Air Density Equations and Calculator
Air density is a critical factor in various fields, including aerospace, meteorology, and engineering. The density of air is influenced by temperature, pressure, and humidity, making it essential to have accurate equations and calculators to determine its value. This article provides an overview of the most commonly used air density equations, including the ideal gas law and the barometric formula, as well as a calculator to simplify the calculation process. By understanding and applying these equations, professionals can make more accurate predictions and calculations in their respective fields. Accurate air density calculations are crucial for precise results.
- Air Density Equations and Calculator: Understanding the Fundamentals
- What is the formula for air density calculator?
- What is the density of air at 25 C in kg m3?
- What is the density of air at 50 C and 300 kPa?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the key factors that affect air density and how are they used in air density equations?
- How do air density equations and calculators account for the variations in air density with altitude and location?
- What are the limitations and assumptions of air density equations and calculators, and how can they be improved?
- How can air density equations and calculators be applied in real-world scenarios, such as aviation and engineering, to improve safety and performance?
Air Density Equations and Calculator: Understanding the Fundamentals
The air density equations and calculator are essential tools for various fields, including aerospace engineering, meteorology, and aviation. Air density is a critical factor in determining the performance of aircraft, the behavior of weather patterns, and the efficiency of wind turbines. In this section, we will delve into the world of air density equations and calculators, exploring their applications, formulas, and limitations.
Introduction to Air Density Equations
Air density equations are mathematical formulas used to calculate the density of air under different temperature and pressure conditions. The most common equation used to calculate air density is the ideal gas law, which states that the density of air is directly proportional to the pressure and inversely proportional to the temperature. This equation is widely used in various fields, including engineering and scientific research.
Understanding the Air Density Calculator
An air density calculator is a tool used to calculate the density of air based on input parameters such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. These calculators can be found online or in scientific software and are essential for quick calculations and estimations. The air density calculator takes into account various factors that affect air density, including altitude, temperature, and pressure, to provide an accurate calculation of air density.
Applications of Air Density Equations and Calculators
The applications of air density equations and calculators are diverse and widespread. In aerospace engineering, air density is crucial for determining the aerodynamic performance of aircraft and spacecraft. In meteorology, air density is used to predict weather patterns and storm systems. In aviation, air density is essential for flight planning and navigation. The following table highlights some of the key applications of air density equations and calculators:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Aerospace Engineering | Design and development of aircraft and spacecraft |
| Meteorology | Prediction of weather patterns and storm systems |
| Aviation | Flight planning and navigation |
| Wind Energy | Optimization of wind turbine performance |
| Scientific Research | Study of atmospheric conditions and climate change |
Limitations of Air Density Equations and Calculators
While air density equations and calculators are powerful tools, they have limitations. For example, the ideal gas law assumes that air is an ideal gas, which is not always the case. Additionally, air density calculators may not take into account complex factors such as turbulence and atmospheric conditions. Therefore, it is essential to understand the assumptions and limitations of air density equations and calculators to use them effectively.
Future Developments in Air Density Equations and Calculators
The field of air density equations and calculators is constantly evolving, with new research and technological advancements being made regularly. Future developments are expected to include more accurate models of air density, advanced calculators that can handle complex inputs, and integration with other fields such as computer science and data analysis. As the field continues to evolve, we can expect to see new applications and innovations in areas such as sustainable energy and environmental monitoring.
What is the formula for air density calculator?

The formula for an air density calculator is ρ = P / (R T), where ρ is the air density, P is the pressure, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This formula is used to calculate the density of air at a given temperature and pressure.
Understanding the Variables
The variables in the formula are crucial to understanding how to calculate air density. The pressure is typically measured in Pascals (Pa), the gas constant is approximately 287.058 J/(kgK) for dry air, and the temperature is measured in Kelvin (K). To use the formula, one needs to ensure that all units are consistent. Here are the key points to consider:
- The pressure should be measured at the same location as the air density calculation.
- The gas constant may vary depending on the composition of the air, but 287.058 J/(kgK) is a commonly used value for dry air.
- The temperature should be converted to Kelvin by adding 273.15 to the temperature in Celsius.
Applications of Air Density Calculators
Air density calculators have various practical applications in fields such as aviation, engineering, and meteorology. By calculating the air density, one can determine the lift of an aircraft, the efficiency of a wind turbine, or the dispersion of pollutants in the air. Here are some examples of applications:
- Aircraft performance: Air density affects the lift and thrust of an aircraft, so calculating air density is crucial for determining an aircraft's performance.
- Wind turbine efficiency: The air density affects the energy production of wind turbines, so calculating air density is essential for optimizing their performance.
- Pollutant dispersion: Air density affects the dispersion of pollutants in the air, so calculating air density is important for modeling the spread of pollutants.
Factors Affecting Air Density
Several factors can affect air density, including temperature, humidity, and pressure. As the temperature increases, the air density decreases, and as the humidity increases, the air density also decreases. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Temperature: As the temperature increases, the air molecules spread out, decreasing the air density.
- Humidity: As the humidity increases, the air density decreases due to the addition of water vapor, which has a higher molecular weight than dry air.
- Pressure: As the pressure increases, the air density increases due to the compression of air molecules.
Calculating Air Density at High Altitudes
At high altitudes, the air density is lower due to the decrease in pressure and temperature. To calculate air density at high altitudes, one needs to use the barometric formula to calculate the pressure at the given altitude. Here are the steps:
- Calculate the pressure: Use the barometric formula to calculate the pressure at the given altitude.
- Calculate the temperature: Use the lapse rate to calculate the temperature at the given altitude.
- Calculate the air density: Use the formula ρ = P / (R T) to calculate the air density at the given altitude.
Limitations of Air Density Calculators
While air density calculators are useful tools, they have several limitations, including the assumption of dry air and the neglect of turbulence. In reality, the air is not always dry, and turbulence can affect the air density. Here are some limitations to consider:
- Dry air assumption: Air density calculators typically assume dry air, which may not be accurate in humid environments.
- Turbulence: Air density calculators neglect turbulence, which can affect the air density in certain situations.
- Simplifications: Air density calculators often simplify the complex relationships between temperature, humidity, and pressure, which can lead to inaccuracies.
What is the density of air at 25 C in kg m3?
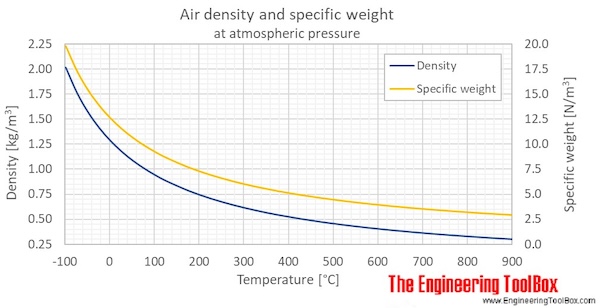
The density of air at 25°C is approximately 1.184 kg/m³. This value can be calculated using the ideal gas law, which states that the density of a gas is equal to its pressure divided by its temperature times the gas constant. The density of air is an important factor in many applications, including aerospace engineering, chemical engineering, and environmental science.
Density of Air at Different Temperatures
The density of air changes with temperature, and it is essential to consider this variation in various applications. At 25°C, the density of air is 1.184 kg/m³, but it decreases to 1.165 kg/m³ at 30°C and increases to 1.204 kg/m³ at 20°C. The following list shows the density of air at different temperatures:
- 20°C: 1.204 kg/m³
- 25°C: 1.184 kg/m³
- 30°C: 1.165 kg/m³
Factors Affecting Air Density
Several factors can influence the density of air, including humidity, pressure, and temperature. An increase in humidity can decrease the density of air, while an increase in pressure can increase the density. The following list shows the factors that affect air density:
- Humidity: increases in humidity decrease air density
- Pressure: increases in pressure increase air density
- Temperature: increases in temperature decrease air density
Calculating Air Density
The density of air can be calculated using the ideal gas law, which states that the density of a gas is equal to its pressure divided by its temperature times the gas constant. The following list shows the steps to calculate air density:
- Find the pressure of the air
- Find the temperature of the air
- Use the ideal gas law to calculate the density
Importance of Air Density in Aerospace Engineering
The density of air is a critical factor in aerospace engineering, as it affects the lift and drag of aircraft. The density of air changes with altitude, and it is essential to consider this variation in the design of aircraft. The following list shows the importance of air density in aerospace engineering:
- Lift: air density affects the lift of aircraft
- Drag: air density affects the drag of aircraft
- Altitude: air density changes with altitude
Applications of Air Density in Environmental Science
The density of air is an essential factor in environmental science, as it affects the dispersion of pollutants in the air. The density of air changes with temperature and humidity, and it is crucial to consider this variation in the modeling of air pollution. The following list shows the applications of air density in environmental science:
- Dispersion modeling: air density affects the dispersion of pollutants
- Air quality modeling: air density affects the air quality modeling
- Climate modeling: air density affects the climate modeling
What is the density of air at 50 C and 300 kPa?
The density of air at 50°C and 300 kPa can be calculated using the ideal gas law, which states that the density of a gas is equal to the pressure divided by the temperature times the gas constant. By plugging in the given values, we can determine that the density of air is approximately 1.1 kg/m³.
Calculating Air Density
To calculate the density of air, we need to know the temperature, pressure, and gas constant. The ideal gas law can be used to calculate the density of air as follows: density = pressure / (temperature gas constant). The temperature is given as 50°C, which needs to be converted to Kelvin, and the pressure is given as 300 kPa. The gas constant for air is approximately 287 J/kg·K. Using these values, we can calculate the density of air.
- The temperature in Kelvin is calculated as 50°C + 273.15 = 323.15 K.
- The pressure is given as 300 kPa, which is equivalent to 300,000 Pa.
- The density of air is then calculated as 300,000 Pa / (323.15 K 287 J/kg·K) = 1.1 kg/m³.
Factors Affecting Air Density
The density of air is affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and humidity. As the temperature increases, the density of air decreases, and as the pressure increases, the density of air also increases. Additionally, the humidity of the air can also affect its density, with higher humidity resulting in lower density. Understanding these factors is important for calculating the density of air in different environments.
- Temperature has a significant impact on air density, with higher temperatures resulting in lower densities.
- Pressure also affects air density, with higher pressures resulting in higher densities.
- Humidity can also impact air density, with higher humidity resulting in lower densities.
Importance of Air Density
The density of air is an important parameter in many fields, including aviation, engineering, and meteorology. In aviation, the density of air affects the performance of aircraft, with lower densities resulting in reduced lift and thrust. In engineering, the density of air is used to calculate the load on structures, such as bridges and buildings. In meteorology, the density of air is used to predict weather patterns and climate conditions.
- Aviation relies on accurate air density calculations to ensure safe and efficient flight operations.
- Engineering applications require air density calculations to design and construct safe and durable structures.
- Meteorology uses air density to predict weather patterns and climate conditions, which is essential for public health and safety.
Methods for Measuring Air Density
There are several methods for measuring the density of air, including the use of barometers, thermometers, and hygrometers. These instruments can be used to measure the pressure, temperature, and humidity of the air, which can then be used to calculate the density. Additionally, modern technologies, such as lidar and radar, can also be used to measure air density.
- Barometers measure the pressure of the air, which is essential for calculating air density.
- Thermometers measure the temperature of the air, which is also necessary for calculating air density.
- Hygrometers measure the humidity of the air, which can affect air density calculations.
Applications of Air Density Calculations
The density of air has many practical applications, including aircraft performance, wind turbine design, and building insulation. By understanding the density of air, engineers and scientists can design and optimize systems and structures to improve efficiency, safety, and performance. Additionally, air density calculations are also used in weather forecasting and climate modeling to predict weather patterns and climate conditions.
- Aircraft performance is affected by air density, which is critical for safe and efficient flight operations.
- Wind turbine design relies on air density calculations to optimize energy production and reducing costs.
- Building insulation can be optimized using air density calculations to improve energy efficiency and reduce heat transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key factors that affect air density and how are they used in air density equations?
Air density is a critical parameter in various fields, including aviation, engineering, and meteorology. The key factors that affect air density are temperature, pressure, and humidity. These factors are used in air density equations to calculate the density of air under different conditions. The temperature of the air is a significant factor, as it affects the molecular motion and spacing of the air molecules. As the temperature increases, the air molecules move faster and spread out, resulting in a decrease in air density. On the other hand, as the temperature decreases, the air molecules slow down and come closer together, resulting in an increase in air density. The pressure of the air is also an essential factor, as it affects the weight of the air molecules. An increase in pressure results in an increase in air density, while a decrease in pressure results in a decrease in air density. Finally, humidity plays a role in air density, as the presence of water vapor in the air affects its molecular weight and spacing.
How do air density equations and calculators account for the variations in air density with altitude and location?
Air density equations and calculators take into account the variations in air density with altitude and location by incorporating atmospheric models and geographic data. The atmospheric models, such as the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) model, provide a standardized representation of the atmospheric conditions at different altitudes and locations. These models account for the changes in temperature, pressure, and humidity with altitude and location, allowing for more accurate calculations of air density. Additionally, geographic data, such as the latitude and longitude of a location, are used to determine the local atmospheric conditions and topography, which can affect air density. By incorporating these factors, air density equations and calculators can provide accurate calculations of air density for a specific location and altitude, taking into account the unique atmospheric conditions and environmental factors.
What are the limitations and assumptions of air density equations and calculators, and how can they be improved?
Air density equations and calculators are based on simplifying assumptions and empirical models, which can limit their accuracy and applicability. One of the main limitations is the assumption of a uniform atmosphere, which does not account for localized variations in temperature, pressure, and humidity. Additionally, air density equations and calculators often rely on average values and standardized models, which may not reflect the actual atmospheric conditions at a specific location and time. To improve the accuracy and reliability of air density equations and calculators, advanced atmospheric models and high-resolution geographic data can be incorporated. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms and data analytics can be used to develop more sophisticated models that account for non-linear relationships and complex interactions between atmospheric variables.
How can air density equations and calculators be applied in real-world scenarios, such as aviation and engineering, to improve safety and performance?
Air density equations and calculators have numerous applications in real-world scenarios, including aviation and engineering. In aviation, accurate calculations of air density are crucial for flight planning, performance optimization, and safety assessment. By using air density equations and calculators, pilots and aviation professionals can determine the optimal flight trajectory, climb rate, and cruise altitude to ensure safe and efficient flight operations. In engineering, air density equations and calculators are used to design and optimize aerodynamic systems, such as wind turbines and aircraft engines. By accounting for the local atmospheric conditions and air density variations, engineers can develop more efficient and reliable systems that meet the required performance standards. Additionally, air density equations and calculators can be used in weather forecasting and climate modeling to improve our understanding of atmospheric dynamics and climate change.
Deja una respuesta


Entradas Relacionadas