Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator
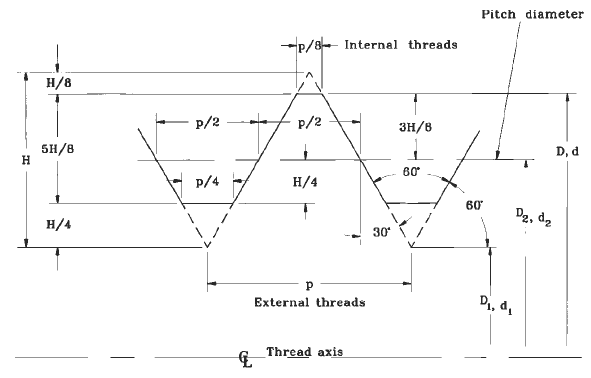
The Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter is a critical parameter in the design and specification! of threaded fasteners. It is defined as the diameter of the circle that passes through the thread peaks, which is essential for ensuring proper fit and function. The equation to calculate this diameter is based on the thread pitch and the number of threads per inch. This article provides an overview of the equation and offers a calculator tool to simplify the calculation process for engineers and designers working with threaded fasteners. The equation is straightforward but requires careful consideration.
- Understanding the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator
- What is the formula for thread pitch diameter?
- How to calculate pitch circle diameter?
- What is the formula for pitch of a fastener?
- What is the formula for calculating tpi?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and how is it used in engineering applications?
- How does the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Calculator work, and what are its advantages over manual calculations?
- What are the key factors that affect the accuracy of the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation, and how can they be controlled?
- How can the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator be applied in real-world engineering applications, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries?
Understanding the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator
The fastener thread pitch circle diameter equation and calculator are essential tools in the field of engineering, particularly in the design and manufacturing of fasteners. The pitch circle diameter is the diameter of the circle that passes through the threads of a fastener, and it is a critical parameter in determining the strength and stability of the fastener. The equation for calculating the pitch circle diameter is based on the thread pitch and the number of threads.
Introduction to Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter
The fastener thread pitch circle diameter is a fundamental concept in the design of fasteners. It is the diameter of the circle that passes through the threads of a fastener, and it is used to determine the stress and strain on the fastener. The pitch circle diameter is calculated using the thread pitch and the number of threads. The thread pitch is the distance between two adjacent threads, and it is typically measured in inches or millimeters.
Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation
The equation for calculating the fastener thread pitch circle diameter is as follows:
Pitch Circle Diameter = (Thread Pitch x Number of Threads) / (2 x π)
This equation is used to calculate the pitch circle diameter of a fastener, given the thread pitch and number of threads. The π symbol represents the mathematical constant pi, which is approximately equal to 3.14159.
Calculator for Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter
A calculator for fastener thread pitch circle diameter is a useful tool for engineers and designers. It allows them to quickly and easily calculate the pitch circle diameter of a fastener, given the thread pitch and number of threads. The calculator can be used to determine the strength and stability of the fastener, as well as to optimize the design of the fastener.
Applications of Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter
The fastener thread pitch circle diameter has a number of applications in the field of engineering. It is used to determine the stress and strain on a fastener, as well as to optimize the design of the fastener. The pitch circle diameter is also used to calculate the torque required to tighten or loosen a fastener. The applications of the fastener thread pitch circle diameter include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Used to determine the strength and stability of fasteners in aircraft and spacecraft |
| Automotive | Used to optimize the design of fasteners in vehicles |
| Construction | Used to determine the stress and strain on fasteners in buildings and bridges |
| Industrial | Used to optimize the design of fasteners in machinery and equipment |
| Medical | Used to determine the strength and stability of fasteners in medical devices |
Importance of Accurate Calculation of Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter
The accurate calculation of the fastener thread pitch circle diameter is critical in the design and manufacturing of fasteners. An inaccurate calculation can result in a fastener that is weak or unstable, which can lead to failure and injury. The importance of accurate calculation of the fastener thread pitch circle diameter cannot be overstated, and it is essential that engineers and designers use reliable and accurate methods to calculate the pitch circle diameter.
What is the formula for thread pitch diameter?
The formula for thread pitch diameter is: D = (Major Diameter - (1 / (2 threads per inch))) or D = (Major Diameter - (0.5 / threads per inch)). This formula is used to calculate the diameter of a thread at a point where the thread is in contact with a nut or other mating part.
Understanding Thread Pitch Diameter
The thread pitch diameter is an important parameter in the design and manufacture of screw threads. It is the diameter of the thread at a point where the thread is in contact with a nut or other mating part. To calculate the thread pitch diameter, you need to know the major diameter and the threads per inch. The formula involves subtracting a fraction of the major diameter to account for the thread depth. Here are the key factors:
- Major Diameter: The largest diameter of the thread.
- Threads per Inch: The number of threads per inch of thread length.
- Thread Depth: The depth of the thread, which affects the pitch diameter.
Calculating Thread Pitch Diameter
To calculate the thread pitch diameter, you can use the formula: D = (Major Diameter - (1 / (2 threads per inch))) or D = (Major Diameter - (0.5 / threads per inch)). This formula takes into account the thread depth and the threads per inch to calculate the pitch diameter. It is essential to use the correct units and to ensure that the threads per inch are correctly counted. Here are the steps to follow:
- Measure the major diameter of the thread.
- Count the threads per inch of the thread.
- Apply the formula using the correct units.
Importance of Thread Pitch Diameter
The thread pitch diameter is crucial in ensuring that mating parts fit together properly. A correct pitch diameter ensures that the thread engages correctly with the nut or other mating part, providing a secure and reliable connection. An incorrect pitch diameter can result in a poor fit, leading to leakage, wear, or even failure of the joint. Here are the key benefits:
- Secure Connection: A correct pitch diameter ensures a secure connection between mating parts.
- Reliable Performance: A correct pitch diameter ensures reliable performance of the joint.
- Reduced Maintenance: A correct pitch diameter reduces the need for maintenance and repair.
Thread Pitch Diameter Measurement
Measuring the thread pitch diameter requires precision instruments, such as micrometers or calipers. It is essential to use the correct measurement technique to ensure accurate results. The measurement should be taken at the point where the thread is in contact with the nut or other mating part. Here are the key considerations:
- Precision Instruments: Use precision instruments, such as micrometers or calipers.
- Measurement Technique: Use the correct measurement technique to ensure accurate results.
- Measurement Point: Measure at the point where the thread is in contact with the nut or other mating part.
Thread Pitch Diameter Standards
The thread pitch diameter is governed by industry standards, such as ISO or ASME. These standards specify the tolerances and limits for thread pitch diameter to ensure interchangeability and compatibility between mating parts. Here are the key standards:
- ISO Standards: ISO standards specify the tolerances and limits for thread pitch diameter.
- ASME Standards: ASME standards specify the tolerances and limits for thread pitch diameter.
- Industry Standards: Industry standards ensure interchangeability and compatibility between mating parts.
How to calculate pitch circle diameter?

To calculate the pitch circle diameter, you need to understand the concept of gear geometry and the relationship between the number of teeth, pitch, and diameter. The pitch circle diameter is the distance between the centers of two adjacent teeth on a gear, and it is a critical parameter in determining the gear ratio and torque transmission. The calculation involves using the pitch and number of teeth to find the diameter of the pitch circle.
Understanding Pitch Circle Diameter
The pitch circle diameter is a crucial parameter in gear design, as it affects the gear ratio, efficiency, and noise characteristics of the gear set. To calculate the pitch circle diameter, you need to know the pitch and number of teeth. The pitch is the distance between two adjacent teeth, and the number of teeth is the total number of teeth on the gear. The formula to calculate the pitch circle diameter is: pitch circle diameter = (number of teeth x pitch) / π.
- Determine the number of teeth on the gear.
- Measure the pitch of the gear.
- Calculate the pitch circle diameter using the formula.
Importance of Pitch Circle Diameter in Gear Design
The pitch circle diameter plays a vital role in gear design, as it affects the gear ratio, efficiency, and noise characteristics of the gear set. A smaller pitch circle diameter results in a higher gear ratio, which can increase the torque output but may also increase the noise level. On the other hand, a larger pitch circle diameter results in a lower gear ratio, which can decrease the torque output but may also reduce the noise level.
- Determine the required gear ratio.
- Calculate the pitch circle diameter based on the gear ratio.
- Consider the noise and efficiency implications of the pitch circle diameter.
Calculation Methods for Pitch Circle Diameter
There are several methods to calculate the pitch circle diameter, including the direct calculation method, graphical method, and computer-aided design (CAD) method. The direct calculation method involves using the formula: pitch circle diameter = (number of teeth x pitch) / π. The graphical method involves drawing a diagram of the gear and measuring the pitch circle diameter. The CAD method involves using software to design and analyze the gear.
- Choose the calculation method.
- Enter the input values (number of teeth and pitch).
- Calculate the pitch circle diameter.
Common Applications of Pitch Circle Diameter
The pitch circle diameter has various applications in mechanical engineering, including gear design, gear manufacturing, and gear analysis. In gear design, the pitch circle diameter is used to determine the gear ratio and torque output. In gear manufacturing, the pitch circle diameter is used to machine the gear teeth. In gear analysis, the pitch circle diameter is used to analyze the noise and efficiency characteristics of the gear set.
- Identify the application of the pitch circle diameter.
- Determine the required precision of the pitch circle diameter.
- Calculate the pitch circle diameter using the chosen method.
Limitations and Challenges of Pitch Circle Diameter Calculation
The calculation of the pitch circle diameter has several limitations and challenges, including measurement errors, manufacturing tolerances, and complex gear geometries. Measurement errors can occur when measuring the number of teeth and pitch. Manufacturing tolerances can affect the accuracy of the pitch circle diameter. Complex gear geometries can make it difficult to calculate the pitch circle diameter.
- Identify the potential limitations and challenges.
- Develop a strategy to overcome the limitations and challenges.
- Use advanced calculation methods or software to improve accuracy.
What is the formula for pitch of a fastener?

The formula for pitch of a fastener is the distance between two adjacent threads, measured in a straight line parallel to the axis of the fastener. It is an important parameter in determining the thread characteristics of a fastener, such as screws, bolts, and nuts. The pitch can be calculated using the formula: pitch = 1 / threads per inch (TPI), where TPI is the number of threads per inch.
Importance of Pitch in Fasteners
The pitch of a fastener is crucial in determining its strength and durability. A coarse pitch fastener has a larger thread spacing, which can provide a stronger grip and better resistance to vibration and loosening. On the other hand, a fine pitch fastener has a smaller thread spacing, which can provide a smoother surface finish and better precision. Some of the key points to consider when selecting a fastener based on its pitch are:
- The application of the fastener, including the type of material it will be used with and the environmental conditions it will be exposed to.
- The required strength of the fastener, including the tensile strength and shear strength.
- The desired level of precision, including the thread accuracy and surface finish.
Types of Pitch in Fasteners
There are two main types of pitch in fasteners: coarse pitch and fine pitch. Coarse pitch fasteners have a larger thread spacing, typically ranging from 1/4 inch to 1 inch, and are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as construction and manufacturing. Fine pitch fasteners have a smaller thread spacing, typically ranging from 1/16 inch to 1/4 inch, and are often used in precision applications, such as electronics and aerospace. Some of the key characteristics of each type of pitch are:
- Coarse pitch: larger thread spacing, stronger grip, and better resistance to vibration and loosening.
- Fine pitch: smaller thread spacing, smoother surface finish, and better precision.
- Standard pitch: a balance between coarse and fine pitch, offering a compromise between strength and precision.
Factors Affecting Pitch in Fasteners
Several factors can affect the pitch of a fastener, including the material it is made of, the manufacturing process, and the environmental conditions it will be exposed to. For example, temperature and humidity can cause expansion and contraction of the fastener, affecting its pitch and thread accuracy. Some of the key factors to consider when selecting a fastener based on its pitch are:
- The thermal expansion of the fastener, including the coefficient of thermal expansion.
- The corrosion resistance of the fastener, including the material and coatings used.
- The mechanical properties of the fastener, including the tensile strength and yield strength.
Measurement of Pitch in Fasteners
The pitch of a fastener can be measured using various techniques, including thread gauges, micrometers, and optical comparators. The most common method of measurement is using a thread gauge, which is a precision instrument that measures the thread spacing and thread accuracy of the fastener. Some of the key points to consider when measuring the pitch of a fastener are:
- The accuracy of the measurement instrument, including the resolution and repeatability.
- The calibration of the measurement instrument, including the certification and traceability.
- The procedure for measuring the pitch, including the sampling plan and data analysis.
Applications of Pitch in Fasteners
The pitch of a fastener has various applications in different industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics. For example, in aerospace, the pitch of a fastener is critical in ensuring the structural integrity of aircraft and spacecraft. In construction, the pitch of a fastener is important in ensuring the strength and durability of buildings and bridges. Some of the key applications of pitch in fasteners are:
- Aerospace: critical in ensuring the structural integrity of aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: important in ensuring the strength and durability of vehicles.
- Construction: critical in ensuring the strength and durability of buildings and bridges.
What is the formula for calculating tpi?

The formula for calculating Threads Per Inch (TPI) is: TPI = 1 / pitch, where pitch is the distance between threads. This formula is used to calculate the number of threads per inch of a screw or bolt. The TPI value is an important factor in determining the strength and stability of a threaded joint.
Understanding Threads Per Inch (TPI)
Threads Per Inch (TPI) is a measure of the density of threads on a screw or bolt. A higher TPI value indicates a finer thread, while a lower TPI value indicates a coarser thread. The following are some key points to understand about TPI:
- The TPI value is typically measured in units of threads per inch.
- The TPI value can range from 2 to 64 or more, depending on the application.
- A higher TPI value can provide a stronger grip and better resistance to stripping.
Importance of TPI in Screw Design
The TPI value is a critical factor in screw design, as it affects the strength and stability of the threaded joint. A TPI value that is too low can result in a weak joint, while a TPI value that is too high can result in a joint that is prone to stripping. The following are some key considerations for TPI in screw design:
- The TPI value must be compatible with the material being used.
- The TPI value must be suitable for the application and load requirements.
- The TPI value can affect the ease of assembly and disassembly.
Calculating TPI for Different Materials
The TPI value can vary depending on the material being used. For example, steel and aluminum have different TPI values due to their different properties. The following are some key points to consider when calculating TPI for different materials:
- The TPI value for steel is typically higher than for aluminum.
- The TPI value for plastics can be lower than for metals.
- The TPI value can be affected by the surface finish and coating of the material.
TPI and Screw Strength
The TPI value is closely related to the strength of a screw or bolt. A higher TPI value can provide a stronger grip and better resistance to stripping. The following are some key points to consider when evaluating the relationship between TPI and screw strength:
- A higher TPI value can result in a stronger joint.
- A lower TPI value can result in a weaker joint.
- The TPI value can affect the fatigue life of a screw or bolt.
Applications of TPI in Industry
The TPI value has a wide range of applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. The following are some key points to consider when evaluating the applications of TPI:
- The TPI value is critical in aerospace applications where strength and stability are paramount.
- The TPI value is important in automotive applications where reliability and durability are essential.
- The TPI value can affect the cost and efficiency of construction projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and how is it used in engineering applications?
The Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation is a mathematical formula used to calculate the diameter of the pitch circle of a threaded fastener, such as a screw or a bolt. This equation is essential in engineering applications, particularly in the design and manufacture of mechanical components that require threaded connections. The pitch circle diameter is the diameter of the circle that passes through the threads of the fastener, and it is a critical parameter in determining the thread engagement, which is the distance that the threads of the fastener engage with the threads of the mating component. The equation takes into account the nominal diameter of the fastener, the thread pitch, and the thread angle, and it provides a precise calculation of the pitch circle diameter, which is necessary for ensuring proper thread fit and assembly of the components.
How does the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Calculator work, and what are its advantages over manual calculations?
The Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Calculator is a software tool that uses the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation to calculate the pitch circle diameter of a threaded fastener. This calculator works by inputting the nominal diameter, thread pitch, and thread angle of the fastener, and then it calculates the pitch circle diameter using the equation. The advantages of using this calculator over manual calculations are numerous. Firstly, it saves time and reduces errors, as manual calculations can be prone to mistakes and are often time-consuming. Secondly, it increases accuracy, as the calculator uses a precise algorithm to calculate the pitch circle diameter. Thirdly, it improves efficiency, as engineers can quickly and easily calculate the pitch circle diameter for multiple fasteners, which is essential in design optimization and parameterization. Finally, it enhances collaboration, as the calculator provides a standardized method for calculating the pitch circle diameter, which can be shared and communicated among team members.
What are the key factors that affect the accuracy of the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation, and how can they be controlled?
The accuracy of the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation is affected by several key factors, including the nominal diameter, thread pitch, and thread angle of the fastener. These factors must be carefully controlled to ensure accurate calculations. The nominal diameter of the fastener must be precisely measured, as small variations can significantly affect the calculation. The thread pitch and thread angle must also be accurately specified, as these parameters determine the thread geometry and engagement. Additionally, the material properties of the fastener and the mating component, such as the coefficient of friction and yield strength, can also impact the accuracy of the calculation. To control these factors, engineers can use dimensional tolerancing and geometric dimensioning to ensure precise measurement and specification of the fastener dimensions. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis can be performed to determine the impact of variations in these factors on the calculation, and tolerance stacking can be used to account for the cumulative effect of these variations.
How can the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator be applied in real-world engineering applications, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries?
The Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator can be applied in various real-world engineering applications, particularly in the aerospace and automotive industries, where threaded connections are critical to the safety and performance of the components. In the aerospace industry, for example, the equation and calculator can be used to design and optimize the threaded fasteners used in aircraft structures, such as the fuselage and wings. In the automotive industry, the equation and calculator can be used to design and optimize the threaded fasteners used in engine components, such as the cylinder head and block. The equation and calculator can also be used in other industries, such as the construction and manufacturing industries, where threaded connections are used in building structures and machinery. By applying the Fastener Thread Pitch Circle Diameter Equation and Calculator, engineers can ensure that the threaded connections are properly designed and optimized, which is critical to the safety, performance, and reliability of the components and systems.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas