions behind them.
What assumptions should be clearly outlined in a SaaS pro forma for angel or seed investors?
In a SaaS pro forma, it’s crucial to clearly outline the assumptions driving the financial projections. These include customer growth rates, churn rates, pricing strategies, and sales cycle lengths. Additionally, explain assumptions about marketing spend, hiring plans, and operational costs. Transparency in assumptions helps build credibility with investors, as they can assess the feasibility of the projections and the team’s understanding of the market.
How important is the break-even analysis in an early-stage SaaS pro forma for investors?
A break-even analysis is highly important in an early-stage SaaS pro forma, as it shows investors when the company expects to become self-sustaining. This analysis should include the point at which revenue covers all operating expenses, including fixed and variable costs. It demonstrates the company’s path to profitability and helps investors understand the timeline for achieving financial sustainability. Including a break-even analysis also signals that the founders have a clear plan for managing cash flow and scaling the business efficiently.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas