Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator

The stress-strain curve is a fundamental concept in material science, describing the relationship between stress and strain in a material under tension. The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a mathematical model used to describe the non-linear stress-strain behavior of metals, particularly in the plastic region. This equation provides a more accurate representation of the material's response to stress, allowing engineers to better predict and design for structural integrity. The Ramberg-Osgood equation calculator is a tool used to analyze and visualize the stress-strain behavior of materials, enabling the calculation of key parameters such as yield strength and strain hardening exponent.
- Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator
- What is the formula for stress and strain curve?
- What is Ramberg Osgood Equation steel?
- How do you calculate material stress?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Stress-Strain Curve and its importance in Material Science?
- How do Ramberg-Osgood Equations relate to the Stress-Strain Curve?
- What are the key features of the Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator?
- How can the Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator be used in real-world applications?
Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator
The Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator is a tool used to analyze the stress and strain behavior of materials. This curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress and strain and is typically used to determine the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elastic modulus of a material. The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a mathematical model that describes the non-linear behavior of materials under tensile or compressive loading.
Introduction to Ramberg-Osgood Equations
The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a constitutive model that describes the non-linear behavior of materials. It is commonly used to model the behavior of metals and alloys under cyclic loading. The equation is based on the stress and strain relationship and takes into account the non-linear behavior of the material. The Ramberg-Osgood equation is given by: ε = σ/E + (σ/K)^n, where ε is the strain, σ is the stress, E is the elastic modulus, K is the strength coefficient, and n is the strain hardening exponent.
Stress-Strain Curve
The Stress-Strain Curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress and strain. The curve is typically divided into three regions: the elastic region, the plastic region, and the fracture region. The elastic region is where the material behaves elastically and returns to its original shape when the stress is removed. The plastic region is where the material behaves plastically and deforms permanently. The fracture region is where the material fails and breaks.
Calculator for Stress-Strain Curve
A calculator for the Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations is a tool that can be used to analyze the stress and strain behavior of materials. The calculator takes into account the Ramberg-Osgood equation and the material properties such as the elastic modulus, yield strength, and ultimate tensile strength. The calculator can be used to determine the stress and strain values for a given material and loading condition.
Material Properties
The material properties that are used in the Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator include the elastic modulus, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and strain hardening exponent. These properties are typically determined through experimental testing and are used to characterize the behavior of the material under tensile or compressive loading. The material properties are crucial in determining the stress and strain behavior of the material and are used in a variety of engineering applications.
Applications of Stress-Strain Curve
The Stress-Strain Curve Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator have a variety of applications in engineering and materials science. Some of the applications include designing structures, analyzing material behavior, and predicting material failure. The stress and strain behavior of materials is critical in ensuring safety and preventing failure in a variety of engineering applications.
| Material | Elastic Modulus | Yield Strength | Ultimate Tensile Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | 200 GPa | 250 MPa | 500 MPa |
| Aluminum | 70 GPa | 100 MPa | 200 MPa |
| Copper | 110 GPa | 200 MPa | 400 MPa |
What is the formula for stress and strain curve?
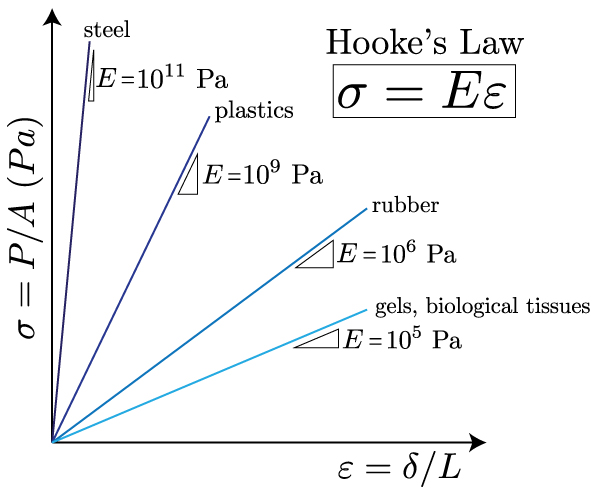
The formula for the stress and strain curve is typically represented by the equation: σ = E ε, where σ is the stress, E is the modulus of elasticity, and ε is the strain. This equation is a fundamental concept in materials science and mechanics of materials.
Understanding the Stress-Strain Curve
The stress-strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress and strain. It is a crucial tool for understanding the mechanical behavior of a material. The curve can be divided into several regions, including the elastic region, plastic region, and fracture region.
- The elastic region represents the range of stress and strain where the material behaves elastically, meaning it returns to its original shape when the stress is removed.
- The plastic region represents the range of stress and strain where the material behaves plastically, meaning it deforms permanently when the stress is removed.
- The fracture region represents the range of stress and strain where the material fails or breaks.
Status of the Material
The status of the material can be determined by analyzing the stress-strain curve. The curve provides valuable information about the material's strength, stiffness, and ductility.
- The yield strength is the stress at which the material begins to deform plastically.
- The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress that the material can withstand before failing.
- The fracture toughness is a measure of the material's resistance to crack propagation and failure.
Factors Affecting the Stress-Strain Curve
Several factors can affect the stress-strain curve, including temperature, strain rate, and microstructure.
- The temperature can affect the material's strength and ductility, with higher temperatures often leading to a decrease in strength and an increase in ductility.
- The strain rate can also affect the material's strength and ductility, with higher strain rates often leading to an increase in strength and a decrease in ductility.
- The microstructure of the material can also affect its mechanical properties, with different microstructures leading to different stress-strain curves.
Material Properties
The stress-strain curve is closely related to the material properties, such as young's modulus, poisson's ratio, and density.
- The young's modulus is a measure of the material's stiffness and is defined as the ratio of stress to strain in the elastic region.
- The poisson's ratio is a measure of the material's lateral strain and is defined as the ratio of lateral strain to axial strain.
- The density of the material can also affect its mechanical properties, with denser materials often having higher strength and stiffness.
Applications of the Stress-Strain Curve
The stress-strain curve has numerous applications in engineering and materials science, including designing structures, selecting materials, and predicting failure.
- The stress-strain curve can be used to design structures that can withstand various types of loading, such as tension, compression, and bending.
- The stress-strain curve can also be used to select materials for specific applications, based on their mechanical properties and performance.
- The stress-strain curve can also be used to predict failure of a material or structure, by analyzing its strength, stiffness, and ductility.
What is Ramberg Osgood Equation steel?
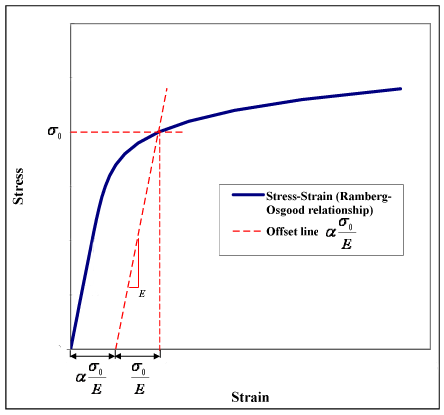
The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a mathematical model used to describe the non-linear behavior of steel materials under tensile stress. It is a widely used equation in the field of materials science and mechanical engineering to predict the stress-strain relationship of steel alloys. The equation is named after William Ramberg and William Osgood, who first proposed it in the 1940s.
Introduction to Ramberg-Osgood Equation
The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a empirical model that describes the relationship between stress and strain in steel materials. It is commonly used to predict the behavior of steel alloys under cyclic loading conditions. The equation is based on the idea that the stress-strain curve of steel can be divided into three distinct regions: elastic, plastic, and strain hardening. The equation uses a set of material parameters to describe the behavior of the steel alloy in each region.
- The equation is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries to design and analyze steel structures.
- The Ramberg-Osgood equation is also used in finite element analysis to simulate the behavior of steel alloys under complex loading conditions.
- The equation has been experimentally validated for a wide range of steel alloys, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel.
Material Parameters in Ramberg-Osgood Equation
The Ramberg-Osgood equation requires a set of material parameters to describe the behavior of the steel alloy. These parameters include the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and strain hardening exponent. The yield strength is the stress at which the steel alloy begins to deform plastically. The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress that the steel alloy can withstand before fracture. The strain hardening exponent describes the rate at which the steel alloy hardens as it is deformed.
- The material parameters must be experimentally determined for each specific steel alloy.
- The material parameters can be used to predict the stress-strain behavior of the steel alloy under different loading conditions.
- The material parameters are sensitive to the microstructure and chemical composition of the steel alloy.
Applications of Ramberg-Osgood Equation
The Ramberg-Osgood equation has a wide range of applications in the field of materials science and mechanical engineering. It is commonly used to design and analyze steel structures subject to cyclic loading conditions. The equation is also used to predict the fatigue life of steel alloys under variable amplitude loading conditions.
- The equation is used in the design of steel bridges, steel buildings, and steel pipelines.
- The equation is used in the analysis of steel components subject to impact loading and blast loading.
- The equation is used in the development of new steel alloys with improved mechanical properties.
Limitations of Ramberg-Osgood Equation
The Ramberg-Osgood equation has several limitations that must be considered when using it to predict the behavior of steel alloys. One of the main limitations is that the equation is empirical and has a limited range of applicability. The equation is also sensitive to the material parameters used to describe the behavior of the steel alloy.
- The equation is not applicable to all types of steel alloys, particularly those with complex microstructures.
- The equation is not suitable for high-temperature applications, where the mechanical properties of the steel alloy can change significantly.
- The equation is not valid for low-cycle fatigue applications, where the stress-strain behavior of the steel alloy can be highly non-linear.
Comparison with Other Equations
The Ramberg-Osgood equation is one of several equations used to describe the stress-strain behavior of steel alloys. Other equations, such as the Ludwik equation and the Swift equation, are also widely used in the field of materials science and mechanical engineering. The Ramberg-Osgood equation is more accurate than these equations for certain types of steel alloys, but it is less accurate for others.
- The Ludwik equation is a simpler equation that is less accurate than the Ramberg-Osgood equation, but it is easier to use.
- The Swift equation is a more complex equation that is more accurate than the Ramberg-Osgood equation, but it is more difficult to use.
- The Ramberg-Osgood equation is a good compromise between accuracy and ease of use, making it a popular choice in the field of materials science and mechanical engineering.
How do you calculate material stress?
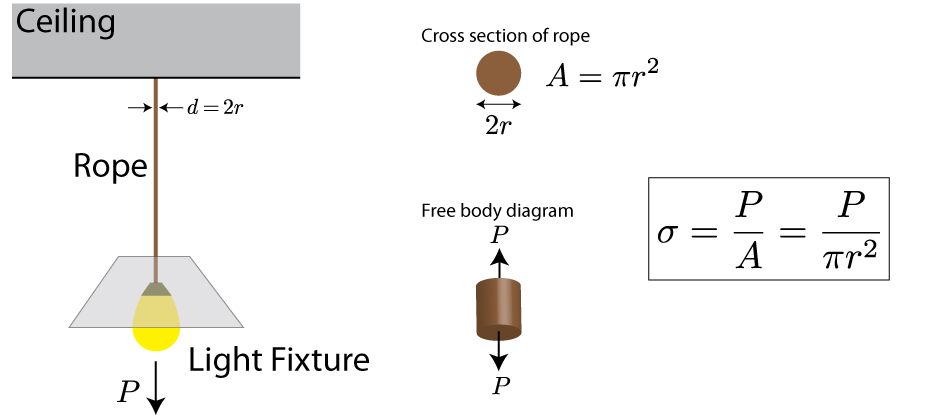
To calculate material stress, you need to understand the concept of stress and strain. Stress is a measure of the internal forces that are acting on a material, while strain is a measure of the resulting deformation. The calculation of material stress involves determining the stress and strain values, which can be done using various formulas and techniques.
Understanding Stress and Strain
To calculate material stress, you need to understand the relationship between stress and strain. The stress value can be calculated using the formula: stress = force / area. The strain value can be calculated using the formula: strain = change in length / original length. The key to calculating material stress is to understand how stress and strain are related, and how they affect the material.
- The stress value can be calculated using the formula: stress = force / area.
- The strain value can be calculated using the formula: strain = change in length / original length.
- The key to calculating material stress is to understand how stress and strain are related, and how they affect the material.
Types of Stress
There are several types of stress that can occur in a material, including tensile stress, compressive stress, and shear stress. Each type of stress has a different effect on the material, and can cause different types of deformation or failure. The calculation of material stress depends on the type of stress that is present, and the properties of the material.
- Tensile stress occurs when a material is stretched or pulled apart.
- Compressive stress occurs when a material is squeezed or compressed.
- Shear stress occurs when a material is subjected to a force that causes it to deform by sliding or rotating.
Calculating Material Stress
To calculate material stress, you need to use the formulas and techniques that are relevant to the type of stress that is present. For example, if you are calculating tensile stress, you would use the formula: tensile stress = force / area. You would also need to consider the properties of the material, such as its elastic modulus and poisson's ratio.
- The elastic modulus of a material is a measure of its stiffness.
- The poisson's ratio of a material is a measure of its lateral strain response to tensile or compressive loading.
- The properties of the material can affect the calculation of material stress, and must be taken into account.
Factors Affecting Material Stress
There are several factors that can affect the calculation of material stress, including the temperature, humidity, and loading conditions. These factors can cause the material to deform or fail in different ways, and must be taken into account when calculating material stress.
- Temperature can affect the properties of the material, and must be considered when calculating material stress.
- Humidity can also affect the properties of the material, and must be considered when calculating material stress.
- The loading conditions can affect the type and magnitude of stress that is present, and must be considered when calculating material stress.
Material Stress Analysis
Material stress analysis is a critical step in the design and development of structures and machines. It involves calculating the stress and strain values, and using this information to predict how the material will behave under different loading conditions. The goal of material stress analysis is to ensure that the material can withstand the stresses and strains that it will experience in service, and to prevent failure.
- Material stress analysis involves calculating the stress and strain values, and using this information to predict how the material will behave.
- The goal of material stress analysis is to ensure that the material can withstand the stresses and strains that it will experience in service.
- Material stress analysis is a critical step in the design and development of structures and machines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Stress-Strain Curve and its importance in Material Science?
The Stress-Strain Curve is a fundamental concept in Material Science that describes the relationship between the stress applied to a material and its resulting strain. This curve is crucial in understanding the mechanical properties of a material, such as its strength, ductility, and elasticity. The curve is typically plotted with stress on the vertical axis and strain on the horizontal axis.
How do Ramberg-Osgood Equations relate to the Stress-Strain Curve?
The Ramberg-Osgood Equations are a set of mathematical equations that describe the non-linear stress-strain behavior of materials, particularly in the plastic region. These equations are used to model the stress-strain curve of materials that exhibit non-linear elastic behavior, such as metals and alloys. The equations take into account the yield strength, ultimate strength, and strain hardening of the material, allowing for a more accurate prediction of its mechanical behavior under different loading conditions.
What are the key features of the Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator?
The Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator provide a user-friendly tool for analyzing the stress-strain behavior of materials. The calculator allows users to input material properties, such as yield strength, ultimate strength, and strain hardening exponent, and then calculates the corresponding stress-strain curve. The calculator also provides key features such as graphical visualization of the stress-strain curve, tabular output of the calculated values, and units conversion for easy use with different unit systems. Additionally, the calculator can be used to analyze and compare the mechanical behavior of different materials, making it a valuable tool for materials scientists and engineers.
How can the Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator be used in real-world applications?
The Ramberg-Osgood Equations and Calculator have a wide range of real-world applications, particularly in the aerospace, automotive, and energy industries. For example, materials scientists and engineers can use the calculator to design and optimize the mechanical properties of materials used in structural components, such as aircraft wings, car chassis, and wind turbine blades. The calculator can also be used to predict the lifetime and reliability of components under different loading conditions, allowing for more accurate and reliable design and maintenance of critical systems. Furthermore, the calculator can be used in research and development to study and understand the mechanical behavior of new materials and structures.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas