Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a valuable tool for engineers and technicians working with threaded fasteners. This calculator determines the tensile stress area of a single thread, which is essential for evaluating the strength and durability of bolts and screws. By inputting the thread diameter, pitch, and other relevant parameters, users can quickly and accurately calculate the tensile stress area, allowing them to make informed decisions about material selection, design, and safety factors. This calculator is a reliable resource for ensuring the integrity of threaded connections. It provides precise calculations and saves time.
-
Understanding the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- Introduction to Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- How to Use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- Benefits of Using the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- Limitations of the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- Applications of the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
- How do you calculate the tensile stress area of a thread?
- What is the tensile stress area of a 1 4 20 bolt?
- What is the tensile area of a threaded rod?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator and how does it work?
- What are the key inputs required to use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator?
- How is the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator used in engineering and design applications?
- What are the benefits of using the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator in comparison to traditional calculation methods?
Understanding the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a tool used to calculate the tensile stress area of a single thread, which is an important parameter in determining the strength and integrity of a threaded connection. This calculator is commonly used in the field of engineering, particularly in the design and analysis of mechanical systems and Structures.
Introduction to Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a software tool that uses a mathematical formula to calculate the tensile stress area of a single thread. The formula takes into account the thread diameter, thread pitch, and thread root radius to determine the tensile stress area. This calculator is essential in designing and analyzing threaded connections, such as bolts and screws, to ensure that they can withstand the expected loads and stresses.
How to Use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
To use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator, the user needs to input the thread diameter, thread pitch, and thread root radius into the calculator. The calculator then uses these inputs to calculate the tensile stress area using a complex mathematical formula. The result is then displayed in a user-friendly format, allowing the user to easily understand the tensile stress area of the single thread.
Benefits of Using the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator offers several benefits to engineers and designers. It allows them to quickly and accurately calculate the tensile stress area of a single thread, which is essential in designing and analyzing threaded connections. The calculator also helps to reduce errors and improve efficiency in the design process, as it eliminates the need for manual calculations and complex formulas.
Limitations of the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
While the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations. It is only applicable to single threads and does not account for multi-threaded connections or complex geometries. Additionally, the calculator assumes that the thread is perfectly circular and does not account for manufacturing tolerances or imperfections.
Applications of the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator has a wide range of applications in various fields, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. It is used to design and analyze critical components, such as engine parts, gearbox components, and structural elements. The calculator is also used in research and development to optimize and improve the performance of threaded connections.
| Parameter | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Diameter | mm or in | The diameter of the thread |
| Thread Pitch | mm or in | The distance between two consecutive threads |
| Thread Root Radius | mm or in | The radius of the thread root |
| Tensile Stress Area | mm^2 or in^2 | The area of the thread that resists tensile stress |
How do you calculate the tensile stress area of a thread?

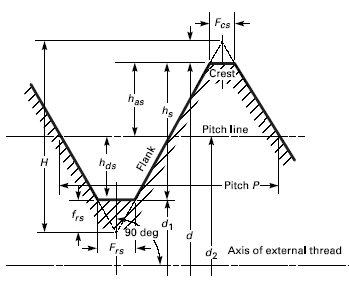
The tensile stress area of a thread is a critical parameter in determining the strength and performance of a threaded joint. To calculate the tensile stress area of a thread, you need to know the thread diameter, pitch, and thread form. The tensile stress area is typically calculated using the following formula: A = (π/4) (d - 0.9382 p)^2, where A is the tensile stress area, d is the thread diameter, and p is the pitch.
Understanding Thread Geometry
The geometry of a thread plays a crucial role in determining the tensile stress area. To calculate the tensile stress area, you need to understand the thread profile, including the major diameter, minor diameter, and pitch diameter. The thread profile is typically defined by the thread standard, such as the Unified Thread Standard (UTS) or the ISO metric thread standard. Some key factors to consider when understanding thread geometry include:
- Thread pitch: The distance between two adjacent threads, measured in a parallel plane to the axis of the thread.
- Thread angle: The angle between the thread and the axis of the thread, which affects the tensile stress area.
- Thread form: The shape of the thread, which can be LH (left-hand) or RH (right-hand), and affects the tensile stress area.
Calculating Tensile Stress Area using the Formula
The formula for calculating the tensile stress area of a thread is based on the thread diameter and pitch. The formula is: A = (π/4) (d - 0.9382 p)^2, where A is the tensile stress area, d is the thread diameter, and p is the pitch. This formula is applicable to most thread standards, including the Unified Thread Standard (UTS) and the ISO metric thread standard. Some key considerations when using this formula include:
- Thread diameter: The major diameter of the thread, which is the largest diameter of the thread.
- Pitch: The distance between two adjacent threads, measured in a parallel plane to the axis of the thread.
- Constants: The constant 0.9382 is used in the formula, which is based on the thread geometry and stress distribution.
Importance of Tensile Stress Area in Threaded Joints
The tensile stress area of a thread is a critical parameter in determining the strength and performance of a threaded joint. A larger tensile stress area generally indicates a stronger threaded joint, while a smaller tensile stress area indicates a weaker joint. The tensile stress area is also affected by the thread material, surface finish, and assembly torque. Some key factors to consider when evaluating the importance of tensile stress area include:
- Thread material: The material properties of the thread, such as yield strength and ultimate tensile strength.
- Surface finish: The surface roughness of the thread, which affects the friction and stress distribution.
- Assembly torque: The torque applied during assembly, which affects the stress and strain on the thread.
Factors Affecting Tensile Stress Area
Several factors can affect the tensile stress area of a thread, including the thread geometry, thread material, surface finish, and assembly torque. The thread standard and manufacturing process can also impact the tensile stress area. Some key factors to consider when evaluating the factors affecting tensile stress area include:
- Thread standard: The thread standard used, such as the Unified Thread Standard (UTS) or the ISO metric thread standard.
- Manufacturing process: The manufacturing process used to produce the thread, such as machining or forming.
- Thread coating: The coating or plating applied to the thread, which can affect the friction and stress distribution.
Applications of Tensile Stress Area in Engineering
The tensile stress area of a thread has numerous applications in engineering, including the design of threaded joints, fasteners, and mechanical components. The tensile stress area is also used in failure analysis and quality control to evaluate the strength and performance of threaded joints. Some key applications of tensile stress area include:
- Threaded joint design: The design of threaded joints, including the selection of thread standard and thread material.
- Fastener design: The design of fasteners, including bolts, nuts, and screws.
- Mechanical component design: The design of mechanical components, including gears, bearings, and shafts.
What is the tensile stress area of a 1 4 20 bolt?
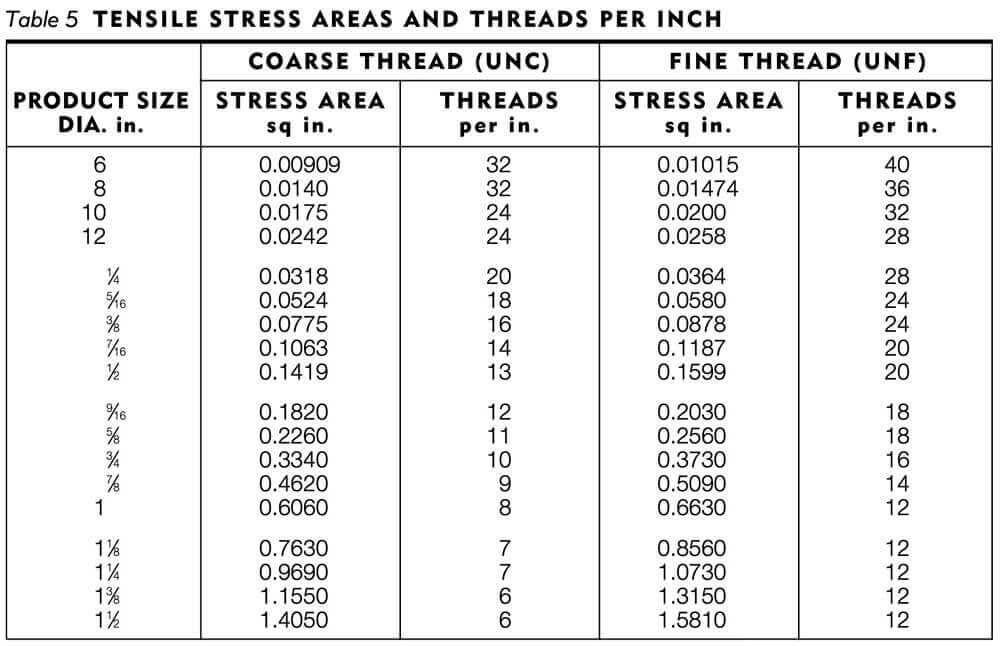
The tensile stress area of a 1/4-20 bolt is approximately 0.0318 square inches. This value is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing. The tensile stress area is calculated by subtracting the area of the thread root from the area of the bolt shank.
Introduction to Tensile Stress Area
The tensile stress area is an important factor in determining the strength ... of a bolt. It is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing. The tensile stress area is calculated by subtracting the area of the thread root from the area of the bolt shank.
- The tensile stress area is typically provided by the manufacturer of the bolt.
- The tensile stress area can vary depending on the size and type of bolt.
- The tensile stress area is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing.
Calculating Tensile Stress Area
The tensile stress area can be calculated using the diameter of the bolt and the thread pitch. The tensile stress area is calculated by subtracting the area of the thread root from the area of the bolt shank. This calculation is typically performed by the manufacturer of the bolt, and the resulting tensile stress area is provided in the product specifications.
- The diameter of the bolt is used to calculate the area of the bolt shank.
- The thread pitch is used to calculate the area of the thread root.
- The tensile stress area is calculated by subtracting the area of the thread root from the area of the bolt shank.
Importance of Tensile Stress Area
The tensile stress area is an important factor in determining the strength of a bolt. It is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing. A higher tensile stress area indicates a stronger bolt, while a lower tensile stress area indicates a weaker bolt.
- A higher tensile stress area indicates a stronger bolt.
- A lower tensile stress area indicates a weaker bolt.
- The tensile stress area is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing.
Factors Affecting Tensile Stress Area
The tensile stress area can be affected by several factors, including the size and type of bolt, as well as the material used to manufacture the bolt. The tensile stress area can also be affected by the thread pitch and the diameter of the bolt.
- The size and type of bolt can affect the tensile stress area.
- The material used to manufacture the bolt can affect the tensile stress area.
- The thread pitch and diameter of the bolt can affect the tensile stress area.
Applications of Tensile Stress Area
The tensile stress area has several applications in the field of engineering, including the design of bolts and fasteners. The tensile stress area is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt, which is the maximum amount of stress that the bolt can withstand without failing.
- The tensile stress area is used to calculate the tensile strength of the bolt.
- The tensile stress area is used in the design of bolts and fasteners.
- The tensile stress area is an important factor in determining the strength of a bolt.
What is the tensile area of a threaded rod?

The tensile area of a threaded rod is the area of the rod that is subject to tensile stress when it is loaded in tension. This area is typically smaller than the overall cross-sectional area of the rod due to the presence of threads, which reduce the amount of material available to resist tensile forces.
Calculating Tensile Area
To calculate the tensile area of a threaded rod, you need to know the diameter of the rod and the pitch of the threads. The tensile area can be calculated using the formula: tensile area = (diameter - (number of threads thread depth))^2 / 4. This formula takes into account the reduction in area due to the threads. Some key points to consider when calculating tensile area are:
- The diameter of the rod must be measured accurately to ensure a correct calculation.
- The pitch of the threads must be known to determine the thread depth.
- The number of threads per inch must be known to calculate the total thread depth.
Factors Affecting Tensile Area
Several factors can affect the tensile area of a threaded rod, including the material used to make the rod, the thread type, and the surface finish. The material used to make the rod can affect its tensile strength, which in turn affects the tensile area. Some key factors to consider are:
- The yield strength of the material can affect the tensile area.
- The thread type can affect the tensile area, with coarse threads typically resulting in a smaller tensile area than fine threads.
- The surface finish can affect the tensile area, with a smooth finish typically resulting in a larger tensile area than a rough finish.
Importance of Tensile Area
The tensile area of a threaded rod is critical in determining its load-carrying capacity. A larger tensile area typically results in a higher load-carrying capacity, while a smaller tensile area can result in a lower load-carrying capacity. Some key points to consider are:
- A larger tensile area can result in a higher safety factor.
- A smaller tensile area can result in a lower safety factor.
- The tensile area must be carefully calculated to ensure that the threaded rod can withstand the expected loads.
Applications of Tensile Area
The tensile area of a threaded rod is used in a variety of applications, including construction, manufacturing, and engineering. In construction, threaded rods are used to support heavy loads, and the tensile area must be carefully calculated to ensure that the rod can withstand the expected loads. Some key points to consider are:
- The tensile area must be calculated for each application to ensure that the threaded rod can withstand the expected loads.
- The tensile area can affect the cost of the threaded rod, with a larger tensile area typically resulting in a higher cost.
- The tensile area can affect the weight of the threaded rod, with a larger tensile area typically resulting in a heavier rod.
Standards for Tensile Area
There are several standards that govern the tensile area of threaded rods, including ASTM and ISO standards. These standards provide guidelines for calculating the tensile area and ensure that threaded rods meet minimum strength and safety requirements. Some key points to consider are:
- The ASTM standard for threaded rods provides guidelines for calculating the tensile area.
- The ISO standard for threaded rods provides guidelines for calculating the tensile area.
- The standards must be carefully followed to ensure that the threaded rod meets minimum strength and safety requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator and how does it work?
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a tool used to calculate the tensile stress area of a single thread, which is an essential parameter in determining the strength and integrity of a threaded joint. This calculator takes into account the thread diameter, pitch, and thread form to calculate the stress area, which is the area of the thread that resists tensile forces. The calculator uses complex mathematical formulas to calculate the stress area, taking into account the geometry of the thread and the material properties of the threaded component. By using this calculator, engineers and designers can quickly and accurately determine the tensile stress area of a single thread, which is critical in designing and analyzing threaded joints and fasteners.
What are the key inputs required to use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator?
To use the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator, several key inputs are required, including the thread diameter, pitch, and thread form. The thread diameter is the nominal diameter of the thread, which is typically specified in inches or millimeters. The pitch is the distance between adjacent threads, which is also typically specified in inches or millimeters. The thread form refers to the shape of the thread, which can be rounded, flat, or trapezoidal. Additionally, the calculator may require material properties such as the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of the threaded component. By inputting these key parameters, the calculator can accurately determine the tensile stress area of the single thread.
How is the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator used in engineering and design applications?
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is widely used in engineering and design applications, particularly in the aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors. Engineers and designers use this calculator to design and analyze threaded joints and fasteners, such as bolts, screws, and studs. By determining the tensile stress area of a single thread, engineers can predict the strength and integrity of the threaded joint, which is critical in ensuring the safety and reliability of the component or system. Additionally, the calculator can be used to optimize the design of threaded joints, by minimizing the weight and cost of the component while maximizing its strength and performance. The calculator is also used in research and development applications, where it is used to investigate the behavior of threaded joints under various loading conditions.
What are the benefits of using the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator in comparison to traditional calculation methods?
The Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator offers several benefits over traditional calculation methods, including increased accuracy, speed, and efficiency. Traditional calculation methods often rely on complex mathematical formulas and manual calculations, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. In contrast, the calculator uses advanced algorithms and numerical methods to quickly and accurately determine the tensile stress area of a single thread. Additionally, the calculator can handle complex thread geometries and material properties, which can be difficult or impossible to analyze using traditional methods. The calculator also provides detailed output and visualizations, which can be used to gain insight into the behavior of the threaded joint and optimize its design. Overall, the Single Thread Tensile Stress Area Calculator is a powerful tool that can save time, reduce errors, and improve the design and analysis of threaded joints.
Deja una respuesta

Entradas Relacionadas