Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator

The Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator is a valuable tool for engineers and technicians working with threaded fasteners. It calculates the required torque to achieve a specified bolt tension, taking into account the thread pitch and other factors. This calculator helps ensure that bolts are properly tightened, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring safety. By using this calculator, users can determine the optimal torque values for their specific applications, reducing the risk of over-tightening or under-tightening. Accurate calculations are crucial in various industries, including construction and manufacturing.
- Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
- How do you calculate thread tightening torque?
- Does thread pitch affect torque?
- What is the formula for threaded torque?
- How do you calculate the torque of a bolt from an angle?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator and how does it work?
- What are the key factors that affect the calculation of bolt torque from thread pitch?
- How accurate is the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator and what are its limitations?
- What are the benefits of using the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator in engineering and construction applications?
Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator is a tool used to calculate the torque required to tighten or loosen a bolt based on its thread pitch. This calculator is essential in various industries, including construction, automotive, and aerospace, where bolts and fasteners play a critical role in ensuring the structural integrity of buildings, vehicles, and equipment.
What is Thread Pitch and How Does it Affect Torque?
Thread pitch refers to the distance between two consecutive threads on a bolt or screw. The thread pitch affects the torque required to tighten or loosen a bolt because it determines the friction between the threads. A coarse thread pitch requires less torque than a fine thread pitch because there is less friction between the threads.
How to Use a Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator
To use a Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator, you need to input the bolt diameter, thread pitch, and material of the bolt. The calculator then uses a formula to calculate the required torque. The formula takes into account the friction coefficient of the bolt material and the thread pitch.
Factors that Affect Bolt Torque
Several factors affect the torque required to tighten or loosen a bolt, including:
Bolt material: Different materials have different friction coefficients, which affect the required torque.
Thread pitch: As mentioned earlier, thread pitch affects the friction between the threads.
Lubrication: Lubrication can reduce the friction between the threads, reducing the required torque.
Temperature: Temperature can affect the friction coefficient of the bolt material, which in turn affects the required torque.
| Bolt Material | Friction Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Steel | 0.1-0.2 |
| Aluminum | 0.05-0.1 |
| Copper | 0.05-0.1 |
Benefits of Using a Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator
Using a Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator offers several benefits, including:
Accuracy: The calculator provides an accurate calculation of the required torque, reducing the risk of over-tightening or under-tightening.
Efficiency: The calculator saves time and effort by providing a quick and easy way to calculate the required torque.
Safety: The calculator helps ensure the structural integrity of buildings, vehicles, and equipment by providing the correct torque values.
Common Applications of Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculators
Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculators are commonly used in various industries, including:
Construction: To calculate the required torque for bolts used in building construction.
Automotive: To calculate the required torque for bolts used in vehicle assembly.
Aerospace: To calculate the required torque for bolts used in aircraft and spacecraft assembly.
How do you calculate thread tightening torque?
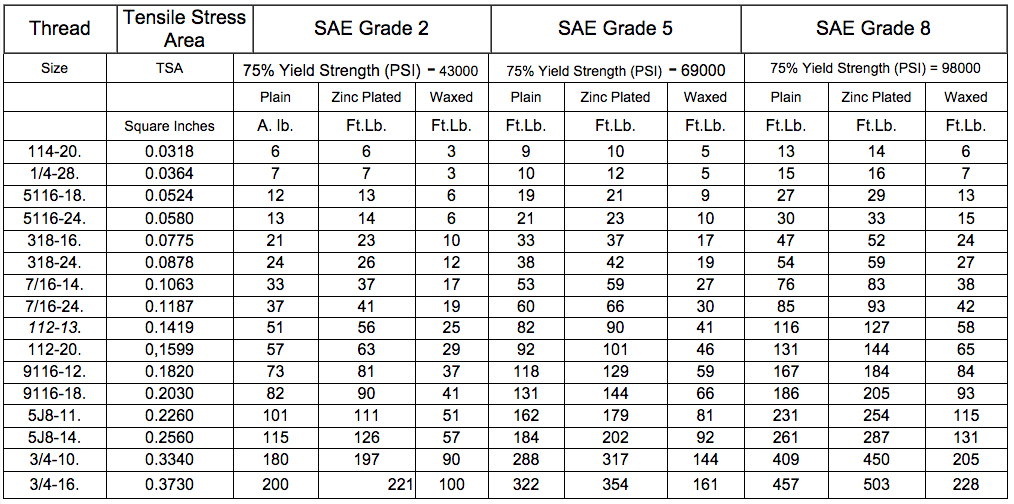
To calculate thread tightening torque, you need to consider several factors, including the bolt material, thread size, and friction coefficients. The torque required to tighten a thread is directly proportional to the bolt diameter and the friction between the bolt and the nut. The formula to calculate the torque is: Torque = (Bolt Diameter x Friction Coefficient x Preload Force) / (2 x Thread Pitch). This formula takes into account the bolt properties, thread geometry, and friction characteristics to determine the required torque.
Understanding the Components of Torque Calculation
To calculate the thread tightening torque, you need to understand the components involved in the calculation. The bolt diameter and thread size are critical in determining the torque required. The friction coefficient between the bolt and the nut also plays a significant role. The preload force is the amount of force applied to the bolt to achieve the desired clamp load. The thread pitch is the distance between two adjacent threads. The calculation involves the following steps:
- Determine the bolt diameter and thread size to calculate the thread area.
- Measure the friction coefficient between the bolt and the nut.
- Calculate the preload force required to achieve the desired clamp load.
Importance of Friction Coefficients in Torque Calculation
The friction coefficients play a crucial role in the torque calculation. The friction coefficient between the bolt and the nut affects the torque required to tighten the thread. A higher friction coefficient requires more torque to achieve the same clamp load. The friction coefficients can vary depending on the bolt material, nut material, and surface finish. The following factors can affect the friction coefficients:
- Bolt material: Different bolt materials have varying friction coefficients.
- Nut material: The nut material can also affect the friction coefficient.
- Surface finish: The surface finish of the bolt and nut can influence the friction coefficient.
Effect of Thread Size on Torque Calculation
The thread size is a critical factor in the torque calculation. The thread size affects the thread area, which in turn affects the torque required. A larger thread size requires more torque to achieve the same clamp load. The following factors can affect the thread size:
- Bolt diameter: The bolt diameter determines the thread size.
- Thread pitch: The thread pitch affects the thread area.
- Thread form: The thread form can influence the thread area and torque required.
Calculating Preload Force for Torque Calculation
The preload force is the amount of force applied to the bolt to achieve the desired clamp load. The preload force is critical in the torque calculation. The following steps can be used to calculate the preload force:
- Determine the desired clamp load.
- Calculate the thread area based on the bolt diameter and thread size.
- Use the thread area and desired clamp load to calculate the preload force.
Applying the Torque Calculation Formula
The torque calculation formula can be applied once the bolt diameter, thread size, friction coefficient, and preload force are determined. The formula is: Torque = (Bolt Diameter x Friction Coefficient x Preload Force) / (2 x Thread Pitch). The following steps can be used to apply the formula:
- Plug in the values for bolt diameter, friction coefficient, preload force, and thread pitch.
- Calculate the torque using the formula.
- Verify the calculated torque is within the recommended torque range for the specific bolt and application.
Does thread pitch affect torque?

The thread pitch of a screw or bolt can have a significant impact on the torque required to tighten or loosen it. The thread pitch refers to the distance between two consecutive threads, and it can affect the friction and effort required to turn the screw or bolt. A finer thread pitch, which means more threads per inch, can increase the torque required to tighten the screw or bolt, as there is more surface area in contact between the threads.
Understanding Thread Pitch and Torque Relationship
The relationship between thread pitch and torque is complex, but it can be understood by considering the mechanics of screw threads. A finer thread pitch can increase the torque required to tighten the screw or bolt, as there is more friction between the threads. This can be beneficial in applications where high torque is required, but it can also make it more difficult to tighten or loosen the screw or bolt.
- The thread pitch affects the torque required to tighten or loosen a screw or bolt.
- A finer thread pitch can increase the torque required to tighten the screw or bolt.
- The friction between the threads is a key factor in determining the torque required.
Factors Influencing Thread Pitch and Torque
Several factors can influence the relationship between thread pitch and torque, including the material of the screw or bolt, the surface finish of the threads, and the lubrication used. A smooth surface finish can reduce the friction between the threads, making it easier to tighten or loosen the screw or bolt. Lubrication can also reduce friction, but it can also reduce the torque required to tighten the screw or bolt.
- The material of the screw or bolt can affect the torque required.
- A smooth surface finish can reduce the friction between the threads.
- Lubrication can reduce friction and make it easier to tighten or loosen the screw or bolt.
Applications Where Thread Pitch Affects Torque
The thread pitch can have a significant impact on the torque required in various applications, including aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. In aerospace applications, high torque is often required to ensure the safety and reliability of the aircraft. A finer thread pitch can provide the high torque required, but it can also make it more difficult to tighten or loosen the screw or bolt.
- Aerospace applications often require high torque to ensure safety and reliability.
- Automotive applications can also benefit from a finer thread pitch.
- Industrial applications often require high torque to ensure the efficiency and productivity of the equipment.
Calculating Thread Pitch and Torque
Calculating the thread pitch and torque required for a specific application can be complex, but it can be done using various formulas and equations. The thread pitch can be calculated using the thread diameter and the number of threads, while the torque required can be calculated using the friction and effort required to turn the screw or bolt.
- The thread pitch can be calculated using the thread diameter and the number of threads.
- The torque required can be calculated using the friction and effort required to turn the screw or bolt.
- Formulas and equations can be used to calculate the thread pitch and torque required.
Best Practices for Working with Thread Pitch and Torque
When working with thread pitch and torque, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure the safety and reliability of the equipment. This includes using the correct tools and techniques to tighten or loosen the screw or bolt, as well as following the recommended torque specifications. Regular maintenance can also help to ensure the efficiency and productivity of the equipment.
- Using the correct tools and techniques is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of the equipment.
- Following the recommended torque specifications is crucial to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Regular maintenance can help to ensure the efficiency and productivity of the equipment.
What is the formula for threaded torque?

The formula for threaded torque is a complex calculation that involves several factors, including the coefficient of friction, thread pitch, and bolt diameter. The formula is: T = (K F d) / 12, where T is the torque, K is the coefficient of friction, F is the force applied, and d is the bolt diameter. This formula is used to calculate the torque required to tighten or loosen a threaded fastener.
Understanding the Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction is a critical factor in calculating threaded torque. It is a measure of the friction between the threaded surfaces and is typically represented by the Greek letter μ (mu). The coefficient of friction can vary depending on the materials and surface finish of the threaded components. The formula for coefficient of friction is: μ = F / N, where F is the force of friction and N is the normal force. Some common values for coefficient of friction are:
- Steel on steel: 0.1-0.2
- Steel on aluminum: 0.1-0.3
- Aluminum on aluminum: 0.1-0.2
Importance of Thread Pitch
The thread pitch is another critical factor in calculating threaded torque. It is the distance between threads and is typically measured in inches or millimeters. The thread pitch affects the torque required to tighten or loosen a threaded fastener. A coarse thread pitch requires less torque than a fine thread pitch. Some common thread pitches are:
- Coarse thread: 1/4-20, 1/2-13
- Fine thread: 1/4-28, 1/2-20
- Extra fine thread: 1/4-32, 1/2-24
Role of Bolt Diameter
The bolt diameter is also an important factor in calculating threaded torque. The bolt diameter affects the torque required to tighten or loosen a threaded fastener. A larger bolt diameter requires more torque than a smaller bolt diameter. Some common bolt diameters are:
- Small diameter: 1/4 inch, 6 mm
- Medium diameter: 1/2 inch, 12 mm
- Large diameter: 1 inch, 24 mm
Calculating Threaded Torque
To calculate threaded torque, you need to know the coefficient of friction, thread pitch, and bolt diameter. You can use the formula: T = (K F d) / 12, where T is the torque, K is the coefficient of friction, F is the force applied, and d is the bolt diameter. Some common values for threaded torque are:
- Low torque: 10-20 ft-lbs
- Medium torque: 20-50 ft-lbs
- High torque: 50-100 ft-lbs
Applications of Threaded Torque
Threaded torque is used in a variety of applications, including mechanical engineering, automotive engineering, and aerospace engineering. It is used to calculate the torque required to tighten or loosen threaded fasteners in machines, vehicles, and aircraft. Some common applications of threaded torque are:
- Engine assembly: calculating torque for engine bolts
- Gearbox assembly: calculating torque for gearbox bolts
- Aircraft assembly: calculating torque for aircraft bolts
How do you calculate the torque of a bolt from an angle?

To calculate the torque of a bolt from an angle, you need to understand the relationship between the angle, force, and distance. The formula for calculating torque is: Torque = Force x Distance. However, when calculating torque from an angle, you need to consider the moment arm, which is the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
Understanding the Moment Arm
The moment arm is a critical component in calculating the torque of a bolt from an angle. The moment arm is the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied, and it is measured perpendicular to the force. To calculate the torque, you need to know the length of the moment arm and the force applied. Here are the steps to calculate the moment arm:
- Measure the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
- Calculate the length of the moment arm using the angle and the distance.
- Use the moment arm and the force to calculate the torque.
Calculating Torque from an Angle
To calculate the torque of a bolt from an angle, you need to use the torque formula: Torque = Force x Distance. However, since you are calculating the torque from an angle, you need to consider the angle between the force and the moment arm. Here are the steps to calculate the torque:
- Measure the angle between the force and the moment arm.
- Calculate the force applied to the bolt.
- Use the torque formula to calculate the torque, considering the angle and the force.
Using the Correct Units
When calculating the torque of a bolt from an angle, it is essential to use the correct units. The units of torque are typically measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lb). The units of force are typically measured in Newtons (N) or pounds (lb), and the units of distance are typically measured in meters (m) or feet (ft). Here are the steps to ensure you are using the correct units:
- Check the units of the force and distance measurements.
- Convert the units to the correct units if necessary.
- Use the correct units in the torque calculation.
Considering Friction and Other Factors
When calculating the torque of a bolt from an angle, it is essential to consider friction and other factors that may affect the calculation. Friction can reduce the torque applied to the bolt, and other factors such as the bolt material and the surface texture can also affect the calculation. Here are some factors to consider:
- Consider the friction coefficient between the bolt and the surface.
- Consider the bolt material and its strength.
- Consider the surface texture and its roughness.
Using Torque Calculators and Software
To simplify the calculation of torque from an angle, you can use torque calculators and software. These tools can help you calculate the torque quickly and accurately, considering the angle, force, and distance. Here are some benefits of using torque calculators and software:
- Torque calculators and software can simplify the calculation process.
- They can provide accurate results, considering the angle, force, and distance.
- They can help you optimize the torque calculation for specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator and how does it work?
The Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator is a tool designed to calculate the required torque for tightening or loosening a bolt based on its thread pitch. This calculator uses the principles of mechanics and engineering to determine the torque required to achieve a specific clamp load. The calculator takes into account the bolt diameter, thread pitch, and coefficient of friction to provide an accurate calculation of the required torque. By using this calculator, users can ensure that their bolts are tightened or loosened to the correct torque specification, which is essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of the assembly or structure.
What are the key factors that affect the calculation of bolt torque from thread pitch?
The calculation of bolt torque from thread pitch is affected by several key factors, including the bolt diameter, thread pitch, coefficient of friction, and clamp load. The bolt diameter and thread pitch determine the thread engagement and the frictional forces that resist the torque. The coefficient of friction is a measure of the frictional forces between the bolt and the nut or material, and it can significantly affect the required torque. The clamp load is the force applied to the bolt to achieve the desired tightening or loosening. These factors are all taken into account by the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator to provide an accurate calculation of the required torque. Additionally, other factors such as the bolt material, surface roughness, and lubrication can also affect the calculation, but they are typically considered secondary factors.
How accurate is the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator and what are its limitations?
The Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator is a highly accurate tool that uses established engineering principles to calculate the required torque. However, like any calculator or tool, it is not without its limitations. The accuracy of the calculator depends on the input values provided by the user, and any errors or inaccuracies in these values can affect the calculated torque. Additionally, the calculator assumes a specific set of conditions, such as a clean and dry thread, and any deviations from these conditions can affect the accuracy of the calculation. The calculator is also limited to calculating torque for standard bolts and threads, and it may not be applicable to custom or specialized fasteners. Furthermore, the calculator does not take into account dynamic loads or fatigue effects, which can be important considerations in certain applications.
What are the benefits of using the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator in engineering and construction applications?
The Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator offers several benefits in engineering and construction applications. One of the primary benefits is increased accuracy, as the calculator provides a precise calculation of the required torque based on the input values. This can help to prevent over-tightening or under-tightening, which can lead to damage or failure of the assembly or structure. The calculator also helps to reduce the risk of injury or accidents caused by loose or over-tightened bolts. Additionally, the calculator can help to improve efficiency and productivity by reducing the time and effort required to determine the correct torque specification. The calculator is also a valuable training tool for engineers and technicians, as it helps to develop a deeper understanding of the principles and concepts involved in bolt tightening and loosening. Overall, the Bolt Torque from Thread Pitch Calculator is a powerful tool that can help to ensure the integrity and safety of assemblies and structures in a wide range of engineering and construction applications.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas