Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator is a vital tool for engineers and researchers in the renewable energy sector. This calculator helps determine the power and torque output of wind turbines, taking into account factors such as wind speed, turbine blade angle, and rotor diameter. By accurately calculating these parameters, users can optimize wind turbine performance, increase energy production, and reduce costs. The calculator's user-friendly interface and advanced algorithms make it an essential resource for designing and analyzing wind energy systems, enabling the efficient harnessing of wind power. Accurate calculations are crucial for wind farm development.
- Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to calculate wind turbine torque?
- How much power does a 500 watt wind turbine produce?
- How much power does a 3000 watt wind turbine produce?
- How do you calculate the power of a wind turbine?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator and how does it work?
- What are the key parameters that affect the power and torque output of a wind turbine, and how are they accounted for in the calculator?
- How can the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator be used in the design and optimization of wind energy systems, and what are its limitations?
- What are some potential applications and benefits of using the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator in the wind energy industry, and how can it contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable wind energy systems?
Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator is a tool used to calculate the power and torque produced by a wind turbine. This calculator is essential for wind turbine designers, engineers, and operators to determine the performance of their turbines and optimize their energy production. The calculator takes into account various factors such as wind speed, turbine diameter, and blade angle to provide accurate calculations.
Introduction to Wind Turbine Power Calculation
The power calculation of a wind turbine is based on the kinetic energy of the wind, which is converted into mechanical energy by the turbine blades. The power output of a wind turbine is calculated using the Betz limit, which is the maximum theoretical efficiency of a wind turbine. The power calculation is also affected by factors such as air density, wind speed, and turbine efficiency.
Understanding Torque Calculation in Wind Turbines
The torque calculation of a wind turbine is critical to determine the rotational speed of the turbine and the mechanical stress on the blades and gearbox. The torque calculation is based on the momentum of the wind, which is transferred to the turbine blades. The torque output of a wind turbine is calculated using the torque coefficient, which is a function of the blade angle and wind speed.
Factors Affecting Wind Turbine Power and Torque
Several factors affect the power and torque output of a wind turbine, including:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Wind Speed | The speed of the wind, which affects the kinetic energy of the wind |
| Turbine Diameter | The diameter of the turbine, which affects the swept area of the blades |
| Blade Angle | The angle of the blades, which affects the torque coefficient |
| Air Density | The density of the air, which affects the kinetic energy of the wind |
| Turbine Efficiency | The efficiency of the turbine, which affects the power output |
Applications of Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator has various applications in the wind energy industry, including:
Wind turbine design: to optimize the design of wind turbines for maximum energy production
Wind farm planning: to determine the optimal layout and configuration of wind turbines in a wind farm
Performance monitoring: to monitor the performance of wind turbines and identify areas for improvement
Maintenance scheduling: to schedule maintenance activities based on the mechanical stress on the turbine components
Benefits of Using a Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator
Using a Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator offers several benefits, including:
Improved accuracy: in calculating the power and torque output of wind turbines
Optimized design: of wind turbines for maximum energy production
Reduced maintenance costs: by identifying areas for improvement and scheduling maintenance activities
Increased energy production: by optimizing the performance of wind turbines and wind farms. The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator is a valuable tool for the wind energy industry, enabling the optimization of wind turbine design, performance, and maintenance. By using this calculator, wind turbine designers, engineers, and operators can improve the efficiency and productivity of their turbines, leading to increased energy production and reduced costs.
How to calculate wind turbine torque?

To calculate wind turbine torque, you need to understand the relationship between the torque and the power output of the turbine. The torque is a measure of the rotational force that causes the turbine to spin, and it is directly related to the power output. The power output of a wind turbine is calculated using the formula: Power = Torque x Angular Velocity. The torque can be calculated using the formula: Torque = Power / Angular Velocity.
Understanding Wind Turbine Power Curve
The power curve of a wind turbine is a graphical representation of the relationship between the wind speed and the power output. To calculate the torque, you need to understand the power curve and how it relates to the rotor diameter and the hub height. The power curve is typically provided by the manufacturer and is used to determine the expected power output at different wind speeds.
- The power curve is used to determine the cut-in speed, which is the minimum wind speed required for the turbine to start producing power.
- The power curve is also used to determine the rated speed, which is the wind speed at which the turbine produces its maximum power output.
- The power curve can be used to calculate the annual energy production of the turbine, which is the total amount of energy produced by the turbine in a year.
Calculating Torque using the Power Formula
The torque can be calculated using the power formula: Torque = Power / Angular Velocity. The power output of the turbine is calculated using the formula: Power = 0.5 x Air Density x Swept Area x Wind Speed^3 x Power Coefficient. The angular velocity is calculated using the formula: Angular Velocity = Rotational Speed x (2 x Pi / 60).
- The power coefficient is a measure of the efficiency of the turbine and is typically provided by the manufacturer.
- The swept area is the area of the rotor and is calculated using the formula: Swept Area = Pi x (Rotor Diameter / 2)^2.
- The air density is a measure of the density of the air and is typically calculated using the barometric pressure and the temperature.
Understanding the Relationship between Torque and Rotor Speed
The torque and rotor speed are directly related, and the relationship is typically represented by a torque-speed curve. The torque-speed curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the torque and the rotor speed. The curve is typically provided by the manufacturer and is used to determine the expected torque output at different rotor speeds.
- The torque-speed curve is used to determine the stall speed, which is the wind speed at which the turbine produces its maximum torque output.
- The torque-speed curve is also used to determine the cut-out speed, which is the maximum wind speed at which the turbine can operate safely.
- The torque-speed curve can be used to calculate the optimal rotor speed, which is the rotor speed at which the turbine produces its maximum power output.
Measuring Torque using Sensors and Data Loggers
The torque can be measured using sensors and data loggers. The sensors are typically installed on the turbine and measure the rotational speed, torque, and power output. The data loggers are used to collect and store the data from the sensors, and the data can be used to calculate the torque and power output.
- The sensors are typically strain gauges or torque meters and are installed on the rotor shaft or the generator.
- The data loggers are typically computer-based systems and are used to collect and store the data from the sensors.
- The data can be used to calculate the torque and power output and can be used to optimize the performance of the turbine.
Optimizing Torque and Power Output using Control Systems
The torque and power output can be optimized using control systems. The control systems are typically computer-based systems and are used to control the rotor speed, pitch angle, and yaw angle. The control systems can be used to optimize the torque and power output by adjusting the rotor speed and pitch angle to match the wind speed and direction.
- The control systems are typically PID controllers or model predictive controllers and are used to control the rotor speed and pitch angle.
- The control systems can be used to optimize the torque and power output by adjusting the rotor speed and pitch angle to match the wind speed and direction.
- The control systems can also be used to reduce loads and increase efficiency by optimizing the torque and power output.
How much power does a 500 watt wind turbine produce?

A 500 watt wind turbine is designed to produce 500 watts of electric power under standard test conditions. However, the actual power output of the turbine can vary depending on several factors, including the wind speed, turbine efficiency, and air density. The power output of the turbine is typically measured in watts (W) and is calculated using the formula: Power (W) = 0.5 air density swept area wind speed^3 turbine efficiency.
Understanding Wind Turbine Power Output
The power output of a 500 watt wind turbine is affected by several factors, including the wind speed, turbine design, and operating conditions. To understand the power output of the turbine, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Wind speed: The power output of the turbine increases with the cube of the wind speed, making it a critical factor in determining the turbine's performance.
- Turbine design: The design of the turbine, including the blade angle and hub height, can affect its efficiency and power output.
- Operating conditions: The turbine's power output can be affected by temperature, humidity, and turbulence, which can impact its efficiency and performance.
Factors Affecting Wind Turbine Efficiency
The efficiency of a 500 watt wind turbine is crucial in determining its power output. Several factors can affect the turbine's efficiency, including:
- Aerodynamic losses: The drag and lift forces acting on the turbine blades can reduce its efficiency and power output.
- Mechanical losses: The friction and wear on the turbine's mechanical components can also affect its efficiency and performance.
- Electrical losses: The resistance and reactance in the turbine's electrical system can reduce its efficiency and power output.
Calculating Wind Turbine Power Output
To calculate the power output of a 500 watt wind turbine, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Swept area: The swept area of the turbine blades, which is the area covered by the blades as they rotate, affects the turbine's power output.
- Wind speed: The wind speed at the turbine's hub height is critical in determining the turbine's power output.
- Air density: The air density at the turbine's location can affect its power output, with denser air resulting in higher power output.
Measuring Wind Turbine Power Output
Measuring the power output of a 500 watt wind turbine is crucial to ensure its performance and efficiency. The power output can be measured using:
- Anemometers: To measure the wind speed and direction.
- Power meters: To measure the electrical power output of the turbine.
- Data loggers: To record the turbine's performance data, including power output, wind speed, and direction.
Optimizing Wind Turbine Power Output
To optimize the power output of a 500 watt wind turbine, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Turbine positioning: The orientation and elevation of the turbine can affect its power output, with optimal positioning resulting in higher power output.
- Turbine maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspection of the turbine can ensure its optimal performance and power output.
- Performance monitoring: Continuously monitoring the turbine's performance using data loggers and power meters can help identify areas for improvement and optimize its power output.
How much power does a 3000 watt wind turbine produce?
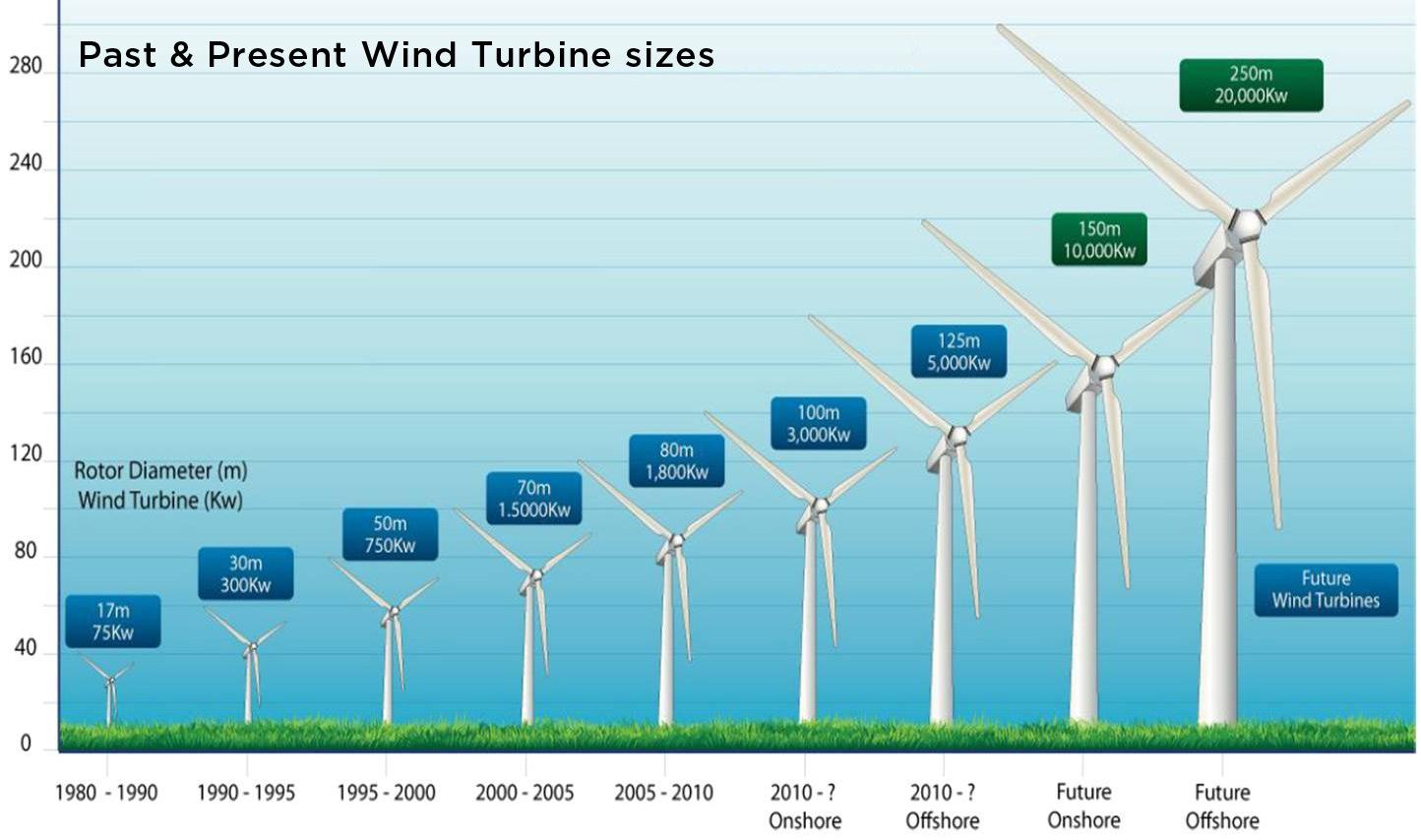
A 3000 watt wind turbine produces a significant amount of power, but the actual amount of energy it generates depends on various factors such as wind speed, turbine efficiency, and operating hours. To give you a better idea, let's consider that a 3000 watt wind turbine can produce around 7,000 to 10,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year, assuming an average wind speed of 5 meters per second. This is equivalent to powering a small to medium-sized home, depending on the energy consumption habits of the occupants.
Understanding Wind Turbine Power Output
The power output of a 3000 watt wind turbine is determined by the turbine's design, blade size, and generator efficiency. Here are some key factors that affect the power output:
- The wind speed at which the turbine operates, with higher speeds resulting in more power generation.
- The turbine's capacity factor, which is the ratio of actual energy produced to the maximum potential energy that could be produced.
- The efficiency of the turbine's generator and power electronics, which can affect the overall power output.
Factors Affecting Wind Turbine Performance
The performance of a 3000 watt wind turbine can be affected by various factors, including environmental conditions, maintenance, and operating practices. Some of the key factors that can impact performance include:
- Wind direction and turbulence, which can affect the turbine's ability to capture energy.
- Turbine maintenance, including regular lubrication and inspection of moving parts.
- Operating practices, such as start-up and shutdown procedures, which can affect the turbine's overall efficiency.
Calculating Energy Production
To calculate the energy production of a 3000 watt wind turbine, you need to consider the turbine's power curve, which shows the relationship between wind speed and power output. Here are some steps to follow:
- Determine the average wind speed at the turbine location.
- Use the power curve to determine the power output at the average wind speed.
- Multiply the power output by the number of operating hours per year to get the total energy production.
Comparing Wind Turbine Sizes
When comparing different wind turbine sizes, it's essential to consider the power output, cost, and installation requirements. Here are some key differences between small and large wind turbines:
- Small wind turbines (less than 10 kW) are often used for residential or small commercial applications.
- Medium wind turbines (10-50 kW) are commonly used for farm or small industrial applications.
- (greater than 50 kW) are typically used for utility-scale wind farms.
Optimizing Wind Turbine Performance
To optimize the performance of a 3000 watt wind turbine, it's crucial to monitor and maintain the turbine regularly, as well as optimize the turbine's operating settings. Some strategies for optimizing performance include:
- Regular maintenance, including blade cleaning and generator inspection.
- Performance monitoring, using data logging and remote monitoring systems.
- Operating settings optimization, including pitch and yaw adjustments.
How do you calculate the power of a wind turbine?

To calculate the power of a wind turbine, you need to consider several factors, including the wind speed, turbine efficiency, and blade size. The power output of a wind turbine can be calculated using the following formula: P = 0.5 ρ A v^3 Cp, where P is the power output, ρ is the air density, A is the swept area of the turbine blades, v is the wind speed, and Cp is the power coefficient. This formula takes into account the kinetic energy of the wind and the mechanical energy converted by the turbine.
Understanding Wind Turbine Components
The calculation of a wind turbine's power involves understanding its components, including the rotor blades, hub, and generator. The rotor blades are responsible for capturing the kinetic energy of the wind, while the hub connects the blades to the main shaft. The generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. To calculate the power, you need to consider the following factors:
- The length and shape of the rotor blades, which affect the swept area and angle of attack.
- The materials used to manufacture the blades, which affect their weight and strength.
- The design of the hub and main shaft, which affect the torque and rotational speed.
Measuring Wind Speed and Direction
Measuring wind speed and direction is crucial in calculating the power of a wind turbine. Anemometers are used to measure the wind speed, while wind vanes measure the direction. The wind speed affects the power output of the turbine, with higher speeds resulting in higher power output. To measure wind speed and direction, you need to consider the following factors:
- The height and location of the anemometer, which affect the accuracy of the measurement.
- The type of anemometer used, which affects the sensitivity and response time.
- The data logging system used to record the measurements, which affects the frequency and duration of the data.
Calculating Power Coefficient
The power coefficient (Cp) is a key factor in calculating the power of a wind turbine. It represents the efficiency of the turbine in converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy. The power coefficient depends on the design of the turbine and the operating conditions. To calculate the power coefficient, you need to consider the following factors:
- The blade angle and pitch, which affect the angle of attack and lift.
- The tip speed ratio, which affects the efficiency of the turbine.
- The airfoil shape and cambered surface, which affect the lift and drag.
Assessing Air Density and Turbulence
Air density and turbulence affect the power output of a wind turbine. Air density affects the kinetic energy of the wind, while turbulence affects the flow and efficiency of the turbine. To assess air density and turbulence, you need to consider the following factors:
- The temperature and humidity of the air, which affect the density and viscosity.
- The wind shear and turbulence intensity, which affect the flow and stability.
- The terrain and obstacles, which affect the flow and turbulence.
Adjusting for Losses and Efficiency
To calculate the actual power output of a wind turbine, you need to adjust for losses and efficiency. Losses occur due to mechanical and electrical inefficiencies, while efficiency affects the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. To adjust for losses and efficiency, you need to consider the following factors:
- The mechanical losses, such as friction and wear, which affect the efficiency of the turbine.
- The electrical losses, such as resistance and reactance, which affect the efficiency of the generator.
- The control systems and power electronics, which affect the efficiency and stability of the turbine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator and how does it work?
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator is a tool designed to calculate the power and torque output of a wind turbine, taking into account various parameters such as wind speed, turbine blade diameter, and air density. This calculator uses complex algorithms and mathematical models to simulate the behavior of a wind turbine and estimate its performance under different operating conditions. By inputting the relevant parameters, users can obtain accurate calculations of the turbine's power and torque output, which is essential for designing and optimizing wind energy systems. The calculator also provides a detailed breakdown of the calculations, allowing users to understand the underlying physics and engineering principles that govern wind turbine performance.
What are the key parameters that affect the power and torque output of a wind turbine, and how are they accounted for in the calculator?
The power and torque output of a wind turbine are influenced by several key parameters, including wind speed, turbine blade diameter, air density, and blade angle. The calculator takes these parameters into account using sophisticated models that simulate the aerodynamic and mechanical behavior of the turbine. For example, the calculator uses the power coefficient (Cp) to account for the efficiency of the turbine's blades in converting wind energy into mechanical energy. The calculator also considers the wind speed profile and the turbulence intensity to estimate the turbine's performance under different operating conditions. By accounting for these parameters, the calculator provides accurate and reliable calculations of the turbine's power and torque output.
How can the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator be used in the design and optimization of wind energy systems, and what are its limitations?
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator is a valuable tool for designing and optimizing wind energy systems, as it allows users to quickly and accurately estimate the power and torque output of a wind turbine under different operating conditions. This information can be used to size the turbine and its components, such as the generator and gearbox, and to optimize the turbine's performance for specific wind regimes. However, the calculator has some limitations, such as assuming a steady-state operating condition and neglecting dynamic effects such as turbulence and blade vibration. Additionally, the calculator relies on empirical models and simplifying assumptions, which may not always accurately capture the complex behavior of a wind turbine. Therefore, the calculator should be used in conjunction with other design tools and validation methods to ensure accurate and reliable results.
What are some potential applications and benefits of using the Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator in the wind energy industry, and how can it contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable wind energy systems?
The Wind Turbine Power and Torque Calculator has a wide range of potential applications and benefits in the wind energy industry, from turbine design and optimization to performance monitoring and maintenance scheduling. By providing accurate and reliable calculations of power and torque output, the calculator can help reduce uncertainty and improve decision-making in the design and operation of wind energy systems. Additionally, the calculator can contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable wind energy systems by allowing users to explore different design scenarios and operating strategies. For example, the calculator can be used to evaluate the potential benefits of advanced turbine designs, such as larger rotors or more efficient blades, or to optimize the performance of wind farms and wind power plants. By facilitating the development of more efficient and sustainable wind energy systems, the calculator can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas