Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator

The Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is a valuable tool for investors and traders who engage in short selling activities. This calculator allows users to quickly and easily determine potential profits and losses from short selling transactions. By inputting the initial stock price, the short selling price, and the number of shares, users can calculate their expected gains or losses. This calculator is essential for making informed decisions and managing risk in short selling strategies, providing a clear and concise picture of potential outcomes. It simplifies complex calculations and promotes data-driven decision making.
- Understanding the Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator
- How do you calculate profit from short selling?
- How loss of profit is calculated on short sales?
- How can I calculate my profit or loss after selling stock?
- How do you make money if you short sell a stock?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the purpose of a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator?
- How does a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator work?
- What are the benefits of using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator?
- Can a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator be used for other types of trades?
Understanding the Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator
The Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is a tool used to calculate the potential profit or loss from a short selling transaction. Short selling is a trading strategy in which an investor sells a security they do not own with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. The calculator takes into account the initial short sale price, the buyback price, and the number of shares sold short to determine the profit or loss.
How the Calculator Works
The calculator works by using the following formula: Profit = (Short Sale Price - Buyback Price) x Number of Shares. If the result is positive, it represents a profit, and if it is negative, it represents a loss. The calculator also takes into account any fees or commissions associated with the transaction. For example, if an investor sells short 100 shares of stock at $50 per share and buys them back at $40 per share, the profit would be (50 - 40) x 100 = $1000.
Key Components of the Calculator
The Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator has several key components, including:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Short Sale Price | The price at which the security is sold short |
| Buyback Price | The price at which the security is bought back |
| Number of Shares | The number of shares sold short |
| Fees and Commissions | Any additional costs associated with the transaction |
Benefits of Using the Calculator
Using the Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator can provide several benefits, including:
- Accurate calculations: The calculator provides accurate calculations of potential profit or loss, helping investors make informed decisions.
- Risk management: By understanding the potential profit or loss, investors can better manage their risk and adjust their trading strategy accordingly.
- Improved trading performance: By using the calculator, investors can optimize their trading performance and make more profitable trades.
Limitations of the Calculator
While the Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is a useful tool, it does have some limitations. For example, it does not take into account market volatility or unforeseen events that may affect the price of the security. Additionally, the calculator assumes that the investor will be able to buy back the security at the predicted price, which may not always be the case.
Best Practices for Using the Calculator
To get the most out of the Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator, investors should follow best practices, such as:
- Using accurate data: Enter accurate and up-to-date data into the calculator to ensure accurate calculations.
- Considering multiple scenarios: Use the calculator to consider multiple scenarios and potential outcomes to make more informed decisions.
- Combining with other tools: Use the calculator in combination with other trading tools and strategies to optimize trading performance.
How do you calculate profit from short selling?
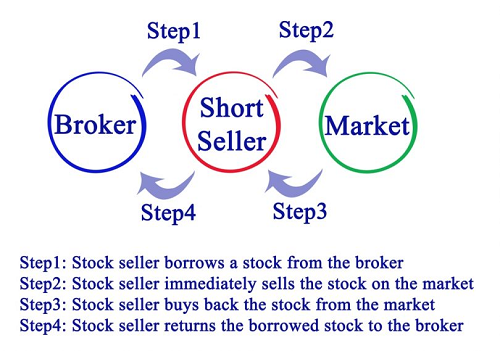
To calculate profit from short selling, you need to understand the mechanics of short selling and how it generates profits. Short selling involves borrowing shares of a stock from a broker or another investor, selling them at the current market price, and then buying them back at a lower price to return to the lender. The profit is made from the difference between the selling price and the buying price.
Understanding Short Selling Transactions
To calculate profit from short selling, it's essential to understand the short selling transaction process. This involves borrowing shares, selling them at the current market price, and then buying them back at a lower price. The key to making a profit is to ensure that the buying price is lower than the selling price. Here are the steps involved:
- The short seller borrows shares from a broker or another investor.
- The short seller sells the borrowed shares at the current market price.
- The short seller buys back the shares at a lower price to return to the lender.
Calculating Profit from Short Selling
The profit from short selling is calculated by subtracting the buying price from the selling price. The formula for calculating profit is: Profit = Selling Price - Buying Price. For example, if you sell a stock short at $50 and buy it back at $40, your profit would be $10. Here are the key factors to consider:
- The selling price is the price at which you sell the borrowed shares.
- The buying price is the price at which you buy back the shares.
- The profit is the difference between the selling price and the buying price.
Risks Involved in Short Selling
Short selling involves significant risks, including the potential for unlimited losses. If the stock price rises instead of falls, the short seller will incur a loss. Additionally, short sellers may be subject to margin calls if the stock price rises, which can result in the short seller being forced to buy back the shares at a higher price. Here are some risks to consider:
- The stock price may rise instead of fall, resulting in a loss.
- The short seller may be subject to margin calls if the stock price rises.
- The loss can be unlimited if the stock price continues to rise.
Short Selling Strategies
There are several short selling strategies that investors use to maximize profits and minimize losses. These strategies include identifying overvalued stocks, using technical analysis, and setting stop-loss orders. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Identify overvalued stocks that are likely to decline in price.
- Use technical analysis to identify trends and patterns in the stock price.
- Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if the stock price rises.
Regulations and Restrictions on Short Selling
There are regulations and restrictions on short selling in many countries, including the United States. These regulations are designed to prevent manipulation and abuse of the short selling process. Here are some regulations to consider:
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates short selling in the United States.
- Short selling restrictions may be imposed during times of market volatility.
- Disclosure requirements may apply to short sellers, including the identity of the short seller and the amount of shares sold short.
How loss of profit is calculated on short sales?

The calculation of loss of profit on short sales involves determining the difference between the expected profit and the actual profit. This difference is then used to calculate the loss of profit. The expected profit is calculated based on the sales price and the cost of goods sold, while the actual profit is calculated based on the short sale price and the cost of goods sold. The loss of profit is then calculated as the difference between the expected profit and the actual profit.
Understanding Short Sales
To calculate the loss of profit on short sales, it is essential to understand what short sales are. Short sales occur when a seller sells a product or asset that they do not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to make a profit. The loss of profit on short sales can be significant if the seller is unable to buy back the product or asset at a lower price. Some key points to consider when understanding short sales include:
- The seller does not own the product or asset being sold.
- The seller expects to buy back the product or asset at a lower price.
- The loss of profit can be significant if the seller is unable to buy back the product or asset at a lower price.
Calculating Expected Profit
The expected profit is calculated based on the sales price and the cost of goods sold. The sales price is the price at which the product or asset is sold, and the cost of goods sold is the cost of producing or acquiring the product or asset. The expected profit is calculated as the difference between the sales price and the cost of goods sold. Some key points to consider when calculating the expected profit include:
- The sales price is the price at which the product or asset is sold.
- The cost of goods sold is the cost of producing or acquiring the product or asset.
- The expected profit is calculated as the difference between the sales price and the cost of goods sold.
Calculating Actual Profit
The actual profit is calculated based on the short sale price and the cost of goods sold. The short sale price is the price at which the product or asset is sold in a short sale, and the cost of goods sold is the cost of producing or acquiring the product or asset. The actual profit is calculated as the difference between the short sale price and the cost of goods sold. Some key points to consider when calculating the actual profit include:
- The short sale price is the price at which the product or asset is sold in a short sale.
- The cost of goods sold is the cost of producing or acquiring the product or asset.
- The actual profit is calculated as the difference between the short sale price and the cost of goods sold.
Determining Loss of Profit
The loss of profit is determined by calculating the difference between the expected profit and the actual profit. This difference represents the loss of profit due to the short sale. Some key points to consider when determining the loss of profit include:
- The loss of profit is calculated as the difference between the expected profit and the actual profit.
- The difference represents the loss of profit due to the short sale.
- The loss of profit can be significant if the seller is unable to buy back the product or asset at a lower price.
Minimizing Loss of Profit
To minimize the loss of profit on short sales, it is essential to carefully consider the risks and rewards of short selling. This includes conducting thorough research, setting realistic expectations, and monitoring market trends. Some key points to consider when minimizing the loss of profit include:
- Conducting thorough research to understand the market and the product or asset being sold.
- Setting realistic expectations for the short sale.
- Monitoring market trends to adjust the short sale strategy as needed.
How can I calculate my profit or loss after selling stock?
To calculate your profit or loss after selling stock, you need to know the purchase price and the selling price of the stock, as well as any fees associated with the transaction. The profit or loss is calculated by subtracting the purchase price and any fees from the selling price. For example, if you sell a stock for $100 that you purchased for $80, and you paid a $5 fee to buy and sell the stock, your profit would be $15.
Understanding Stock Transactions
To calculate your profit or loss, it's essential to understand the different types of stock transactions, including buy and sell orders. Here are some key points to consider:
- Purchase price: The price you pay to buy a stock, including any fees associated with the transaction.
- Selling price: The price you receive when you sell a stock, minus any fees associated with the transaction.
- Fees: Commissions, brokerage fees, and other charges that can affect your !profit or loss.
Calculating Profit and Loss
Calculating your profit or loss involves subtracting the purchase price and any fees from the selling price. Here are the steps:
- Determine the purchase price and any fees associated with buying the stock.
- Determine the selling price and any fees associated with selling the stock.
- Subtract the purchase price and any fees from the selling price to calculate your profit or loss.
Impact of Fees on Profit and Loss
Fees can have a significant impact on your profit or loss, especially if you're buying and selling stock frequently. Here are some key points to consider:
- Commission fees: Brokers may charge a fee for each trade, which can eat into your profit.
- Management fees: Some investment accounts may charge a management fee, which can affect your profit or loss.
- Other fees: Transfer fees, maintenance fees, and other charges can also impact your profit or loss.
Tax Implications of Profit and Loss
The tax implications of your profit or loss can be significant, especially if you're selling stock at a gain. Here are some key points to consider:
- Capital gains tax: You may be subject to capital gains tax on your profit, which can reduce your return.
- Tax deductions: You may be able to claim a tax deduction for your loss, which can reduce your tax liability.
- Tax planning: It's essential to consider the tax implications of your profit or loss and plan accordingly.
Using Financial Tools to Track Profit and Loss
There are many financial tools available to help you track your profit and loss, including spreadsheets, accounting software, and investment apps. Here are some key points to consider:
- Spreadsheets: You can use spreadsheets to track your stock transactions and calculate your profit or loss.
- Accounting software: Accounting software can help you track your stock transactions and generate financial reports.
- Investment apps: Investment apps can provide you with real-time market data and help you track your profit or loss.
How do you make money if you short sell a stock?
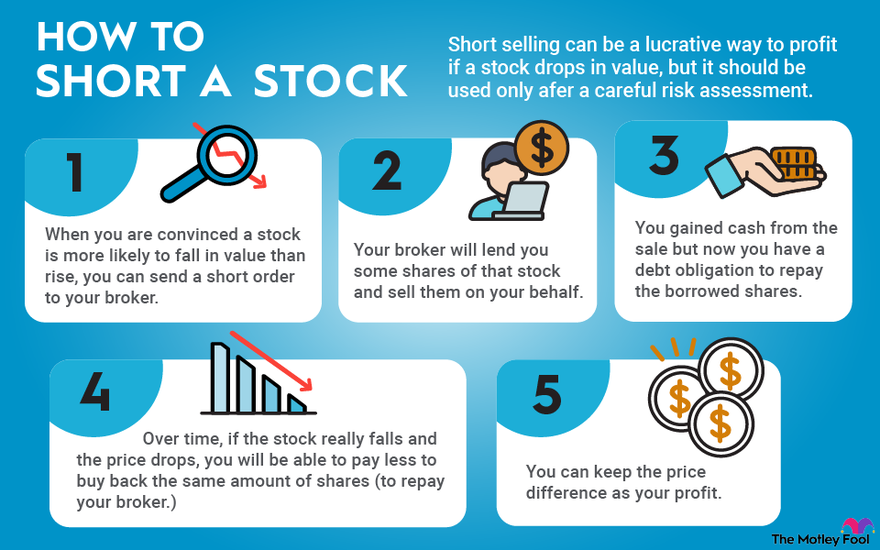
When you short sell a stock, you are essentially betting that the price of the stock will go down. To make money from a short sale, you need to sell the stock at a higher price than you buy it back for. Here's how it works: you borrow a certain number of shares of the stock from a broker or another investor, and then you sell those shares at the current market price. Then, you wait for the price of the stock to fall, and when it does, you buy back the same number of shares at the lower price. You then return the shares to the lender and keep the difference between the selling price and the buying price as your profit.
Understanding the Short Selling Process
The short selling process involves several steps, including researching the stock, borrowing the shares, selling the shares, waiting for the price to fall, and buying back the shares. To make money from a short sale, you need to have a good understanding of the market trends and the company's financials. Here are some key points to consider:
- The short interest in a stock can indicate the number of shares that have been sold short, which can affect the stock's price.
- The short squeeze can occur when a large number of short sellers try to cover their positions at the same time, which can drive up the stock's price.
- The margin requirements for short selling can be higher than for buying stocks, which can increase the risk of losses.
Risks and Rewards of Short Selling
Short selling can be a high-risk strategy, as there is no limit to the potential losses. If the stock price rises instead of falls, you could lose a significant amount of money. However, if you are able to time the market correctly and the stock price falls, you can make a substantial profit. Here are some key points to consider:
- The unlimited potential losses can make short selling a risky strategy, especially for inexperienced investors.
- The high margin requirements can increase the cost of short selling, which can reduce the potential profits.
- The short selling fees can add up quickly, which can eat into your profits.
Short Selling Strategies
There are several short selling strategies that you can use to make money from a short sale. One popular strategy is to short sell stocks with poor fundamentals, such as a high debt-to-equity ratio or a low return on equity. Another strategy is to short sell stocks with overvalued prices, which can be indicated by a high price-to-earnings ratio. Here are some key points to consider:
- The fundamental analysis can help you identify stocks with poor fundamentals that may be overvalued.
- The technical analysis can help you identify trends and patterns in the stock's price movement.
- The market sentiment can affect the stock's price, which can be indicated by sentiment indicators such as put-call ratios.
Short Selling Regulations
There are several regulations that govern short selling, including the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rules. The SEC requires that short sellers disclose their short positions and short interest in certain stocks. Additionally, there are circuit breakers in place to prevent excessive short selling, which can destabilize the market. Here are some key points to consider:
- The SEC rules require short sellers to disclose their short positions and short interest in certain stocks.
- The circuit breakers can halt trading in a stock if the price falls by a certain percentage, which can prevent excessive short selling.
- The short selling restrictions can be imposed by exchanges or regulators to prevent market manipulation.
Best Practices for Short Selling
To make money from a short sale, you need to have a solid understanding of the market trends and the company's financials. You also need to have a disciplined approach to risk management, which includes setting stop-loss orders and monitoring your positions. Here are some key points to consider:
- The risk management is crucial to minimizing losses and maximizing profits.
- The stop-loss orders can help you limit losses if the stock price rises instead of falls.
- The position sizing can help you manage risk and increase potential profits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator?
The purpose of a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is to help investors and traders calculate the potential profit or loss from a short selling transaction. Short selling is a trading strategy where an investor sells a security they do not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. The calculator takes into account the initial stock price, the short selling price, and the buyback price to calculate the profit or loss. This tool is essential for investors who want to mitigate risks and make informed decisions when engaging in short selling activities. By using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator, investors can quickly and easily calculate the potential outcomes of their trades and adjust their strategies accordingly.
How does a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator work?
A Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator works by using a formula to calculate the profit or loss from a short selling transaction. The formula takes into account the initial stock price, the short selling price, and the buyback price. The calculator first calculates the difference between the short selling price and the buyback price, and then multiplies this difference by the number of shares sold short. The result is the profit or loss from the transaction. The calculator can also take into account fees and commissions associated with the trade, as well as taxes and other expenses. By using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator, investors can quickly and easily calculate the potential outcomes of their trades and make informed decisions about their investment strategies. The calculator is typically user-friendly and requires only a few inputs to calculate the profit or loss.
What are the benefits of using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator?
The benefits of using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator are numerous. One of the main benefits is that it helps investors to mitigate risks associated with short selling. By calculating the potential profit or loss from a trade, investors can make informed decisions about whether to engage in a particular trade. The calculator also helps investors to set realistic expectations about their potential returns and to manage their expectations accordingly. Additionally, a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator can help investors to identify potential pitfalls and to avoid costly mistakes. By using a calculator, investors can also save time and reduce stress associated with calculating profits and losses manually. Overall, a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is a valuable tool for investors who want to maximize their returns and minimize their risks.
Can a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator be used for other types of trades?
While a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator is specifically designed for short selling transactions, it can also be used for other types of trades. For example, investors can use the calculator to calculate the profit or loss from a long position or from a options trade. The calculator can also be used to calculate the break-even point for a trade, which is the point at which the profit or loss from the trade is zero. Additionally, investors can use the calculator to calculate the return on investment (ROI) for a trade, which is the profit or loss from the trade divided by the initial investment. By using a Simple Stock Short Selling Profit and Loss Calculator in a flexible and creative way, investors can gain a better understanding of their trades and make more informed decisions about their investment strategies. However, it's essential to note that the calculator is primarily designed for short selling transactions, and investors should use it in conjunction with other tools and resources to get a complete picture of their trades.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas